What Is the Sacral Nerve Root Sleeve?
The sacral nerve root sleeve is a vital component of the human nervous system, playing a crucial role in sensory perception and motor functions. Located within the sacrum, a triangular bone at the base of the spine, this anatomical structure connects the spinal cord to various other nerves throughout the body. Understanding the function and potential disorders associated with the sacral nerve root sleeve is essential for maintaining optimal health and well-being. In this article, we will explore the significance of this intricate nerve network and discuss its impact on overall health.
Understanding the Human Nervous System
The human nervous system is a complex network that controls and coordinates various bodily functions. It comprises two primary divisions: the central nervous system (CNS) and the peripheral nervous system (PNS). The CNS consists of the brain and spinal cord, while the PNS extends throughout the body, connecting these central structures to the rest of the body.
The central nervous system, consisting of the brain and spinal cord, is the command center of the body. It receives and processes information from the sensory organs and sends out signals to initiate appropriate responses. The brain, with its billions of neurons, is responsible for higher cognitive functions, such as thinking, memory, and emotions. The spinal cord, on the other hand, acts as a relay station, transmitting signals between the brain and the rest of the body.
The peripheral nervous system, on the other hand, is responsible for connecting the central nervous system to the various organs, muscles, and glands throughout the body. It consists of nerves that extend from the brain and spinal cord to every part of the body. These nerves serve as the communication pathways of the body, transmitting electrical impulses between the brain, spinal cord, and other body parts.
The Role of Nerves in the Body
Nerves serve as the communication pathways of the body, transmitting electrical impulses between the brain, spinal cord, and other body parts. They play a crucial role in relaying sensory information, such as touch, temperature, and pain, as well as controlling voluntary and involuntary movements.
When you touch a hot stove, sensory nerves in your skin send signals to your brain, alerting you to the danger and triggering a reflex action to withdraw your hand. Similarly, when you hear a loud noise, sensory nerves in your ears transmit the sound waves to your brain, allowing you to perceive and interpret the sound.
In addition to sensory information, nerves also play a vital role in controlling voluntary and involuntary movements. Motor nerves, which carry signals from the central nervous system to the muscles, allow you to move your limbs, speak, and perform various actions. These nerves transmit signals that initiate muscle contractions, enabling you to walk, run, and perform intricate tasks with precision.
Different Types of Nerves and Their Functions
There are three primary types of nerves in the human body: sensory nerves, motor nerves, and mixed nerves. Sensory nerves carry sensory information from the peripheral organs to the CNS, allowing us to perceive the environment. These nerves are responsible for transmitting signals related to touch, temperature, pain, and other sensory experiences.
Motor nerves, on the other hand, send signals from the CNS to the muscles and glands, enabling voluntary movements and bodily functions. These nerves play a crucial role in controlling muscle contractions, allowing us to perform a wide range of movements, from simple actions like picking up a pen to complex activities like playing a musical instrument.
Mixed nerves contain both sensory and motor fibers, ensuring bidirectional communication between the central nervous system and the rest of the body. These nerves are involved in complex processes that require both sensory input and motor output, such as reflex actions and coordinated movements.
Understanding the different types of nerves and their functions is essential in comprehending the intricate workings of the human nervous system. The complex interplay between sensory and motor nerves allows us to interact with our environment, experience sensations, and perform a myriad of physical activities.
Anatomy of the Sacral Nerve Root Sleeve
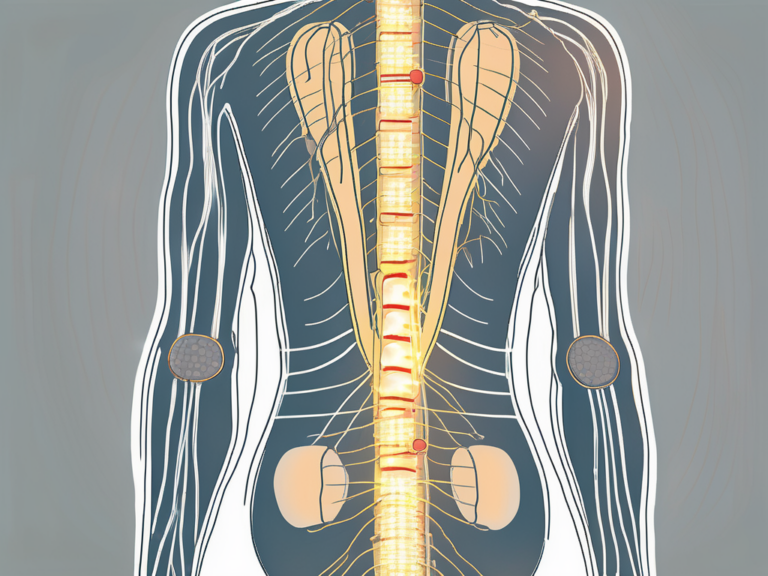
The sacral nerve root sleeve, also known as the cauda equina, is a bundle of nerve roots that extends from the lower end of the spinal cord. It is named after its resemblance to a horse’s tail. Located within the sacrum, it is responsible for transmitting signals between the lower body and the central nervous system.
