Which Sacral Nerve Innervates the Penis?
The topic of which sacral nerve innervates the penis is an intriguing area of study that brings together the fields of anatomy, neurology, and sexual medicine. In this article, we will delve into the complexities of the sacral nerves, their role in sexual function, and the medical implications of their innervation of the penis. It is important to note that while this article aims to provide information and insights, it is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice. If you have any concerns or questions about your sexual health, it is always best to consult with a qualified healthcare provider.
Understanding the Sacral Nerves
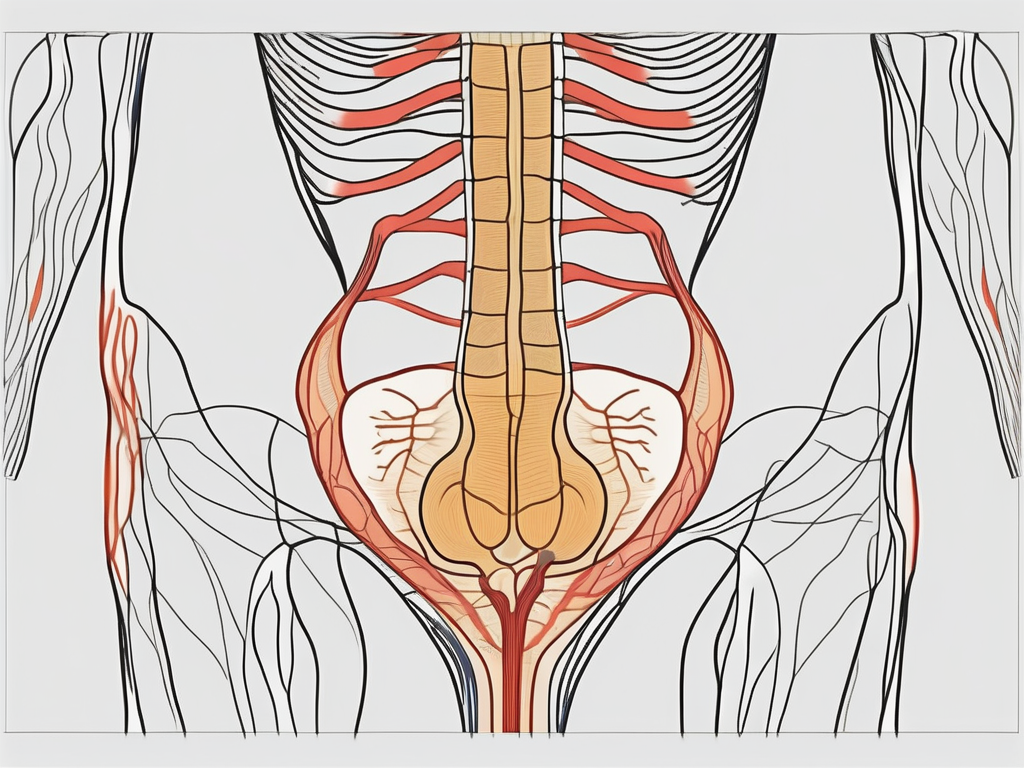
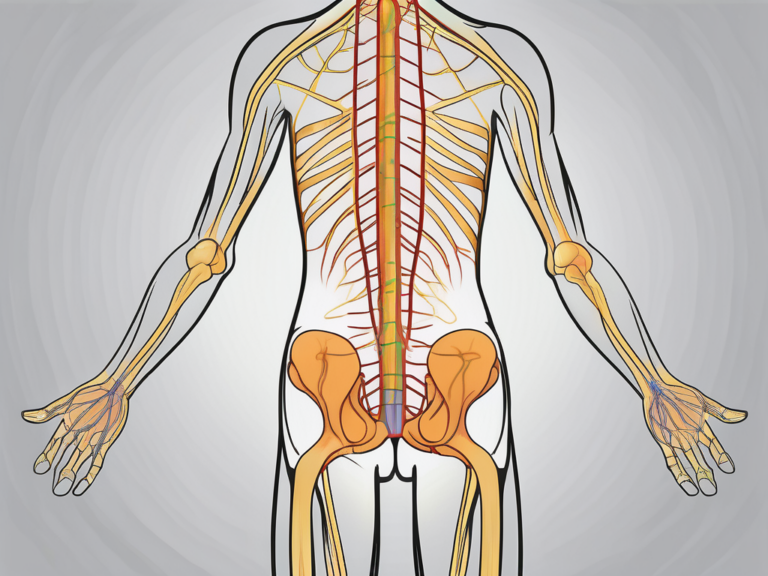
The sacral nerves are a critical component of the peripheral nervous system, responsible for transmitting signals between the brain and various organs and tissues located in the pelvic region. The sacral nerves emerge from the sacral region of the spinal cord and branch out to innervate different structures, including the penis.
