What Does a Sacral Nerve Stimulator Do?
A sacral nerve stimulator is a specialized medical device that plays a crucial role in managing various medical conditions related to the sacral nerve. To truly understand the significance and effectiveness of this device, it is essential to delve into the intricacies of the sacral nerve itself. By exploring the anatomy and function of the sacral nerve, we can gain insight into how this innovative device works and its immense therapeutic potential. Additionally, it is vital to discuss the medical conditions that can be treated through sacral nerve stimulation, the procedure involved, and the benefits and risks associated with the treatment. This article aims to provide an in-depth analysis of the sacral nerve stimulator, shedding light on its significant advancements in the medical field.
Understanding the Sacral Nerve
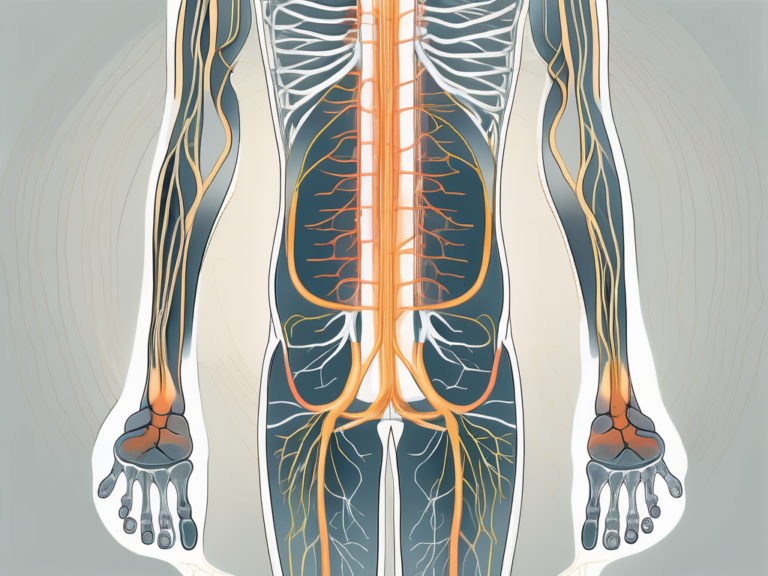
The sacral nerve, also known as the sacral plexus, is an essential part of the nervous system. It originates from the spinal cord and plays a critical role in controlling various bodily functions, particularly those related to the pelvic region. The sacral nerve is responsible for regulating bladder, bowel, and sexual functions. It also has a role in providing sensory information to these areas of the body. Understanding the anatomy and function of this nerve is crucial in understanding the mechanisms behind sacral nerve stimulation.
Anatomy of the Sacral Nerve
The sacral nerve originates from the lower back, specifically the third and fourth lumbar vertebrae. It then travels through the sacrum, which is the triangular bone located at the base of the spine. From the sacrum, the nerve branches out and innervates various pelvic organs, including the bladder, urethra, rectum, and genitals. This intricate network of nerves allows for the transmission of signals between the brain and these organs, ensuring proper functioning.
Within the sacral nerve, there are multiple nerve roots that contribute to its overall function. These nerve roots arise from the spinal cord and merge together to form the sacral plexus. The sacral plexus is a complex network of nerves that extends from the lower back into the pelvis. It is within this plexus that the sacral nerve gains its strength and ability to control the pelvic organs.
As the sacral nerve travels through the sacrum, it gives off smaller branches that supply specific areas of the pelvic region. These branches form a web-like structure, ensuring that every part of the pelvic organs receives the necessary nerve supply. This intricate branching pattern allows for precise control and coordination of bladder, bowel, and sexual functions.
Function of the Sacral Nerve
The sacral nerve serves as a connection between the brain and the pelvic organs, enabling voluntary and involuntary control over their activities. It plays a crucial role in regulating bladder function, maintaining continence, and controlling bowel movements. Through its sensory fibers, the sacral nerve also provides feedback to the brain, allowing us to perceive sensations related to the pelvic region.
When it comes to bladder function, the sacral nerve plays a vital role in coordinating the storage and emptying of urine. It sends signals to the bladder muscles, instructing them to contract or relax at the appropriate times. This coordination ensures that urine is stored in the bladder until it is convenient to empty it, preventing involuntary leakage.
