What Is a Sacral Nerve Root Sleeve Cyst?
A sacral nerve root sleeve cyst is a condition that affects the nerves in the sacrum, a triangular bone at the base of the spine. These cysts can cause a range of symptoms and may require medical intervention for management.
Understanding the Anatomy of the Sacral Nerve
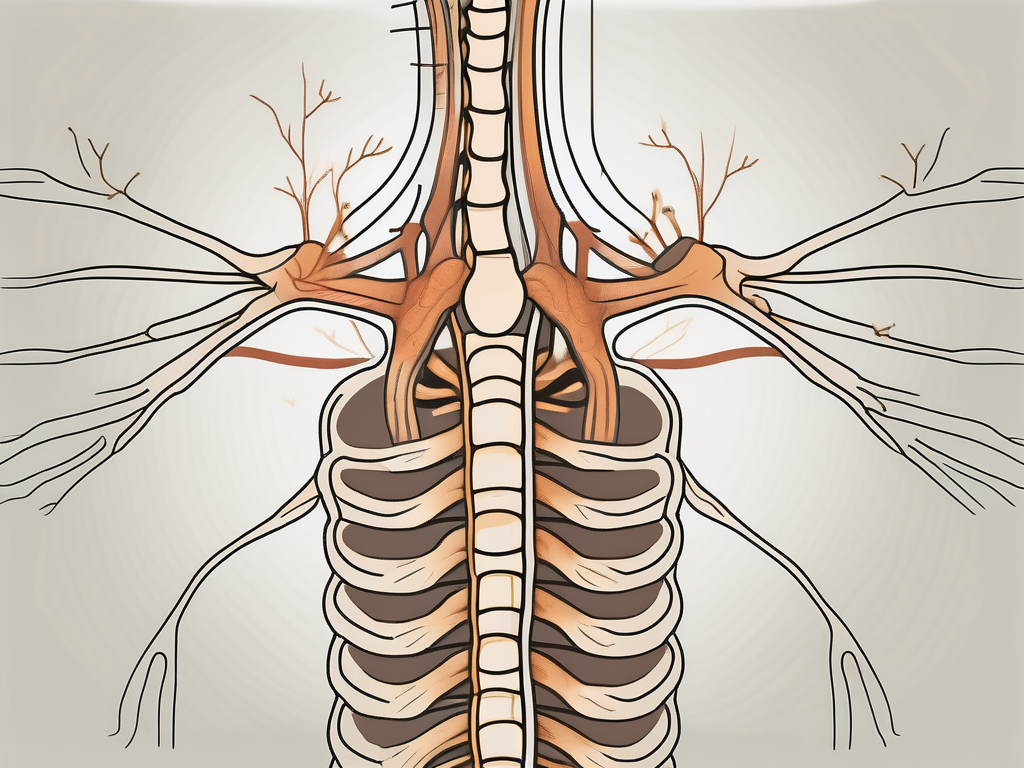
The sacral nerve plays a crucial role in the functioning of the body. It is a major nerve that arises from the spinal cord and travels through the sacrum. The sacrum is a strong, curved bone formed by the fusion of five vertebrae. The sacral nerve branches out and connects with various parts of the lower body, including the muscles, skin, and organs.
Let’s delve deeper into the fascinating world of the sacral nerve and explore its intricate structure and vital functions.
The Role of the Sacral Nerve in the Body
The sacral nerve is responsible for transmitting signals between the brain and the lower body. It controls the movement and sensation of the legs, allowing us to walk, run, and engage in various physical activities. Without the sacral nerve, our lower body would be devoid of sensation and motion, rendering us immobile.
But the sacral nerve’s significance doesn’t end there. It also plays a crucial role in maintaining bladder and bowel function. It sends signals to the muscles that control these organs, ensuring proper urination and defecation. Without the sacral nerve’s guidance, these essential bodily functions would be disrupted, leading to discomfort and potential health issues.
Furthermore, the sacral nerve contributes to sexual function. It plays a vital role in transmitting signals that stimulate sexual arousal and facilitate sexual activity. This intricate network of nerves allows for the pleasurable sensations experienced during intimate moments.
Additionally, the sacral nerve is involved in the regulation of blood pressure. It helps to maintain the balance between high and low blood pressure by transmitting signals that regulate blood vessel constriction and dilation. This intricate control mechanism ensures that our cardiovascular system functions optimally.
