Where Is the Location of the Sacral Nerve?
The sacral nerve is a crucial component of the human nervous system, playing a vital role in various bodily functions. Understanding the location of the sacral nerve is essential for diagnosing and treating any related issues that may arise. In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of the human nervous system, explore the function and anatomy of the sacral nerve, and discuss common conditions associated with this nerve. We will also touch upon the available treatment options for individuals dealing with sacral nerve problems.
Understanding the Human Nervous System
The human nervous system is a complex network of nerves and cells that transmit signals between different parts of the body. It comprises two main components: the central nervous system (CNS) and the peripheral nervous system (PNS). The CNS consists of the brain and spinal cord, while the PNS consists of the nerves that branch out from the spinal cord to the rest of the body.
The central nervous system, which includes the brain and spinal cord, is often referred to as the command center of the body. It is responsible for processing and interpreting sensory information, as well as coordinating and controlling the activities of the body. The brain, with its billions of neurons, is the most complex organ in the human body and plays a crucial role in our ability to perceive our environment, think, reason, and respond to various stimuli.
The Role of the Nervous System
The primary function of the nervous system is to coordinate and control the activities of the body. It allows us to perceive our environment, think, reason, and respond to various stimuli. The nervous system also regulates bodily functions such as digestion, breathing, and movement.
When we touch a hot surface, for example, the nervous system quickly sends signals to the brain, which interprets the sensation as pain and sends signals back to the muscles, causing them to pull away from the source of heat. This rapid response is made possible by the intricate network of neurons that make up the nervous system.
Major Components of the Nervous System
The nervous system can be further divided into various components, each with its own specific functions. These components include the brain, spinal cord, nerves, and ganglia. The brain is responsible for processing and interpreting sensory information, while the spinal cord acts as a conduit for transmitting signals between the brain and the rest of the body.
Nerves, which are bundles of fibers, connect the CNS to different parts of the body. They transmit signals to and from the brain, allowing us to move our muscles, feel sensations, and perform various bodily functions. Without nerves, our bodies would be unable to communicate with the brain, rendering us immobile and unable to interact with the world around us.
Ganglia, on the other hand, are clusters of nerve cells that act as relay stations. They are found outside the brain and spinal cord, and their main function is to receive and transmit signals between different parts of the body. Ganglia play a crucial role in the autonomic nervous system, which controls involuntary bodily functions such as heart rate, digestion, and breathing.
In conclusion, the human nervous system is a remarkable and intricate network that allows us to interact with the world around us. From the brain’s processing of sensory information to the transmission of signals through the spinal cord and nerves, every component plays a vital role in our ability to perceive, think, reason, and respond. Understanding the complexity of the nervous system is key to understanding the complexity of human beings.
An Overview of the Sacral Nerve
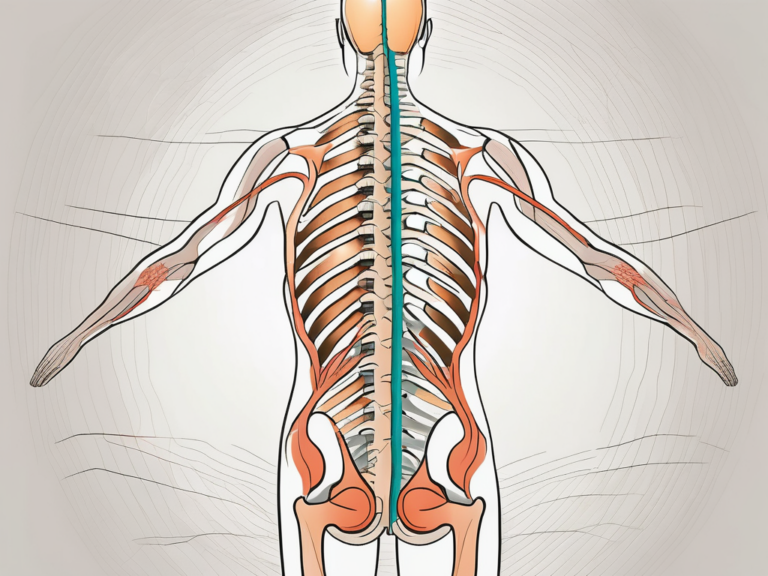
The sacral nerve is a crucial part of the Peripheral Nervous System (PNS), located in the lower part of the spine known as the sacrum. It arises from the merging of nerve roots originating from the lumbar and sacral regions of the spinal cord.
The sacral nerve, also known as the sacral plexus, is a complex network of nerves that extends from the lower back to the pelvis. It is responsible for transmitting signals between the brain and the lower part of the body, playing a vital role in various bodily functions.