The sacral nerve root sleeve is a fascinating structure that plays a crucial role in our body’s functioning. Let’s delve deeper into its location, structure, and connection to the spinal cord and other nerves.
Location and Structure of the Sacral Nerve Root Sleeve
The sacral nerve root sleeve starts at the level of the lumbar 1 (L1) vertebra and descends through the vertebral canal until it reaches the sacrum. The sacrum, a triangular bone formed by the fusion of five vertebrae, provides a protective housing for the nerve roots.
Within the sacral nerve root sleeve, there are multiple individual nerve roots that combine to form a complex network. These roots arise from the spinal cord and travel through the vertebral canal. As they descend, they gradually merge together, forming the cauda equina.
The cauda equina, with its numerous nerve roots, resembles a horse’s tail in appearance. This unique structure allows for the distribution of nerve signals to various parts of the lower body.
As the sacral nerve root sleeve continues its journey through the vertebral canal, it encounters small openings called intervertebral foramina. These foramina serve as exit points for the nerve roots, allowing them to branch out and connect with other nerves.
Connection to the Spinal Cord and Other Nerves
The sacral nerve root sleeve plays a vital role in connecting the lower body to the central nervous system. It connects with the spinal cord at the lower end of the spinal column, ensuring efficient communication between the two.
From its connection with the spinal cord, the sacral nerve root sleeve branches out to form various nerves that supply the pelvis, legs, and feet. These nerves enable the transmission of sensory information, such as touch, pain, and temperature, from these regions to the brain.
In addition to sensory information, the sacral nerve root sleeve also coordinates motor activities in the pelvis, legs, and feet. It allows for the control of muscle movements, enabling us to walk, run, and perform various physical activities with precision.
The intricate connection between the sacral nerve root sleeve and other nerves ensures the smooth functioning of our lower body. It is responsible for our ability to feel sensations, move our limbs, and maintain balance.
In conclusion, the sacral nerve root sleeve is a remarkable structure that deserves our attention. Its location within the sacrum, complex network of nerve roots, and connection to the spinal cord and other nerves make it an essential component of our nervous system. Understanding its anatomy helps us appreciate the intricate workings of our body and the importance of maintaining its health.
Functions of the Sacral Nerve Root Sleeve
The sacral nerve root sleeve plays a significant role in sensory perception and motor functions, contributing to our overall well-being and quality of life.
The sacral nerve root sleeve, located in the lower back region, is a complex network of nerves that extends from the spinal cord. It is an integral part of the peripheral nervous system, connecting the central nervous system to various organs and muscles in the lower body.
Role in Sensory Perception
The sensory nerves within the sacral nerve root sleeve enable us to perceive sensations from the lower body. This includes sensations such as touch, pain, temperature, and proprioception. Proprioception is the body’s ability to sense its position and movement without relying on visual cues. This crucial sensory input helps us maintain balance, coordination, and spatial awareness.
For example, when walking on an uneven surface, the sacral nerve root sleeve sends signals to the brain, informing it about the changes in the terrain. This allows us to adjust our movements and prevent falls or injuries. Similarly, when we touch something hot, the sensory nerves in the sacral nerve root sleeve quickly transmit the information to the brain, triggering a reflex action to withdraw our hand, protecting us from potential harm.
Contribution to Motor Functions
The sacral nerve root sleeve is also responsible for controlling the motor functions of the pelvic organs, lower limbs, and feet. Motor nerves originating from this structure play a vital role in muscle movement, allowing us to walk, run, and perform various daily activities. Dysfunction in these motor pathways can result in muscle weakness, coordination difficulties, and impaired mobility.
When we decide to take a step forward, the brain sends signals through the sacral nerve root sleeve to the muscles in our legs and feet, initiating the necessary movements. These signals travel along the nerve fibers, activating the appropriate muscles and coordinating their contractions. Without the sacral nerve root sleeve, our ability to move our lower body would be severely compromised.
In addition to controlling voluntary movements, the sacral nerve root sleeve also plays a role in involuntary actions, such as bladder and bowel control. The nerves within this structure help regulate the muscles responsible for these functions, ensuring proper coordination and timing.
Furthermore, the sacral nerve root sleeve is involved in sexual function. It plays a crucial role in transmitting signals related to sexual arousal and orgasm, contributing to a healthy and satisfying sexual experience.
In conclusion, the sacral nerve root sleeve is a vital component of our nervous system, enabling us to perceive sensations from the lower body and control motor functions. Its intricate network of nerves ensures that we can move, feel, and function properly, enhancing our overall well-being and quality of life.
Disorders Related to the Sacral Nerve Root Sleeve
Several disorders can affect the sacral nerve root sleeve, leading to various symptoms and impairments. The sacral nerve root sleeve is a crucial part of the nervous system, responsible for transmitting signals between the brain and the lower extremities. When this delicate network is disrupted, it can result in debilitating conditions that significantly impact an individual’s quality of life.