The Structure of the Sacral Nerve
The sacral nerve is composed of multiple nerve roots that emerge from the spinal cord. These nerve roots pass through small openings called foramina in the sacrum. The sacrum acts as a protective tunnel, guiding the nerve roots on their journey to various parts of the lower body.
Each nerve root consists of a delicate bundle of nerve fibers that transmit electrical signals. These signals allow for communication between the brain and the lower body. The sacral nerve’s intricate structure ensures the efficient transmission of these signals, enabling smooth coordination and control of our lower body functions.
It’s fascinating to think about the complex interplay between the sacral nerve and the rest of our body. Every step we take, every sensation we feel, and every bodily function we perform is made possible by the intricate network of nerves that make up the sacral nerve.
Understanding the anatomy and function of the sacral nerve not only deepens our appreciation for the complexity of the human body but also highlights the importance of maintaining its health and well-being.
Defining a Sacral Nerve Root Sleeve Cyst
A sacral nerve root sleeve cyst, also known as a Tarlov cyst, is a fluid-filled sac that develops within the nerve root sleeve. The nerve root sleeve is a protective covering that surrounds the nerve root and provides nourishment and support. When a cyst forms within this sleeve, it can put pressure on the surrounding nerves, leading to various symptoms and complications.
The Formation Process of Sacral Nerve Root Sleeve Cysts
The exact cause of sacral nerve root sleeve cysts is not yet fully understood. However, they are believed to develop as a result of the weakening of the nerve root sleeve, leading to the trapping of cerebrospinal fluid. This accumulation of fluid can cause the cyst to grow over time and exert pressure on the nerves.
Several factors may contribute to the weakening of the nerve root sleeve. One possible cause is trauma or injury to the sacral region, such as a fall or a car accident. The impact can disrupt the integrity of the nerve root sleeve, making it more susceptible to the formation of cysts. Additionally, genetic factors may play a role in the development of sacral nerve root sleeve cysts. Some individuals may inherit a predisposition to the weakening of the nerve root sleeve, increasing their likelihood of developing cysts.
It’s important to note that sacral nerve root sleeve cysts are relatively rare. They are more commonly found in women than men and tend to occur in middle-aged individuals. However, they can also be present in children and older adults.
The Different Types of Sacral Nerve Root Sleeve Cysts
There are different types of sacral nerve root sleeve cysts, including intradural and extradural cysts. Intradural cysts develop within the dura mater, which is the membrane that surrounds the spinal cord. Extradural cysts, on the other hand, occur outside the dura mater but within the nerve root sleeve.
Intradural cysts are typically larger in size and can cause more severe symptoms. They may compress the spinal cord or nerve roots, leading to pain, numbness, weakness, and bowel or bladder dysfunction. Extradural cysts, on the other hand, tend to be smaller and may cause milder symptoms. However, they can still lead to discomfort and affect the normal functioning of the nerves in the sacral region.
It’s worth mentioning that the diagnosis of sacral nerve root sleeve cysts can be challenging. The symptoms can be similar to other spinal conditions, such as herniated discs or spinal stenosis. Therefore, a thorough evaluation, including medical history, physical examination, and imaging tests, is necessary to accurately diagnose and differentiate these conditions.
Treatment options for sacral nerve root sleeve cysts depend on various factors, including the size and location of the cyst, as well as the severity of symptoms. Conservative approaches, such as pain management and physical therapy, may be initially recommended. In cases where the cyst is causing significant compression or neurological deficits, surgical intervention may be necessary to remove or drain the cyst and relieve the pressure on the nerves.
It’s important for individuals experiencing symptoms suggestive of sacral nerve root sleeve cysts to seek medical attention promptly. Early diagnosis and appropriate management can help alleviate symptoms and improve overall quality of life.
Symptoms and Diagnosis of Sacral Nerve Root Sleeve Cysts
Identifying the symptoms associated with sacral nerve root sleeve cysts is crucial for timely diagnosis and appropriate management. However, it is important to note that not everyone with a cyst will experience symptoms. When symptoms do occur, they can vary from person to person.
Sacral nerve root sleeve cysts can cause a range of symptoms, depending on their size and location. One common symptom is lower back pain, which can be localized or radiate to the buttocks, legs, or feet. This pain may be dull and achy or sharp and shooting, and it can worsen with certain movements or activities.