The Function of the Sacral Nerve
The sacral nerve plays a crucial role in controlling various functions, including bladder and bowel control, sexual function, and the sensation in the lower extremities. It carries both sensory and motor signals, allowing for the transmission of information between the brain and the lower part of the body.
Bladder and bowel control are essential for maintaining proper urinary and digestive functions. The sacral nerve controls the muscles that enable the bladder to contract and relax, allowing for the storage and release of urine. Similarly, it regulates the muscles responsible for bowel movements, ensuring the proper elimination of waste from the body.
In addition to bladder and bowel control, the sacral nerve also plays a significant role in sexual function. It innervates the reproductive organs, including the penis and clitoris, and controls the muscles involved in sexual arousal, erection, and orgasm. Without the proper functioning of the sacral nerve, sexual dysfunction may occur.
Furthermore, the sacral nerve is responsible for transmitting sensory signals from the lower extremities to the brain. It enables us to perceive sensations such as touch, temperature, and pain in our legs, feet, and pelvic region. This sensory feedback is crucial for maintaining balance, coordination, and overall body awareness.
Anatomy of the Sacral Nerve
The sacral nerve consists of a bundle of nerve fibers, which branch out from the spinal cord and travel through the pelvis. These nerve fibers innervate different organs and muscles in the pelvic region, playing a vital role in ensuring proper function.
Within the sacral nerve, there are several individual nerves that carry out specific functions. These include the pudendal nerve, which controls the muscles of the perineum and external genitalia, and the sciatic nerve, which is the largest nerve in the body and provides motor and sensory innervation to the lower extremities.
The sacral nerve also branches out to innervate the pelvic organs, such as the bladder, uterus, and rectum. It controls the contraction and relaxation of the muscles in these organs, allowing for proper function and regulation.
In addition to its role in controlling pelvic organs and muscles, the sacral nerve also communicates with other nerves in the body. It forms connections with the lumbar and thoracic nerves, ensuring the coordination of signals between different regions of the spinal cord and the brain.
In conclusion, the sacral nerve is a crucial component of the PNS, responsible for controlling various functions such as bladder and bowel control, sexual function, and sensation in the lower extremities. Its intricate anatomy and network of nerves enable the transmission of signals between the brain and the lower part of the body, ensuring proper bodily function and overall well-being.
Locating the Sacral Nerve in the Body
The sacral nerve’s location within the body is of great importance when diagnosing and treating related issues. A brief overview of the sacral region will provide a clearer understanding of its location.
The Sacral Region: A Brief Overview
The sacrum, a triangular bone located at the base of the spine, comprises five fused vertebrae. It serves as a strong foundation for the pelvis and supports the weight of the upper body. The sacral region houses the sacral nerve and various other vital structures.
Within the sacral region, the sacral nerve is a crucial component of the body’s nervous system. It originates from the spinal cord and extends downwards, branching out to innervate various muscles and organs in the pelvic area. The sacral nerve plays a significant role in controlling bladder and bowel function, as well as sexual function.
Surrounding the sacral nerve are other important structures that contribute to the overall functionality of the sacral region. These include blood vessels, ligaments, and connective tissues that provide support and nourishment to the surrounding structures.
Furthermore, the sacral region is closely connected to the lumbar and coccygeal regions of the spine. The lumbar region, located above the sacrum, consists of five large vertebrae that provide flexibility and stability to the lower back. The coccygeal region, on the other hand, is made up of the coccyx, commonly known as the tailbone, which serves as an attachment site for various muscles and ligaments.
Identifying the Sacral Nerve
Locating the sacral nerve requires a comprehensive understanding of the body’s anatomy. Medical professionals, such as doctors and neurologists, possess the expertise to perform physical examinations and other diagnostic tests to identify the sacral nerve accurately.
During a physical examination, healthcare providers may assess the sacral nerve by evaluating the patient’s reflexes, muscle strength, and sensation in the pelvic area. They may also use imaging techniques, such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) or computed tomography (CT) scans, to visualize the sacral nerve and surrounding structures in detail.
In some cases, specialized nerve conduction studies or electromyography (EMG) may be conducted to assess the electrical activity and function of the sacral nerve. These tests can help diagnose conditions such as sacral nerve damage, compression, or dysfunction.
Once the sacral nerve is accurately identified, healthcare professionals can develop appropriate treatment plans tailored to the specific condition or issue affecting the nerve. This may include a combination of medication, physical therapy, lifestyle modifications, or, in severe cases, surgical intervention.
Overall, understanding the location and function of the sacral nerve is crucial for diagnosing and treating related issues effectively. Medical professionals play a vital role in identifying and addressing sacral nerve problems, ensuring optimal health and well-being for their patients.