In terms of bowel control, the sacral nerve helps regulate the movement of stool through the intestines. It sends signals to the muscles of the rectum and anus, allowing for voluntary control over bowel movements. Dysfunction of the sacral nerve can lead to conditions such as fecal incontinence or constipation.
Sexual function is also influenced by the sacral nerve. It provides sensory innervation to the genitals, allowing for the perception of touch, temperature, and pressure. Additionally, the sacral nerve plays a role in sexual arousal and orgasm, transmitting signals between the brain and the reproductive organs.
Any dysfunction or damage to the sacral nerve can result in a range of medical conditions affecting these areas. Conditions such as urinary incontinence, fecal incontinence, and sexual dysfunction may arise when the sacral nerve is compromised. Understanding the intricate workings of the sacral nerve is crucial in diagnosing and treating these conditions, as well as developing therapies such as sacral nerve stimulation.
The Science Behind Sacral Nerve Stimulation
Sacral nerve stimulation takes advantage of the remarkable capabilities of the nervous system to manage and alleviate certain medical conditions. By utilizing low levels of electrical impulses, the device can modulate the activity of the sacral nerve, providing relief and controlling symptoms. Understanding the role of electrical impulses and their interaction with the nervous system is fundamental in comprehending the science behind this treatment method.
The nervous system, a complex network of cells and fibers, plays a crucial role in transmitting signals throughout the body. It consists of two main components: the central nervous system, which includes the brain and spinal cord, and the peripheral nervous system, which extends throughout the rest of the body. The peripheral nervous system is further divided into the somatic and autonomic nervous systems, with the latter being responsible for regulating involuntary bodily functions.
The Role of Electrical Impulses
Electrical impulses, when delivered precisely and selectively to the sacral nerve, can alter its activity and restore proper functioning. This stimulation modifies the way signals are transmitted between the brain and the pelvic organs, resulting in improved control and reduced symptoms. The electrical impulses can be adjusted and customized based on the individual’s specific condition, ensuring optimal outcomes.
The sacral nerve, also known as the S3 nerve, is a key player in the regulation of bladder, bowel, and sexual functions. It is located in the lower part of the spinal cord and plays a vital role in transmitting signals between the brain and the pelvic organs. When this nerve is not functioning properly, it can lead to a range of debilitating conditions, such as urinary incontinence, fecal incontinence, and pelvic pain.
By delivering electrical impulses to the sacral nerve, sacral nerve stimulation can restore the balance of signals, improving the coordination and control of the pelvic organs. This can significantly enhance the quality of life for individuals suffering from these conditions, allowing them to regain control and independence.
Interaction with the Nervous System
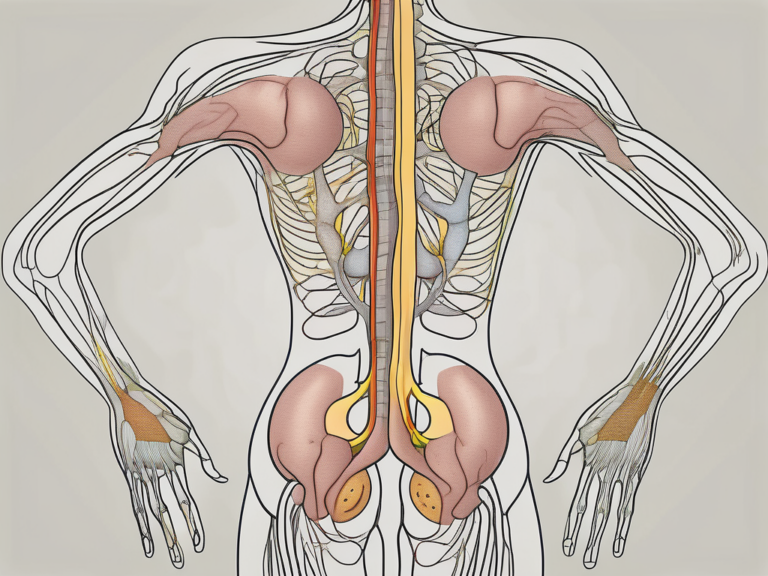
The sacral nerve stimulator is designed to interact with the nervous system in a highly targeted manner. It consists of an implantable pulse generator (IPG) and thin lead wires. The IPG, placed under the skin in the buttock or lower back area, generates the electrical impulses, while the lead wires act as conduits, delivering the impulses to the sacral nerve. The device can be programmed and adjusted externally to cater to the patient’s needs, allowing for personalized treatment plans.