In addition to lower back pain, individuals with sacral nerve root sleeve cysts may experience numbness or tingling sensations in the affected areas. This can manifest as a “pins and needles” sensation or a loss of feeling altogether. These sensory disturbances can be intermittent or constant, and they may affect one side of the body or both.
In more severe cases, sacral nerve root sleeve cysts can lead to muscle weakness and difficulty with bladder and bowel control. This can manifest as difficulty starting or stopping urination, urinary or fecal incontinence, or a feeling of incomplete emptying. These symptoms can significantly impact a person’s quality of life and require prompt medical attention.
Common Symptoms Associated with Sacral Nerve Root Sleeve Cysts
Some individuals may experience lower back pain, which can radiate to the buttocks, legs, or feet. Numbness or tingling sensations in the affected areas may also occur. In severe cases, muscle weakness and difficulty with bladder and bowel control can be present. It is essential to consult with a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis if these symptoms arise.
When evaluating a patient for sacral nerve root sleeve cysts, healthcare professionals will typically start with a comprehensive medical history. This involves gathering information about the patient’s symptoms, medical conditions, and any previous injuries or surgeries. Understanding the patient’s medical background can help healthcare professionals determine the likelihood of a sacral nerve root sleeve cyst and guide further diagnostic steps.
In addition to the medical history, a physical examination is an important component of diagnosing sacral nerve root sleeve cysts. During the examination, healthcare professionals may assess the patient’s range of motion, muscle strength, and reflexes. They may also perform specific tests to evaluate the function of the nerves in the affected areas. These physical findings can provide valuable clues about the presence and severity of a sacral nerve root sleeve cyst.
Diagnostic Procedures for Sacral Nerve Root Sleeve Cysts
Diagnosing a sacral nerve root sleeve cyst typically involves a combination of a comprehensive medical history, physical examination, and diagnostic imaging. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is the most effective tool to visualize the cyst and its impact on the surrounding nerves. In some cases, a computed tomography (CT) scan or a myelogram may be recommended to further evaluate the cyst’s location and structure.
An MRI uses powerful magnets and radio waves to create detailed images of the body’s internal structures. It can provide healthcare professionals with a clear view of the sacral nerve root sleeve cyst, allowing them to assess its size, location, and any compression or displacement of nearby nerves. This information is crucial for determining the most appropriate treatment approach.
In certain situations, a CT scan or a myelogram may be necessary to gather additional information about the sacral nerve root sleeve cyst. A CT scan uses a series of X-ray images taken from different angles to create cross-sectional images of the body. This can help healthcare professionals obtain a more detailed view of the cyst’s structure and its relationship to surrounding tissues.
A myelogram involves injecting a contrast dye into the spinal canal to enhance the visibility of the nerves and spinal cord on X-ray images. This procedure can provide healthcare professionals with valuable information about the cyst’s impact on the spinal cord and nerve roots, helping guide treatment decisions.
In conclusion, identifying the symptoms and diagnosing sacral nerve root sleeve cysts require a comprehensive approach that combines medical history, physical examination, and diagnostic imaging. Prompt and accurate diagnosis is essential for implementing appropriate management strategies and improving the patient’s quality of life.
Treatment Options for Sacral Nerve Root Sleeve Cysts
When it comes to managing sacral nerve root sleeve cysts, the treatment approach may vary depending on the severity of the symptoms and the size and location of the cyst. In some cases, non-surgical treatments can effectively alleviate symptoms, while in other situations, surgical intervention may be necessary.
Sacral nerve root sleeve cysts can cause a range of symptoms, including lower back pain, radiating pain down the legs, numbness, and weakness. These symptoms can significantly impact a person’s quality of life and daily activities. Therefore, finding an appropriate treatment plan is crucial for relieving discomfort and improving overall well-being.
Non-Surgical Treatments for Sacral Nerve Root Sleeve Cysts
Non-surgical treatments focus on relieving symptoms and improving the patient’s quality of life. These may include physical therapy, pain management techniques, and lifestyle modifications.
Physical therapy plays a vital role in the treatment of sacral nerve root sleeve cysts. It involves targeted exercises and stretches that aim to strengthen the surrounding muscles, improve flexibility, and enhance overall mobility. A skilled physical therapist can design a personalized program to address the specific needs of each individual.
In addition to physical therapy, pain management techniques can also be employed to alleviate discomfort. Medications, such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), may be prescribed to reduce inflammation and relieve pain. Nerve blocks, which involve injecting medication directly into the affected area, can provide temporary relief by blocking pain signals.
