How Sacral Nerve Stimulation Aids in Managing Faecal Incontinence
Faecal incontinence is a distressing condition that affects millions of individuals worldwide. It can significantly impact the quality of life, causing embarrassment, social isolation, and decreased self-esteem. Fortunately, advancements in medical technology have opened new possibilities for managing this condition, including the use of sacral nerve stimulation. In this article, we will explore the various aspects of sacral nerve stimulation and how it aids in managing faecal incontinence.
Understanding Faecal Incontinence
Faecal incontinence, also known as bowel incontinence, is the inability to control bowel movements, leading to involuntary leakage of stool. This condition can range from occasional minor leaks to complete loss of control. It can be caused by a variety of factors, including muscle weakness in the rectum, injury to the anal sphincter muscles, nerve damage, or certain medical conditions such as inflammatory bowel disease or diabetes.
The Prevalence and Impact of Faecal Incontinence
Faecal incontinence is more common than one might think. Studies have shown that it affects up to 8.3% of the general population, with the prevalence increasing with age. The impact of faecal incontinence goes beyond the physical discomfort and inconvenience. It can lead to psychological distress, reduced quality of life, and limitations in daily activities.
Living with faecal incontinence can be challenging. Individuals may experience embarrassment and shame, leading to social isolation and a decreased sense of self-worth. The fear of accidents and the constant need to be near a bathroom can cause anxiety and restrict participation in social events or activities. Additionally, the financial burden of managing faecal incontinence, including the cost of absorbent products and medical treatments, can be significant.
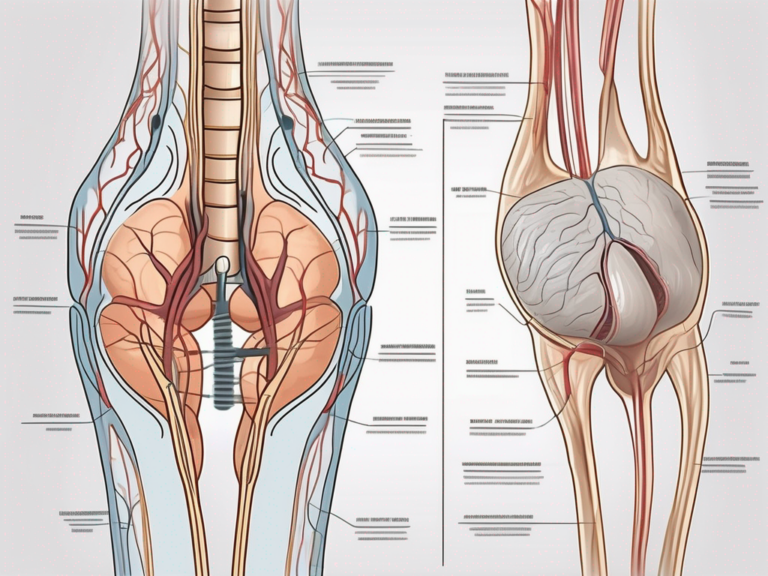
The Anatomy of the Digestive and Nervous System
In order to understand how sacral nerve stimulation aids in managing faecal incontinence, it is important to have a basic understanding of the anatomy of the digestive and nervous system. The digestive system is responsible for the breakdown and absorption of food, while the nervous system controls and coordinates the functions of the body. The sacral nerve plays a crucial role in bowel control, and its stimulation has shown promising results in managing faecal incontinence.
The digestive system is a complex network of organs that work together to process the food we eat. It starts with the mouth, where food is broken down into smaller pieces through chewing and mixed with saliva. From there, the food travels down the esophagus and into the stomach, where it is further broken down by stomach acid and enzymes. The partially digested food then moves into the small intestine, where nutrients are absorbed into the bloodstream. The remaining waste material enters the large intestine, where water is absorbed and the stool is formed.
The nervous system, on the other hand, is responsible for sending and receiving signals throughout the body. It is divided into two main parts: the central nervous system (CNS) and the peripheral nervous system (PNS). The CNS consists of the brain and spinal cord, while the PNS includes all the nerves that branch out from the CNS and extend to the rest of the body.