The implantation of the sacral nerve stimulator is a minimally invasive procedure that involves placing the IPG and lead wires in precise locations. The IPG is typically placed under the skin, where it can be easily accessed for programming and adjustments. The lead wires are carefully positioned to ensure optimal contact with the sacral nerve, maximizing the effectiveness of the electrical impulses.
Once the sacral nerve stimulator is implanted, patients can experience the benefits of this innovative treatment method. The device can be programmed to deliver electrical impulses at specific frequencies, durations, and amplitudes, tailored to the individual’s needs. This customization allows healthcare professionals to fine-tune the treatment and optimize outcomes for each patient.
Furthermore, the sacral nerve stimulator is designed to be reversible. If necessary, the device can be removed, and the electrical stimulation can be discontinued. This flexibility provides patients with the option to explore alternative treatment options or discontinue treatment altogether, depending on their preferences and medical circumstances.
In conclusion, sacral nerve stimulation harnesses the power of electrical impulses and their interaction with the nervous system to alleviate symptoms and restore proper functioning. By precisely modulating the activity of the sacral nerve, this treatment method offers hope and relief for individuals suffering from conditions affecting the pelvic organs. Through ongoing research and advancements in technology, the science behind sacral nerve stimulation continues to evolve, paving the way for improved outcomes and enhanced quality of life.
The Sacral Nerve Stimulator Device
The sacral nerve stimulator device is a marvel of medical engineering, intricately designed to accurately deliver electrical impulses to the sacral nerve. Understanding the components and design of this device, as well as how it operates, is crucial in appreciating its effectiveness and reliability.
Components and Design
The sacral nerve stimulator consists of several key components, including the implantable pulse generator, lead wires, and an external programmer. The implantable pulse generator, often battery-powered, generates the electrical impulses that stimulate the sacral nerve. It is safely implanted under the skin, ensuring ease of use and long-term efficacy. The lead wires connect the implantable pulse generator to the sacral nerve, providing a direct pathway for the electrical impulses to reach the target area. The external programmer allows the healthcare provider to adjust and fine-tune the settings of the device according to the patient’s progress and unique requirements.
How it Works
The sacral nerve stimulator operates by delivering controlled electrical impulses to the sacral nerve, modulating its activity. The electrical impulses disrupt abnormal signals that may be causing medical conditions, effectively “resetting” the nerve’s function. By stimulating the sacral nerve, the device can help regulate bladder and bowel function, alleviate chronic pain, and improve overall quality of life for individuals suffering from related conditions. The pacemaker-like nature of the device ensures consistent and targeted therapy, providing long-lasting benefits.
Medical Conditions Treated by Sacral Nerve Stimulation
Sacral nerve stimulation has shown outstanding efficacy in managing various medical conditions related to the sacral nerve. From overactive bladder and incontinence to chronic pain conditions and bowel dysfunction, this therapy offers hope and relief to countless individuals. Understanding the impact of sacral nerve stimulation on these conditions is essential in appreciating its significance in the medical field.
Overactive Bladder and Incontinence
Overactive bladder and incontinence are common conditions that can significantly impact an individual’s quality of life. Sacral nerve stimulation offers an effective non-surgical treatment option for those who have not found relief through other conservative approaches. By modulating the activity of the sacral nerve, the device can help regulate bladder function, reducing urinary urgency, frequency, and incontinence episodes.
Chronic Pain Conditions
Chronic pain conditions, such as interstitial cystitis, chronic pelvic pain, and pudendal neuralgia, can be debilitating and greatly affect a person’s daily functioning. Sacral nerve stimulation has demonstrated remarkable efficacy in managing chronic pain by targeting and modulating the sacral nerve. The electrical impulses disrupt pain signals, providing relief and improving overall well-being.
Bowel Dysfunction
Bowel dysfunction, including fecal incontinence and constipation, can significantly impact an individual’s quality of life and self-esteem. Sacral nerve stimulation has emerged as an effective treatment option for bowel disorders, offering hope to those who have exhausted other conservative therapies. By modulating the activity of the sacral nerve, the device can regulate bowel function, reducing symptoms and restoring control.