Anatomy of the Sacral Nerves
The sacral nerves consist of five pairs of nerves, known as S1-S5, that originate from the sacral vertebrae. These nerves play a crucial role in the control of bladder and bowel function, as well as sexual function. The precise innervation of the penis involves the interactions between multiple sacral nerves, further emphasizing the complexity of this process.
The S1 nerve, for example, originates from the first sacral vertebra and provides sensory innervation to the skin of the buttocks and back of the thigh. It also plays a role in controlling the muscles that extend the hip joint. On the other hand, the S2 nerve supplies the skin of the posterior thigh, the back of the knee, and the calf muscles, contributing to both sensory and motor functions.
Moving further down the sacral nerves, the S3 nerve innervates the skin of the lower buttocks, perineum, and the back of the thigh. It also controls the external anal sphincter, which is essential for maintaining continence. The S4 nerve, similarly, provides sensory innervation to the perineum and the anal canal, as well as motor control over the external anal sphincter.
Lastly, the S5 nerve, the lowest of the sacral nerves, is responsible for innervating the skin around the anus and the lower part of the rectum. It also plays a role in controlling the external urethral sphincter, which is crucial for maintaining urinary continence.
Function of Sacral Nerves
The sacral nerves have a variety of functions, including motor, sensory, and autonomic functions. Motor functions involve the activation of muscles, such as those responsible for erection and ejaculation. Sensory functions relate to the transmission of stimuli, enabling the brain to perceive sensations from the penis.
For example, when the penis is stimulated, sensory signals are transmitted through the sacral nerves, allowing the brain to interpret the touch, pressure, and temperature sensations. This information is then processed, leading to the experience of pleasure and sexual arousal.
In addition to motor and sensory functions, the sacral nerves also play a crucial role in autonomic functions. These functions govern the involuntary responses of the penis, such as vascular and hormonal regulation. The sacral nerves work in coordination with other parts of the autonomic nervous system to control blood flow to the penis, allowing for the process of erection.
Furthermore, the sacral nerves are involved in the regulation of hormonal signals that influence sexual function. These nerves interact with the hypothalamus, a region of the brain responsible for releasing hormones that control sexual desire and reproductive function.
Overall, the sacral nerves are essential for the proper functioning of the pelvic region, including bladder and bowel control, as well as sexual function. Their intricate anatomy and multifaceted functions highlight their significance in maintaining overall health and well-being.
The Nervous System and Sexual Function
Understanding the relationship between the nervous system and sexual function is essential in comprehending how the sacral nerves contribute to penile innervation. The nervous system plays a central role in sexual response, influencing not only the physical processes but also the emotional and psychological aspects of sexual experiences.
Role of the Nervous System in Sexual Response
The nervous system acts as a coordinator of sexual response, integrating signals from various sources to facilitate sexual arousal and satisfaction. It communicates with different organs and tissues involved in sexual function, including the penis, through a complex network of nerves, neurotransmitters, and hormones.