The sacral nerve, specifically, is a part of the PNS and plays a crucial role in bowel control. It is responsible for transmitting signals between the brain and the muscles of the rectum and anus, allowing for voluntary control over bowel movements. When the sacral nerve is damaged or not functioning properly, it can result in faecal incontinence.
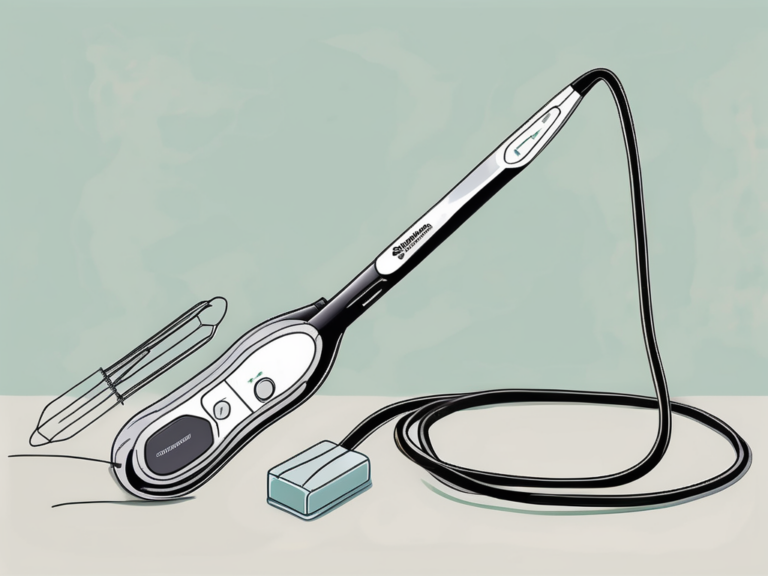
Sacral nerve stimulation is a treatment option that involves the implantation of a small device that delivers electrical impulses to the sacral nerve. These impulses help to regulate the nerve signals and restore control over bowel movements. The device is typically placed under the skin in the lower back, and the electrical stimulation can be adjusted to meet the individual’s needs.
Research has shown that sacral nerve stimulation can significantly improve symptoms of faecal incontinence, including reducing the frequency and severity of accidents. It offers a non-surgical alternative to more invasive procedures and can provide long-term relief for those living with this condition.
The Science Behind Sacral Nerve Stimulation
Sacral nerve stimulation is a surgical procedure that involves the implantation of a small device, similar to a pacemaker, near the sacral nerve in the lower back. This device delivers electrical impulses to the sacral nerve, helping to regulate bowel function. The exact mechanism of how sacral nerve stimulation works is not fully understood, but it is believed to restore the proper coordination between the brain, nerves, and muscles involved in controlling bowel movements.
The Role of the Sacral Nerve in Bowel Control
The sacral nerve is a crucial component of the nervous system that controls the functions of the bladder, bowel, and pelvic floor muscles. It plays a significant role in maintaining bowel continence by coordinating the relaxation and contraction of the muscles involved in controlling bowel movements.
When the sacral nerve is functioning properly, it sends signals from the brain to the muscles in the pelvic floor, instructing them to contract or relax as needed to control bowel movements. These signals are essential for maintaining proper bowel function and preventing involuntary leakage or constipation.
However, in some individuals, the sacral nerve may become damaged or dysfunctional, leading to problems with bowel control. This can result in conditions such as fecal incontinence or chronic constipation, which can significantly impact a person’s quality of life.
The Mechanism of Sacral Nerve Stimulation
During sacral nerve stimulation, a small electrode is placed near the sacral nerve, and a device called a neurostimulator is implanted under the skin. The neurostimulator delivers controlled electrical impulses to the sacral nerve, effectively modulating its activity. This stimulation can improve the coordination and strength of the muscles involved in bowel control, leading to better control over bowel movements.
The electrical impulses delivered by the neurostimulator mimic the signals that the brain would typically send to the sacral nerve. By providing this artificial stimulation, sacral nerve stimulation helps to restore the proper communication between the brain, nerves, and muscles involved in bowel control.