The Procedure of Sacral Nerve Stimulation
The procedure of sacral nerve stimulation involves careful evaluation, implantation of the device, and postoperative care. Understanding the different stages of this treatment pathway is crucial in determining its suitability for each individual and ensuring optimal outcomes.
Preoperative Evaluation
Prior to undergoing sacral nerve stimulation, thorough evaluation and assessment are conducted to determine the patient’s candidacy for the procedure. This evaluation may involve radiological imaging, urodynamic studies, and a comprehensive medical history review. Consulting with a healthcare professional experienced in sacral nerve stimulation is crucial in obtaining accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment plans.
Implantation of the Device
Once deemed suitable for the procedure, the patient undergoes the surgical implantation of the sacral nerve stimulator device. This procedure is performed by a skilled surgeon under the appropriate anesthesia. The implantable pulse generator is carefully placed under the skin, typically in the buttock or lower back area, while the lead wires are strategically positioned to connect with the sacral nerve. The surgery is minimally invasive, ensuring relatively quick recovery and minimal discomfort.
Postoperative Care and Follow-up
Following the successful implantation of the device, postoperative care and regular follow-up appointments are crucial in monitoring the patient’s progress and adjusting the device settings if necessary. Close communication with the healthcare provider is essential, ensuring any concerns or complications are promptly addressed. Additionally, the patient will be guided on proper device maintenance, activities to avoid, and any lifestyle modifications required to maximize the device’s benefits.
Benefits and Risks of Sacral Nerve Stimulation
Sacral nerve stimulation offers numerous benefits to individuals suffering from conditions related to the sacral nerve. From improved bladder and bowel control to decreased pain and enhanced quality of life, the impact of this treatment can be life-changing. However, it is important to consider the potential risks and complications associated with sacral nerve stimulation to make informed decisions regarding treatment options.
Potential Benefits
The potential benefits of sacral nerve stimulation are vast and can vary depending on the individual’s specific condition. Some of the key advantages include improved bladder and bowel control, alleviation of chronic pain, reduced reliance on medications, and enhanced overall quality of life. Many individuals experience significant improvement in symptoms, allowing them to regain control over their daily activities and routines.
Possible Side Effects and Complications
While sacral nerve stimulation is generally well-tolerated and safe, there are potential side effects and complications to consider. These can include temporary pain or discomfort at the implantation site, infection, device migration or malfunction, and the need for revision surgery. It is crucial to discuss these risks thoroughly with a healthcare professional and carefully weigh them against the potential benefits before deciding to undergo the procedure.
Frequently Asked Questions about Sacral Nerve Stimulation
As with any medical procedure or treatment, numerous questions may arise regarding sacral nerve stimulation. Understanding the common concerns and providing informative answers can help individuals make well-informed decisions and alleviate any apprehensions they may have.
Is the Procedure Painful?
The procedure of sacral nerve stimulation is performed under anesthesia, ensuring a pain-free experience during the surgery. However, some individuals may experience mild discomfort or tenderness at the implantation site following the procedure. This discomfort is typically temporary and can be managed with over-the-counter pain medications.
How Long Does the Device Last?
The longevity of the sacral nerve stimulator device can vary. On average, the battery life of the implantable pulse generator is around five to ten years. However, this can depend on various factors, such as the frequency of device usage and individual characteristics. Regular follow-up appointments with the healthcare provider can help monitor and manage the device’s battery life and ensure its ongoing effectiveness.
Can the Device be Removed or Replaced?
In certain circumstances, the sacral nerve stimulator device may need to be removed or replaced. This can occur if the device is no longer providing the desired therapeutic effects, if complications arise, or if the battery life has expired. Removal or replacement procedures are typically straightforward and can be performed by a trained healthcare professional. Prior consultation with the healthcare provider is essential in determining the most appropriate course of action for each individual.
In conclusion, sacral nerve stimulation is a remarkable treatment modality that offers immense therapeutic potential for various medical conditions related to the sacral nerve. By understanding the intricate anatomy and function of the sacral nerve, as well as the science behind the device and its components, we can appreciate the significance and effectiveness of this treatment option. It is essential to carefully consider the medical conditions treated, the procedure involved, and the potential benefits and risks associated with sacral nerve stimulation. Consulting with a healthcare professional experienced in this field can provide individuals with accurate information and guidance, allowing them to make informed decisions regarding their healthcare journey.