One of the most common disorders related to the sacral nerve root sleeve is sciatica. Sciatica occurs when the sciatic nerve, which originates in the lower back and travels down the legs, becomes compressed or irritated. This compression can cause excruciating pain, numbness, and tingling sensations that radiate from the lower back through the buttocks and down the legs. Simple activities like sitting, standing, or walking can exacerbate these symptoms, making it challenging for individuals to carry out their daily routines.
Another disorder that affects the sacral nerve root sleeve is spinal stenosis. Spinal stenosis refers to the narrowing of the spinal canal, which houses the spinal cord and nerve roots. When the spinal canal becomes constricted, it can put pressure on the sacral nerve root sleeve, leading to pain, weakness, and difficulty with mobility. This condition is often associated with aging and degenerative changes in the spine.
Common Symptoms and Causes of Sacral Nerve Disorders
Disorders of the sacral nerve root sleeve can manifest in different ways, depending on the specific nerves affected. In addition to the aforementioned pain, numbness, or tingling in the lower back, buttocks, legs, or feet, individuals may also experience muscle weakness, difficulty controlling bladder or bowel function, and sexual dysfunction. These symptoms can significantly impact an individual’s physical and emotional well-being, making it crucial to seek timely medical attention.
A herniated disc is one of the leading causes of sacral nerve disorders. A herniated disc occurs when the soft, gel-like center of a spinal disc protrudes through a tear in the outer layer. This protrusion can compress the sacral nerve root sleeve, leading to pain and other symptoms. Spinal stenosis, as mentioned earlier, can also contribute to sacral nerve disorders by causing narrowing of the spinal canal and subsequent nerve compression.
Diagnosis and Treatment Options for Sacral Nerve Disorders
Diagnosing sacral nerve disorders typically involves a comprehensive evaluation of the symptoms, medical history, and physical examination. Healthcare providers may also order additional tests, such as imaging studies like magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) or computed tomography (CT) scans, to visualize the affected area in more detail. Nerve conduction studies may also be conducted to assess the speed and strength of nerve signals.
Once a diagnosis is confirmed, treatment options can be explored. In many cases, conservative measures are initially recommended. Physical therapy can help strengthen the muscles surrounding the affected area, improve flexibility, and alleviate pain. Pain management techniques, such as hot or cold therapy, transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS), or acupuncture, may also provide relief. Medications, including nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) or muscle relaxants, may be prescribed to manage pain and inflammation.
In some cases, when conservative measures fail to provide sufficient relief, surgical intervention may be necessary. Surgery aims to alleviate nerve compression or correct underlying structural issues contributing to the disorder. Procedures such as discectomy, laminectomy, or spinal fusion may be performed, depending on the specific condition and its severity. It is crucial to discuss treatment options with a healthcare provider to determine the most appropriate approach for an individual’s specific condition.
In conclusion, disorders related to the sacral nerve root sleeve can cause a range of symptoms and impairments that significantly impact an individual’s daily life. Recognizing the signs of these disorders and seeking appropriate medical attention is essential for accurate diagnosis and timely treatment. With the right interventions, individuals can regain their quality of life and alleviate the pain and discomfort associated with sacral nerve disorders.
The Impact of Sacral Nerve Root Sleeve on Overall Health
The sacral nerve root sleeve’s functioning and well-being significantly impact a person’s overall health, mobility, and quality of life.
The Sacral Nerve Root Sleeve and Quality of Life
As a crucial component of the nervous system, any dysfunction or impairment of the sacral nerve root sleeve can have a profound impact on an individual’s daily life. Difficulties with sensory perception and motor control can lead to decreased mobility, limitations in activities of daily living, and reduced overall quality of life. Seeking early intervention and appropriate treatment can help manage symptoms and improve functioning for individuals with sacral nerve disorders.
Maintaining a Healthy Nervous System
To maintain a healthy nervous system, it is essential to prioritize overall well-being and adopt healthy lifestyle habits. Regular exercise, a balanced diet, and stress management techniques can support optimal nerve functioning. Additionally, avoiding activities that place excessive strain on the lower back and practicing proper posture can help prevent nerve compression and associated disorders. If experiencing any symptoms related to the sacral nerve root sleeve, consulting with a medical professional is highly recommended for accurate diagnosis and personalized guidance.
In conclusion, the sacral nerve root sleeve plays a crucial role in the human nervous system, contributing to sensory perception and motor functions. Understanding its anatomy, functions, and potential disorders is essential for maintaining overall health and well-being. By remaining vigilant of any signs of sacral nerve disorders and seeking appropriate medical attention, individuals can ensure timely intervention and improve their quality of life. Prioritizing a healthy lifestyle and taking steps to prevent nerve compression can also support optimal nervous system functioning. Remember, when it comes to any health-related concerns, consulting with a qualified healthcare professional is the best course of action.