When it comes to sexual response, the nervous system is responsible for transmitting signals between the brain and the genital organs. This intricate communication network allows for the coordination of physiological processes that lead to sexual arousal, such as increased blood flow to the genital area and the release of hormones that heighten sexual desire.
Moreover, the nervous system also plays a crucial role in the emotional and psychological aspects of sexual experiences. It is involved in the regulation of mood, stress levels, and overall well-being, all of which can significantly impact sexual function and satisfaction. For example, high levels of stress can inhibit sexual desire and impair sexual performance, while positive emotions and a relaxed state of mind can enhance sexual pleasure.
Neurological Control of Erection and Ejaculation
In the context of penile innervation, the sacral nerves are instrumental in the neurological control of erection and ejaculation. Erection, the process of achieving and maintaining a firm penile erection, relies on the coordinated activation of both the somatic and autonomic components of the nervous system.
The somatic nervous system, which controls voluntary movements, plays a role in initiating and maintaining an erection. It stimulates the contraction of muscles in the pelvic region, allowing for increased blood flow to the penis and the subsequent engorgement of erectile tissues. At the same time, the autonomic nervous system, specifically the parasympathetic division, promotes the release of nitric oxide, a key molecule in the process of vasodilation that facilitates the influx of blood into the penile chambers.
Ejaculation, on the other hand, involves the rhythmic contractions of muscles under the influence of the sacral nerves. These contractions propel semen from the seminal vesicles and prostate gland, through the urethra, and out of the penis. The sacral nerves coordinate this intricate process, ensuring the proper timing and intensity of muscle contractions for successful ejaculation.
It is worth noting that the nervous system’s involvement in sexual function extends beyond the physical processes of erection and ejaculation. The brain, through its connection with the nervous system, also plays a significant role in sexual desire, arousal, and pleasure. Various regions of the brain, including the hypothalamus and limbic system, are involved in the regulation of sexual behavior and the experience of sexual pleasure.
In conclusion, the nervous system is intricately involved in sexual function, playing a vital role in both the physical and psychological aspects of sexual response. Understanding the complex interplay between the nervous system and sexual function is crucial for comprehending the mechanisms underlying penile innervation and the processes of erection and ejaculation.
Sacral Nerves and the Penis
Now that we have established the significance of the sacral nerves in sexual function, let us explore their specific involvement in penile innervation.
The penis, a complex organ responsible for sexual function and reproduction, receives innervation from various sources, including both the sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions of the autonomic nervous system. This intricate network of nerves ensures the proper functioning of the penis, allowing for pleasurable sexual experiences and successful reproduction.
Innervation of the Penis: An Overview
The sacral nerves, specifically S2-S4, contribute significantly to the innervation of the penis, playing a vital role in the initiation and maintenance of penile erection. These nerves act as messengers, transmitting signals from the brain to the penis and coordinating the intricate processes involved in sexual arousal and response.
When a man becomes sexually aroused, a cascade of events is set in motion. The brain sends signals to the sacral nerves, which then release neurotransmitters that stimulate the blood vessels in the penis to dilate. This increased blood flow fills the spongy tissues within the penis, leading to its enlargement and rigidity, commonly known as an erection.
However, the sacral nerves do not act alone in this process. They work in conjunction with other nerves and structures within the penis to ensure a coordinated response. The parasympathetic division of the autonomic nervous system, for example, plays a crucial role in initiating and maintaining an erection. It releases a neurotransmitter called acetylcholine, which promotes the relaxation of penile smooth muscles, allowing for increased blood flow and erection.
Specific Sacral Nerves Involved
While all the sacral nerves are involved in the complex process of penile innervation, specific attention is given to the S2-S4 nerves due to their direct contributions to erectile function. These nerves serve as the main conduits for the transmission of signals that regulate blood flow, the relaxation of penile smooth muscles, and the release of neurotransmitters involved in the erectile response.
Within the S2-S4 nerves, there are specialized nerve fibers known as cavernous nerves. These nerves are responsible for transmitting the signals that trigger and maintain an erection. They are intricately connected to the blood vessels and smooth muscles within the penis, ensuring a coordinated response to sexual stimulation.