Conditions Related to the Sacral Nerve
Various conditions can affect the sacral nerve, leading to discomfort and dysfunction. Recognizing the common issues associated with this nerve is crucial for appropriate treatment.
The sacral nerve, also known as the sacral plexus, is a complex network of nerves that originates from the lower part of the spinal cord. It plays a vital role in controlling the muscles and organs in the pelvis and lower extremities. When this nerve is affected by certain conditions, it can cause a range of symptoms and complications.
Common Sacral Nerve Disorders
Conditions such as sacral nerve compression, sacral nerve entrapment, and sacral radiculopathy can result in pain, tingling sensations, and muscle weakness in the lower body. Sacral nerve compression occurs when there is pressure on the nerve, often due to a herniated disc, spinal stenosis, or a tumor. Sacral nerve entrapment, on the other hand, happens when the nerve gets trapped or pinched, leading to similar symptoms. Sacral radiculopathy refers to the irritation or inflammation of the nerve roots that make up the sacral plexus.
These disorders may arise from trauma, inflammation, or degenerative changes in the spine. Traumatic injuries, such as a fall or car accident, can cause damage to the sacral nerve. Inflammation, often associated with conditions like arthritis or infections, can also affect the nerve. Additionally, degenerative changes in the spine, such as disc degeneration or bone spurs, can put pressure on the sacral nerve and lead to dysfunction.
Symptoms of Sacral Nerve Damage
Individuals experiencing issues with the sacral nerve may exhibit symptoms such as urinary or fecal incontinence, sexual dysfunction, numbness or tingling in the legs or feet, or difficulty walking. These symptoms can significantly impact a person’s quality of life and daily functioning. However, it is important to note that these symptoms may also be indicative of other underlying conditions. Consulting with a medical professional is crucial for an accurate diagnosis.
When diagnosing sacral nerve damage, healthcare providers will typically perform a thorough physical examination and may order additional tests, such as imaging studies or nerve conduction studies, to assess the extent of the nerve involvement. Treatment options for sacral nerve disorders vary depending on the underlying cause and severity of symptoms. Conservative approaches, such as physical therapy, pain management techniques, and medication, are often the first line of treatment. In more severe cases, surgical intervention may be necessary to relieve pressure on the nerve or repair any damage.
Living with a sacral nerve disorder can be challenging, but with proper management and support, individuals can find relief from their symptoms and improve their overall well-being. It is essential to work closely with a healthcare team to develop an individualized treatment plan that addresses the specific needs and goals of the patient.
Treatment Options for Sacral Nerve Issues
When it comes to addressing sacral nerve problems, multiple treatment options are available depending on the severity and underlying cause of the issue.
The sacral nerve, as part of the peripheral nervous system, plays a vital role in controlling various bodily functions. It is responsible for transmitting signals between the brain and the lower part of the body, including the bladder, bowel, and sexual organs. When the sacral nerve is affected by injury or disease, it can lead to a range of symptoms and complications.
Non-Surgical Treatments for Sacral Nerve Problems
Conservative approaches, such as physical therapy, medications, and lifestyle modifications, are often the first line of treatment for sacral nerve issues. Physical therapy can help strengthen surrounding muscles and improve overall function. It may involve exercises and techniques specifically designed to target the affected area and alleviate symptoms.
In addition to physical therapy, medications may be prescribed to provide pain relief or reduce inflammation. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can help alleviate pain and reduce swelling, while muscle relaxants may be used to relieve muscle spasms that can occur as a result of sacral nerve problems.
Lifestyle modifications can also play a significant role in managing sacral nerve issues. Maintaining a healthy weight can help reduce pressure on the nerve and alleviate symptoms. Engaging in regular exercise, such as low-impact activities like swimming or yoga, can also help improve overall muscle strength and flexibility.
Surgical Interventions for Sacral Nerve Damage
In more severe cases or when conservative treatments prove ineffective, surgical interventions may be considered. Surgical options range from decompression procedures to remove pressure on the nerve to nerve repair or grafting in cases of nerve damage.
Decompression procedures involve removing any structures that may be compressing the sacral nerve, such as herniated discs or bone spurs. This can help relieve pressure and allow the nerve to function properly. Nerve repair or grafting procedures may be necessary in cases where the sacral nerve has been damaged or severed. These procedures aim to restore the continuity of the nerve and promote healing.
It is important to note that surgical interventions should only be pursued after careful evaluation and consultation with a medical professional. The risks and benefits of each procedure should be thoroughly discussed, and the decision should be made based on the individual’s specific condition and needs.
If you experience symptoms or have concerns about your sacral nerve, it is crucial to consult with a medical professional who can provide appropriate guidance and care. They will be able to conduct a thorough evaluation, diagnose the underlying cause of your symptoms, and recommend the most suitable treatment options for your specific situation.