Where Do Sacral Nerve Roots Exit?
The sacral nerve roots play a crucial role in our body’s nervous system. Understanding where they exit is key to grasping their function and potential disorders that may arise. In this article, we will explore the anatomy of the sacral nerve roots, the formation of the sacral plexus, and the exit points of these crucial nerves. We will also delve into common disorders related to sacral nerve roots, treatment options available, and ways to prevent and manage these disorders for better nerve health.
Understanding the Sacral Nerve Roots
For a thorough comprehension of the exit points of sacral nerve roots, we must first understand their anatomy and function.
The sacral nerve roots play a crucial role in the intricate network of the human nervous system. Emerging from the lower part of the spinal cord, specifically the sacral vertebrae, these nerve roots form an essential part of the larger network known as the sacral plexus. This complex web of nerves is responsible for carrying signals to and from the lower limbs, pelvic organs, and various muscles in the lower abdomen and buttocks.
The anatomy of the sacral nerve roots is fascinating. They are named S1 to S5, with each representing a specific level of the spinal cord. These nerve roots branch out into smaller, intricate pathways, providing innervation to different areas of the lower body. It is through these branches that the sacral nerve roots establish connections and facilitate the transmission of signals throughout the body.
Anatomy of the Sacral Nerve Roots
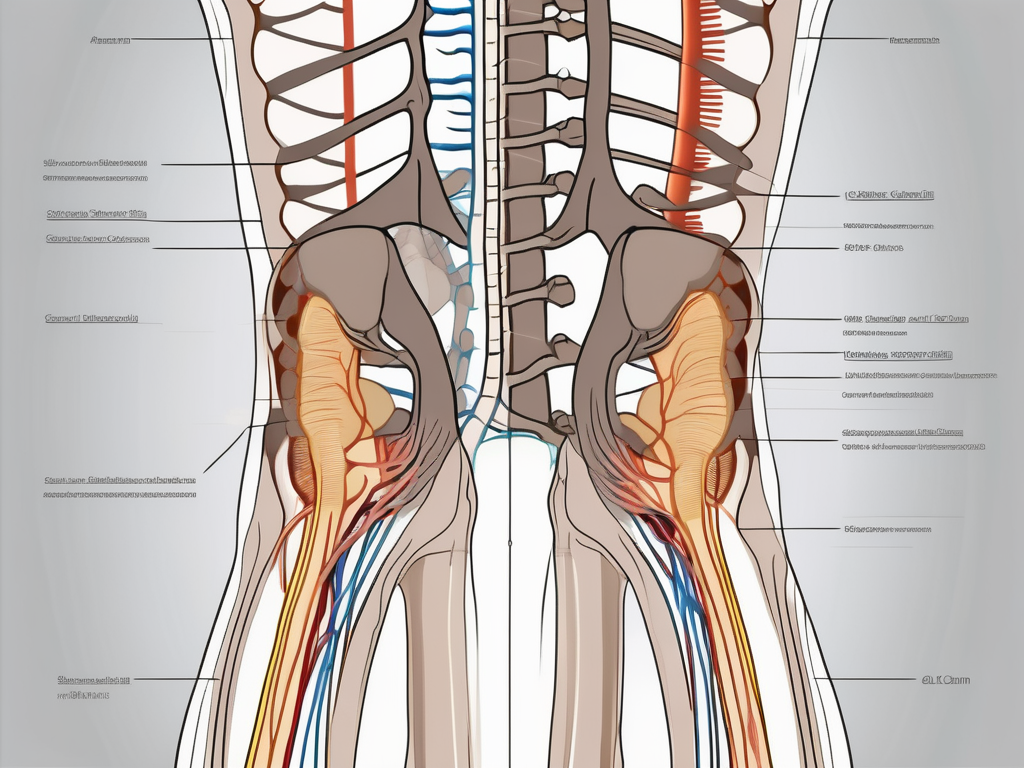
The sacral nerve roots emerge from the sacral vertebrae, which are five bones located at the base of the spine. These vertebrae, known as S1 to S5, form the foundation of the sacrum, a triangular bone situated between the two hip bones.