Research has shown that sacral nerve stimulation can have a positive impact on bowel function in individuals with certain conditions, such as fecal incontinence or chronic constipation. It can help reduce the frequency and severity of symptoms, improve quality of life, and reduce the need for other interventions, such as medication or surgery.
While the exact mechanism of how sacral nerve stimulation works is not fully understood, it is believed to involve a combination of factors. The electrical impulses delivered by the neurostimulator may directly stimulate the sacral nerve, promoting the release of neurotransmitters that help regulate bowel function. Additionally, the stimulation may also trigger changes in the brain and spinal cord, leading to a more coordinated and efficient control of bowel movements.
Overall, sacral nerve stimulation is a promising treatment option for individuals with bowel control problems. It offers a non-invasive alternative to more invasive procedures and can significantly improve the quality of life for those affected by fecal incontinence or chronic constipation.
The Procedure of Sacral Nerve Stimulation
Before undergoing sacral nerve stimulation, it is essential to prepare for the procedure. This may involve medical evaluations, such as bowel function tests and imaging studies, to assess the underlying cause of faecal incontinence and determine if sacral nerve stimulation is a suitable option. It is important to consult with a doctor who specializes in colorectal or pelvic floor disorders to discuss the potential benefits, risks, and alternatives to sacral nerve stimulation.
Sacral nerve stimulation is a minimally invasive procedure that offers hope to individuals suffering from faecal incontinence. By targeting the sacral nerves, which play a crucial role in controlling bowel function, this treatment aims to restore normal bowel control and improve the quality of life for patients.
Preparing for the Procedure
Prior to the procedure, your doctor will provide detailed instructions on how to prepare. This may include fasting for a certain period, discontinuing certain medications, and emptying your bowels. It is crucial to follow these instructions carefully to ensure the procedure’s success and minimize any potential complications.
Furthermore, your doctor may recommend pelvic floor exercises or physical therapy to strengthen the muscles in the pelvic region, which can enhance the effectiveness of sacral nerve stimulation. These exercises can help improve muscle tone and coordination, providing a solid foundation for the treatment.
What to Expect During and After the Procedure
The sacral nerve stimulation procedure is typically performed under local anesthesia, and it may take a few hours to complete. During the procedure, the electrode is precisely placed near the sacral nerve, and the neurostimulator is implanted under the skin. This neurostimulator delivers electrical impulses to the sacral nerves, modulating their activity and restoring normal bowel function.
The placement of the electrode requires precision and expertise. Your doctor will use imaging techniques, such as fluoroscopy or ultrasound, to guide the placement and ensure accurate positioning. This meticulous approach helps maximize the effectiveness of the treatment and minimize the risk of complications.
After the procedure, you may experience some discomfort or soreness, but this can be managed with pain medications prescribed by your doctor. It is important to follow your doctor’s post-procedure guidelines to allow for proper healing and maximize the benefits of sacral nerve stimulation.
Recovery time varies from patient to patient, but most individuals can resume their normal activities within a few days. Your doctor will schedule follow-up appointments to monitor your progress and make any necessary adjustments to the neurostimulator settings.
It is important to note that sacral nerve stimulation is not a cure for faecal incontinence, but rather a management technique that can significantly improve symptoms and quality of life. With proper care and adherence to your doctor’s recommendations, you can experience long-term benefits from this innovative treatment.
The Effectiveness of Sacral Nerve Stimulation
Sacral nerve stimulation has been shown to be an effective treatment option for faecal incontinence. Studies have demonstrated significant improvements in bowel control, with reduced episodes of incontinence and a decreased need for pads or protective garments. This innovative procedure involves the implantation of a small device that delivers electrical impulses to the sacral nerves, which play a crucial role in controlling bowel function.
The effectiveness of sacral nerve stimulation may vary from person to person. Factors such as the severity of the condition, the underlying cause of faecal incontinence, and individual response to the treatment can influence the outcomes. It is crucial to have realistic expectations and discuss your individual case with your doctor to determine if this treatment is appropriate for you.