Damage or dysfunction of the sacral nerves, particularly the S2-S4 nerves, can have a profound impact on erectile function. Conditions such as spinal cord injuries, diabetes, and certain surgical procedures can disrupt the normal functioning of these nerves, leading to difficulties in achieving or maintaining an erection.
Understanding the role of the sacral nerves in penile innervation is crucial for diagnosing and treating erectile dysfunction. By targeting these specific nerves, healthcare professionals can develop targeted interventions to restore sexual function and improve the quality of life for individuals experiencing difficulties in this area.
Medical Implications of Sacral Nerve Innervation
Understanding the implications of sacral nerve innervation on penile function is of significant clinical importance, especially when it comes to addressing conditions such as erectile dysfunction.
The sacral nerves, specifically the S2-S4 nerve roots, play a crucial role in the complex process of achieving and maintaining an erection. These nerves transmit signals from the brain and spinal cord to the penis, coordinating the intricate interplay between blood vessels, muscles, and nerves that is necessary for a healthy erection.
When the sacral nerves are damaged, whether due to trauma, surgical interventions, or certain medical conditions, this delicate balance of signals can be disrupted, leading to erectile dysfunction. It is important to note that sacral nerve damage is not the sole cause of erectile dysfunction, as there can be various contributing factors, including psychological and vascular issues.
Sacral Nerve Damage and Erectile Dysfunction
Damage to the sacral nerves can disrupt the delicate balance of signals required for normal erectile function, leading to erectile dysfunction. Causes of sacral nerve damage can vary, ranging from trauma and surgical interventions to certain medical conditions.
For instance, spinal cord injuries, which often involve damage to the sacral nerves, can result in erectile dysfunction. The severity of the dysfunction depends on the level and extent of the injury. Additionally, conditions such as diabetes, multiple sclerosis, and pelvic surgery can also affect the sacral nerves and contribute to erectile dysfunction.
If you are experiencing persistent difficulties with achieving or maintaining an erection, it is crucial to consult with a healthcare professional who can evaluate your specific situation and provide appropriate guidance. They will conduct a thorough medical history review, physical examination, and may order additional tests to determine the underlying cause of your erectile dysfunction.
Treatment Options for Sacral Nerve Damage
Treatment options for individuals with sacral nerve damage and resulting erectile dysfunction may vary depending on the underlying cause and individual needs. Your healthcare provider may explore conservative measures, such as lifestyle modifications, or recommend more advanced treatments, including medications, penile implants, or surgical interventions.
Lifestyle modifications may include changes in diet, exercise, and stress management techniques. These can help improve overall vascular health and reduce the impact of risk factors such as obesity, smoking, and excessive alcohol consumption. In some cases, addressing psychological factors, such as anxiety or depression, may also be beneficial in managing erectile dysfunction.
Medications, such as phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitors (PDE5 inhibitors), are commonly prescribed to enhance erectile function by increasing blood flow to the penis. These medications include sildenafil (Viagra), tadalafil (Cialis), and vardenafil (Levitra). However, it is important to note that these medications may not be suitable for everyone and can have potential side effects. Your healthcare provider will determine the most appropriate medication and dosage for your specific situation.
In cases where conservative measures and medications are not effective, your healthcare provider may discuss the possibility of more advanced treatments. Penile implants, for example, are devices surgically placed in the penis to provide rigidity for sexual intercourse. There are different types of penile implants available, including inflatable and malleable implants, each with its own advantages and considerations.
Surgical interventions, such as nerve grafting or nerve stimulation procedures, may also be considered in certain cases. These procedures aim to repair or restore the damaged sacral nerves, improving the communication between the brain, spinal cord, and penis.
Always seek professional medical advice for a comprehensive evaluation and personalized treatment plan. Your healthcare provider will consider your specific needs, preferences, and overall health status to determine the most suitable treatment options for you.