As the nerve roots emerge from the sacral vertebrae, they intertwine and form the sacral plexus. This intricate network of nerves resembles a complex tapestry, with each thread representing a specific nerve root. The sacral plexus is a vital hub of communication, allowing signals to flow seamlessly between the brain, lower limbs, pelvic organs, and muscles in the lower abdomen and buttocks.
The sacral nerve roots are not only responsible for transmitting signals but also for receiving sensory information. These nerve roots serve as conduits, carrying sensory signals from the pelvic organs and lower limbs back to the brain. In this way, we are able to perceive sensations such as touch, temperature, and pain in these areas.
Function of the Sacral Nerve Roots
The function of the sacral nerve roots is intricate and multifaceted. These nerve roots play a crucial role in both motor and sensory functions, enabling us to perform a wide range of movements and perceive sensations in the lower body.
Motor signals originating from the brain travel down the spinal cord and through the sacral nerve roots. These signals are responsible for coordinating movements such as walking, running, and controlling the muscles of the lower abdomen and buttocks. Without the sacral nerve roots, these essential motor functions would be impaired, hindering our ability to navigate the world around us.
In addition to motor functions, the sacral nerve roots also carry sensory signals. These signals travel from the pelvic organs and lower limbs back to the brain, allowing us to perceive sensations such as pressure, temperature, and pain. The sacral nerve roots act as messengers, transmitting these sensory signals to the brain, where they are interpreted and processed.
Understanding the intricate anatomy and function of the sacral nerve roots is crucial for comprehending the complex workings of the human nervous system. These nerve roots serve as vital conduits, facilitating communication between the brain and the lower body. Without them, our ability to move, feel, and interact with the world would be greatly compromised.
The Sacral Plexus: A Closer Look
Now that we understand the basics of the sacral nerve roots, let’s examine the formation and components of the sacral plexus.
The sacral nerve roots converge to form the sacral plexus, which is located within the pelvic cavity. This intricate network of nerves is present on both sides of the pelvis and is responsible for distributing nerve supply to the lower limbs, perineum, and pelvic organs.
The formation of the sacral plexus occurs deep within the pelvis, with the nerve roots intertwining and giving rise to major nerve branches. These branches then extend downward, passing through anatomical structures and eventually reaching their respective target areas.
As we delve deeper into the intricacies of the sacral plexus, it becomes evident that its formation is a complex process. The nerve roots, originating from the sacral segments of the spinal cord, undergo a series of intricate interactions, ultimately culminating in the creation of this vital network. The intertwining of these nerve roots not only ensures efficient distribution of nerve supply but also allows for the coordination of various functions within the lower limbs, perineum, and pelvic organs.
Key Components of the Sacral Plexus
The sacral plexus comprises various important nerves, including the sciatic nerve, pudendal nerve, and posterior femoral cutaneous nerve. The sciatic nerve, the largest nerve in the body, is responsible for innervating the muscles of the thigh, leg, and foot.
As we explore the sciatic nerve further, we discover its immense significance in our everyday lives. This nerve plays a crucial role in our ability to walk, run, and perform various lower limb movements. It not only provides motor innervation to the muscles involved in these activities but also enables us to perceive sensations from this region. Without the sciatic nerve, our lower limbs would be rendered immobile, and our ability to navigate the world around us would be severely compromised.
The pudendal nerve, another key component of the sacral plexus, provides sensation to the perineum and controls the muscles of the pelvic floor. This nerve, often overlooked, plays a vital role in our urinary and reproductive functions. It ensures the proper functioning of our bladder and bowel control, as well as the coordination of sexual activities.
As we delve deeper into the intricacies of the pudendal nerve, we uncover its fascinating role in the intricate web of nerves within the sacral plexus. This nerve not only enables us to perceive sensations from the perineum but also allows for the contraction and relaxation of the muscles within the pelvic floor. Without the pudendal nerve, our ability to control our bodily functions and engage in sexual activities would be severely compromised.