Short-term and Long-term Effects
Many individuals experience immediate improvements in bowel control after undergoing sacral nerve stimulation. The electrical impulses delivered by the device help to regulate the muscles responsible for bowel movements, leading to a reduction in episodes of incontinence. Patients often report a renewed sense of confidence and improved quality of life.
However, it is important to note that the long-term effects of sacral nerve stimulation may require ongoing management. Regular follow-up visits with your doctor are necessary to monitor the progress and adjust the settings of the device if needed. It is important to understand that sacral nerve stimulation does not cure faecal incontinence but rather provides a tool for managing the condition.
In addition to the medical aspect, lifestyle adjustments and the development of strategies to maintain bowel health are crucial alongside sacral nerve stimulation. This may include dietary modifications, pelvic floor exercises, and the use of biofeedback techniques to improve muscle control. A multidisciplinary approach involving healthcare professionals such as physiotherapists and dieticians can provide comprehensive support and guidance.
Potential Risks and Complications
Like any surgical procedure, sacral nerve stimulation carries risks and potential complications. It is important to be aware of these and discuss them with your doctor before making a decision. Common risks include infection, bleeding, pain or discomfort, device malfunction, or an adverse reaction to anesthesia.
Your doctor will closely monitor your progress and address any concerns or complications that may arise. It is essential to follow the post-operative instructions provided by your healthcare team to minimize the risk of complications. If you experience any unusual symptoms or have concerns during the recovery period, it is important to seek medical attention promptly.
In conclusion, sacral nerve stimulation is an effective treatment option for faecal incontinence, offering significant improvements in bowel control. However, it is important to have realistic expectations, understand the long-term management required, and be aware of the potential risks and complications associated with the procedure. By working closely with your healthcare team, you can make an informed decision and optimize the outcomes of sacral nerve stimulation.
Living with Sacral Nerve Stimulation
Living with faecal incontinence can be challenging, but sacral nerve stimulation offers a promising solution for managing this condition. While the procedure itself is an important step towards improving bowel control, it is essential to understand that it is not a stand-alone solution. In addition to the procedure, there are several lifestyle adjustments and considerations that can further enhance the benefits of sacral nerve stimulation.
Lifestyle Adjustments Post-Procedure
After undergoing sacral nerve stimulation, your doctor may recommend specific lifestyle adjustments to help optimize the benefits of the procedure. These adjustments may include dietary modifications, such as increasing your fiber intake and avoiding trigger foods that can exacerbate faecal incontinence symptoms. By incorporating more fiber-rich foods into your diet, such as fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, you can promote bowel health and regularity.
In addition to dietary changes, maintaining a healthy weight through regular exercise is crucial for managing faecal incontinence. Engaging in physical activity not only helps to strengthen your overall body, but it also supports the muscles involved in bowel control. Your doctor may suggest specific exercises, such as pelvic floor exercises, to further enhance the effectiveness of sacral nerve stimulation.
Maintaining Health and Wellness with Sacral Nerve Stimulation
Managing faecal incontinence involves more than just the physical aspects. It is essential to prioritize your mental and emotional well-being as well. Dealing with the challenges of faecal incontinence can be emotionally draining, so it is crucial to talk openly with your healthcare provider about your experiences and any difficulties you may face.
Seeking support from loved ones or joining support groups can also be immensely beneficial. Connecting with others who understand what you are going through can provide a sense of community and reassurance. Sharing your experiences, listening to others, and learning from their strategies for coping with faecal incontinence can help you navigate this journey more effectively.
Remember that you are not alone in this journey. There are resources available to support you, and healthcare professionals are there to guide you every step of the way. By combining sacral nerve stimulation with lifestyle adjustments and ongoing support, you can significantly improve the quality of life for those affected by faecal incontinence.
In conclusion, sacral nerve stimulation offers a promising option for managing faecal incontinence. By understanding the principles behind this procedure and its potential benefits and risks, individuals living with faecal incontinence can make informed decisions in consultation with their healthcare providers. The combination of sacral nerve stimulation, lifestyle adjustments, and ongoing support can significantly improve the quality of life for those affected by this condition.