Future Research Directions
As with any field of study, there are numerous unanswered questions and potential avenues for future research in the area of sacral nerve innervation and penile function.
One area of interest for future research is the exploration of the role of specific sacral nerves in penile innervation. While researchers have made significant progress in understanding the general mechanisms involved, there is still much to learn about the precise interplay between different sacral nerves and their contribution to penile function. By gaining a deeper understanding of these complex processes, scientists can develop more targeted and effective treatment strategies for individuals with sexual dysfunctions.
Another unanswered question in sacral nerve research is the impact of age and other factors on penile innervation. It is well-known that sexual function can change as individuals age, but the specific role of sacral nerves in this process is not fully understood. Further research in this area could shed light on the mechanisms behind age-related changes in penile function and potentially lead to interventions that can mitigate these effects.
Unanswered Questions in Sacral Nerve Research
Researchers continue to investigate the precise mechanisms and interplay between various sacral nerves in penile innervation. Further understanding of these complex processes can pave the way for more targeted and effective treatment strategies for individuals with sexual dysfunctions.
In addition to the role of specific sacral nerves, there are also unanswered questions regarding the impact of other factors on penile innervation. For example, the influence of hormonal changes, such as those that occur during puberty or as a result of certain medical conditions, on penile function is an area that warrants further investigation. By elucidating the relationship between hormones and sacral nerve innervation, researchers can gain insights into the underlying mechanisms of sexual dysfunction and potentially develop hormone-based therapies.
Furthermore, the impact of lifestyle factors, such as diet and exercise, on penile innervation is an area that requires more attention. While it is known that a healthy lifestyle can positively influence sexual function, the specific mechanisms through which these lifestyle factors affect sacral nerve innervation are not fully understood. Future research could help uncover the biological pathways involved and provide evidence-based recommendations for optimizing sexual health.
Potential Innovations in Treatment and Diagnosis
Advancements in medical technology and research may yield innovative approaches to diagnose and manage conditions related to sacral nerve innervation. From novel imaging techniques to emerging therapies, ongoing research in this field holds promise for improving patient outcomes and overall sexual well-being.
One potential area of innovation in the diagnosis of sacral nerve-related conditions is the development of non-invasive imaging techniques. Currently, the diagnosis of sacral nerve dysfunction often involves invasive procedures, such as nerve conduction studies or electromyography. However, advancements in imaging technology, such as functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) or positron emission tomography (PET), may provide a less invasive and more accurate means of assessing sacral nerve function. These imaging techniques could potentially offer valuable insights into the neural pathways involved in penile innervation and aid in the diagnosis of various sexual dysfunctions.
In terms of treatment innovations, ongoing research is exploring the potential of emerging therapies, such as neuromodulation techniques, in managing sacral nerve-related conditions. Neuromodulation involves the use of electrical or magnetic stimulation to modulate neural activity and has shown promise in treating various neurological disorders. By applying these techniques to sacral nerve innervation, researchers aim to develop non-invasive and targeted interventions for individuals with sexual dysfunctions. Additionally, advancements in pharmacological research may lead to the development of new medications specifically designed to enhance sacral nerve function and improve penile function.
In conclusion, the field of sacral nerve innervation and penile function is ripe with unanswered questions and potential for future research. By delving deeper into the mechanisms and interplay between sacral nerves, investigating the impact of age and other factors, and exploring innovative approaches to diagnosis and treatment, scientists can pave the way for advancements that will improve the sexual well-being of individuals worldwide.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the innervation of the penis by the sacral nerves is a fascinating area of study. These nerves, along with other components of the nervous system, play a crucial role in sexual function, including erection and ejaculation. Understanding the implications of sacral nerve innervation on penile function is essential for addressing conditions such as erectile dysfunction. However, it is important to remember that this article provides general information and should not replace professional medical advice. If you have concerns about your sexual health, do not hesitate to consult with a knowledgeable healthcare provider who can guide you through a comprehensive evaluation and appropriate management strategies.