The posterior femoral cutaneous nerve, yet another component of the sacral plexus, supplies sensation to the back of the thighs and buttocks. This often overlooked nerve is responsible for our ability to perceive sensations from these regions, allowing us to navigate the world around us with ease.
As we explore the posterior femoral cutaneous nerve further, we uncover its intriguing role in our everyday lives. This nerve not only enables us to perceive sensations from the back of our thighs and buttocks but also plays a crucial role in our overall sense of balance and coordination. Without the posterior femoral cutaneous nerve, our ability to perform various movements, such as walking, running, and even sitting, would be compromised.
Exit Points of Sacral Nerve Roots
Now that we have a solid understanding of the sacral nerve roots and the formation of the sacral plexus, let’s explore the exit points of these important nerves.
The sacral nerve roots exit the pelvic cavity through narrow passageways called the sacral foramina. These foramina are small openings located on the posterior side of the sacrum, allowing the nerve roots to exit and extend into the lower limbs and pelvic region.
Each sacral nerve root has a specific exit point, with S1 exiting through the first sacral foramen and S5 emerging from the fifth sacral foramen.
As the sacral nerve roots make their way through the sacral foramina, they branch out and innervate various structures in the lower limbs and pelvic region. These structures include muscles, skin, and organs, playing a crucial role in their proper functioning.
The exit points of the sacral nerve roots are of great importance, as any structural or functional abnormalities in these areas can lead to various disorders and symptoms. Conditions such as herniated discs, spinal stenosis, or even trauma can impede the smooth passage of the nerve roots, resulting in pain, sensory changes, weakness, or dysfunction in the lower limbs or pelvic organs.
It is crucial to seek medical attention if you experience persistent or worsening symptoms related to the lower limbs or pelvic region. A healthcare professional can diagnose and determine the appropriate treatment options based on the underlying cause.
Furthermore, understanding the exit points of the sacral nerve roots can aid in the diagnosis and treatment of certain conditions. By pinpointing the specific exit point affected, healthcare professionals can better target their interventions, whether through medication, physical therapy, or surgical procedures.
Additionally, the exit points of the sacral nerve roots can vary slightly among individuals. While the general pattern remains consistent, there may be slight variations in the exact location of the sacral foramina and the corresponding exit points of the nerve roots. This anatomical variability highlights the uniqueness of each individual’s nervous system and underscores the importance of personalized medical care.
Research into the exit points of the sacral nerve roots continues to shed light on the intricate connections between the nervous system and the lower limbs and pelvic region. By studying these exit points, scientists and healthcare professionals can gain a deeper understanding of neurological disorders and develop innovative treatment approaches.
Disorders Related to Sacral Nerve Roots
Understanding the disorders associated with sacral nerve roots is important for early detection, proper diagnosis, and timely treatment. The sacral nerve roots play a crucial role in the functioning of the lower back, pelvis, and lower limbs. When these nerve roots are affected by certain disorders, it can lead to a range of symptoms and complications.
One common disorder related to the sacral nerve roots is sciatica. Sciatica often presents as pain that radiates from the lower back down the leg, following the path of the sciatic nerve. This pain can be sharp, shooting, or even a dull ache. In addition to pain, individuals with sciatica may also experience tingling, numbness, or muscle weakness in the affected leg. The intensity of these symptoms can vary from person to person, and they may worsen with certain movements or prolonged sitting or standing.
Another disorder associated with the sacral nerve roots is cauda equina syndrome. Although rare, cauda equina syndrome is a serious condition that requires immediate medical attention. It occurs when the nerve roots at the base of the spinal cord are compressed, leading to a range of symptoms. These symptoms can include bladder and bowel dysfunction, weakness, and numbness in the lower limbs. If left untreated, cauda equina syndrome can result in permanent nerve damage and loss of function.