Furthermore, lifestyle modifications can play a significant role in managing sacral nerve root sleeve cysts. These may include maintaining a healthy weight, practicing good posture, and avoiding activities that exacerbate symptoms. By making these adjustments, individuals can reduce stress on the affected area and potentially prevent further deterioration.
It is important to note that non-surgical treatments may not provide immediate or complete relief for all individuals. The effectiveness of these interventions can vary depending on the specific circumstances and the response of each person’s body. Therefore, it is crucial to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the most appropriate treatment plan.
Surgical Interventions for Sacral Nerve Root Sleeve Cysts
In cases where non-surgical treatment options fail to provide relief or if the cyst continues to grow, surgical intervention may be considered. The decision to undergo surgery is typically made after a comprehensive evaluation of the individual’s condition and a thorough discussion with a healthcare professional.
The specific surgical procedure will depend on the size and location of the cyst, as well as the individual’s overall health. One common surgical approach is cyst drainage, where the cyst is punctured and drained to alleviate pressure on the nerve roots. Another option is cyst excision, which involves removing the cyst and any surrounding tissue that may be causing compression.
It is important to note that surgery carries inherent risks, including infection, bleeding, and nerve damage. Therefore, a thorough discussion with a healthcare professional is necessary to weigh the potential benefits against the risks. The decision to undergo surgery should be based on a careful consideration of the individual’s symptoms, overall health, and the likelihood of achieving significant symptom relief through surgical intervention.
In conclusion, the treatment options for sacral nerve root sleeve cysts range from non-surgical interventions, such as physical therapy and pain management techniques, to surgical procedures like cyst drainage or excision. The choice of treatment depends on various factors, including the severity of symptoms, the size and location of the cyst, and the individual’s overall health. Consulting with a healthcare professional is essential to determine the most appropriate treatment plan and to ensure the best possible outcome for each individual.
The Impact of Sacral Nerve Root Sleeve Cysts on Quality of Life
Sacral nerve root sleeve cysts can have significant physical and psychological implications that can impact a person’s overall quality of life. Understanding and managing these effects is an important part of the treatment process.
Physical Implications of Sacral Nerve Root Sleeve Cysts
The physical implications of sacral nerve root sleeve cysts can vary widely depending on the individual and the severity and location of the cyst. Chronic pain, mobility limitations, and bladder and bowel dysfunction are among the potential physical consequences. Physiotherapy and adaptive strategies can often help improve physical functioning and minimize the impact on daily activities.
Psychological Effects of Living with Sacral Nerve Root Sleeve Cysts
Coping with sacral nerve root sleeve cysts can take a toll on a person’s psychological well-being. Persistent pain, limitations in daily activities, and uncertainty about the future can contribute to feelings of stress, frustration, and anxiety. It is important for individuals affected by these cysts to seek support from friends, family, and mental health professionals to address the emotional challenges they may face.
Preventive Measures and Management of Sacral Nerve Root Sleeve Cysts
Prevention of sacral nerve root sleeve cysts is not currently possible as their exact cause remains unclear. However, there are measures to manage and minimize the impact of these cysts on daily life.
Lifestyle Changes to Manage Sacral Nerve Root Sleeve Cysts
Adopting a healthy lifestyle can support optimal overall well-being and potentially reduce the impact of sacral nerve root sleeve cysts. Regular exercise, a balanced diet, and stress management techniques may help manage symptoms and enhance overall quality of life.
Medical Follow-ups and Regular Check-ups for Sacral Nerve Root Sleeve Cysts
Regular monitoring and follow-up appointments with healthcare professionals are crucial for individuals with sacral nerve root sleeve cysts. These check-ups enable healthcare providers to evaluate the progression of symptoms, assess the effectiveness of treatments, and make any necessary adjustments to the care plan. It is important to maintain open communication with healthcare professionals and report any significant changes or new symptoms that may arise.
In conclusion, a sacral nerve root sleeve cyst is a condition that can have a range of physical and psychological manifestations. Proper diagnosis, individualized treatment plans, and ongoing management are essential for individuals affected by these cysts to maintain an optimal quality of life. Consulting with a healthcare professional is crucial for accurate diagnosis, appropriate treatment, and support throughout the journey of living with a sacral nerve root sleeve cyst.