Sacroiliac joint dysfunction is yet another disorder that can affect the sacral nerve roots. The sacroiliac joint is located at the base of the spine, connecting the sacrum to the pelvis. When this joint becomes inflamed or experiences dysfunction, it can cause lower back pain. This pain may radiate to the buttocks or thighs and can be aggravated by certain movements or prolonged sitting or standing. Sacroiliac joint dysfunction can be challenging to diagnose, as the symptoms can mimic other conditions such as herniated discs or hip problems.
If you experience any of these symptoms, it is advisable to consult with a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment plan. They will be able to evaluate your symptoms, perform a physical examination, and order any necessary diagnostic tests to determine the underlying cause of your discomfort.
Diagnostic Techniques for Sacral Nerve Disorders
When assessing disorders related to sacral nerve roots, healthcare professionals may employ various diagnostic techniques. These techniques are essential for accurate diagnosis and to develop an effective treatment plan tailored to each individual’s needs.
A thorough medical history review is often the first step in diagnosing sacral nerve disorders. This allows healthcare professionals to gather information about the patient’s symptoms, medical history, and any previous injuries or conditions that may be contributing to their current symptoms.
Physical examination is another crucial diagnostic tool. During the examination, the healthcare professional will assess the patient’s range of motion, muscle strength, reflexes, and any areas of tenderness or swelling. These findings can provide valuable insights into the possible causes of the patient’s symptoms.
In some cases, imaging tests such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) or computed tomography (CT) scans may be ordered. These imaging techniques can provide detailed images of the spine, allowing healthcare professionals to identify any structural abnormalities or nerve root compression that may be causing the symptoms.
Nerve conduction studies may also be utilized to evaluate the integrity and functionality of the sacral nerve roots. This test measures the speed and strength of electrical signals as they travel along the nerves. By assessing the conduction of these signals, healthcare professionals can determine if there is any nerve damage or dysfunction present.
It is important to remember that self-diagnosis or relying solely on online information is not recommended. Consulting with a healthcare professional is always the best course of action to ensure accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment. They have the expertise and knowledge to properly evaluate your symptoms and develop an individualized treatment plan that addresses the underlying cause of your sacral nerve disorder.
Treatment Options for Sacral Nerve Disorders
Depending on the specific condition and its severity, treatment options for sacral nerve disorders may vary.
Non-Surgical Treatments
In many cases, non-surgical approaches are the first line of treatment. These can include physical therapy, pain management techniques, medication, and lifestyle modifications that aim to alleviate symptoms and improve function. Rehabilitation exercises, such as stretching and strengthening exercises, can aid in the recovery and management of sacral nerve disorders.
Surgical Treatments and Procedures
In more severe cases or when conservative treatments fail to provide relief, surgical intervention may be necessary. The type of surgery will depend on the underlying cause of the disorder. Surgical procedures may involve decompressing the affected nerve roots, repairing damaged structures, or stabilizing the sacroiliac joint.
It is crucial to consult with a qualified healthcare professional to discuss the benefits, risks, and potential outcomes of any surgical intervention.
Prevention and Management of Sacral Nerve Disorders
While some sacral nerve disorders may be unavoidable, there are steps individuals can take to minimize their risk and effectively manage these conditions.
Lifestyle Changes for Better Nerve Health
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle is essential for overall nerve health. Regular exercise, a balanced diet, and proper posture can all contribute to minimizing the risk of sacral nerve disorders. Engaging in activities that promote good circulation and avoid prolonged pressure on the lower back and pelvic region, such as avoiding prolonged sitting or heavy lifting, can also reduce the likelihood of developing nerve-related issues.
Regular Check-ups and Early Detection
Regular check-ups with a healthcare professional are crucial for early detection and timely intervention. Routine physical examinations, especially for individuals at higher risk or those experiencing symptoms, can help identify potential problems and initiate appropriate treatment early on.
Remember, while this article provides general information about sacral nerve roots and related disorders, it is not a substitute for professional medical advice. If you have concerns or health-related questions, consult with a qualified healthcare professional for personalized guidance.
By understanding the anatomy, function, and disorders associated with sacral nerve roots, we can be better equipped to take care of our nerve health. Being proactive and seeking medical attention when needed will contribute to a healthier and more fulfilling life.