What Causes Sacral Nerve Pain: A Comprehensive Guide
Sacral nerve pain is a debilitating condition that can significantly impact a person’s quality of life. Understanding the causes of sacral nerve pain is crucial for proper diagnosis and treatment. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the various factors that can contribute to sacral nerve pain, as well as the available treatment options and strategies for managing the condition effectively.
Understanding Sacral Nerve Pain
Definition of Sacral Nerve Pain
Sacral nerve pain, also known as sacral radiculopathy, refers to any discomfort or pain that originates from the sacral nerves. These nerves are located in the lower back, specifically in the sacrum, which is the triangular bone at the base of the spine.
Sacral nerve pain can manifest in various ways, ranging from mild to severe. It may present as a dull ache, sharp shooting pain, or even a burning sensation. The intensity and frequency of the pain can vary from person to person, depending on the underlying cause and individual factors.
There are several potential causes of sacral nerve pain, including nerve compression, injury, inflammation, or degenerative conditions such as herniated discs or spinal stenosis. Additionally, conditions like diabetes, infections, and tumors can also contribute to the development of sacral nerve pain.
The Role of Sacral Nerves in the Body
The sacral nerves play a crucial role in the functioning of the lower body. They are responsible for transmitting sensory and motor signals to and from various parts of the pelvis, hips, buttocks, and lower extremities. Additionally, they contribute to bladder and bowel control.
When the sacral nerves are functioning properly, they ensure smooth communication between the brain and the lower body. Sensory signals, such as touch, temperature, and pain, are transmitted from the lower body to the brain, allowing us to perceive and respond to our environment. Motor signals, on the other hand, enable us to move our legs, control our bladder and bowel movements, and maintain balance and stability.
However, when the sacral nerves are compromised or damaged, their ability to transmit signals effectively is disrupted. This can result in a variety of symptoms, including pain, numbness, tingling, muscle weakness, and difficulties with bladder and bowel control.
It’s important to note that sacral nerve pain can have a significant impact on a person’s quality of life. The pain and associated symptoms can limit mobility, interfere with daily activities, and cause emotional distress. Seeking proper diagnosis and treatment is essential in managing sacral nerve pain and improving overall well-being.
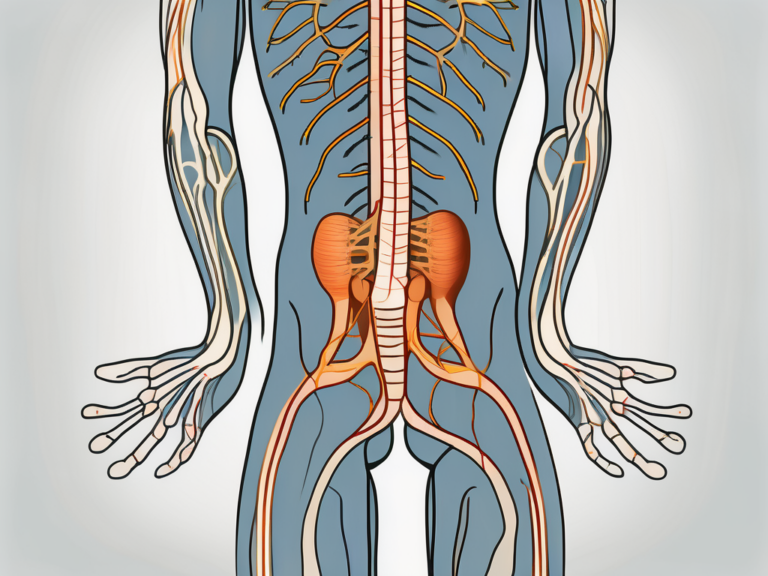
The Anatomy of the Sacral Nerve
The sacral nerve is a crucial component of the human nervous system, playing a vital role in the transmission of sensory information and motor commands. Understanding its location, structure, and function is essential in comprehending the intricate workings of the human body.
Location and Structure of Sacral Nerves
The sacral nerves emerge from the spinal cord, specifically from the sacral region, which is located at the base of the spine. These nerves traverse through the sacrum, a triangular bone formed by the fusion of five vertebrae, creating a complex network known as the sacral plexus.
The sacral plexus is a web-like arrangement of nerve fibers that extends from the lower lumbar region to the coccyx, branching out to various parts of the lower body. This intricate network allows for the efficient transmission of signals between the brain and the lower extremities.
Within the sacral plexus, the sacral nerves divide into multiple branches, each serving a specific region or function. These branches include the superior gluteal nerve, inferior gluteal nerve, sciatic nerve, posterior femoral cutaneous nerve, and pudendal nerve, among others. Each branch is responsible for transmitting sensory information and motor commands to its designated area.
Function of Sacral Nerves
The sacral nerves play a crucial role in the transmission of sensory information from the lower body to the brain. This includes the perception of pain, temperature, and touch. When you stub your toe or feel a gentle caress, it is the sacral nerves that carry these sensations to your brain, allowing you to react accordingly.
In addition to sensory transmission, the sacral nerves also relay motor commands from the brain to the muscles in the lower extremities. This enables movement and coordination, allowing us to walk, run, jump, and perform various physical activities. Without the proper functioning of the sacral nerves, our ability to control our lower body muscles would be severely impaired.
Furthermore, the sacral nerves are responsible for the regulation of various bodily functions, such as bladder and bowel control, sexual function, and reproductive processes. These nerves ensure the proper functioning of the pelvic organs, contributing to overall health and well-being.
Overall, the sacral nerve is a remarkable component of the human body, facilitating the transmission of sensory information and motor commands between the brain and the lower extremities. Its intricate structure and vital functions make it an essential part of our everyday lives, enabling us to navigate the world and experience the wonders of the human body.
Common Causes of Sacral Nerve Pain
Sacral nerve pain, also known as sacralgia, is a condition that can cause discomfort and distress for individuals. It can significantly impact their daily activities and overall quality of life. Understanding the common causes of sacral nerve pain is crucial in managing and treating this condition effectively.
Injuries Leading to Sacral Nerve Pain
Sacral nerve pain can result from various injuries, such as trauma to the lower back or pelvis. These injuries can occur due to accidents, falls, or sports-related incidents. The impact on the lower back or pelvis can lead to nerve compression or damage, resulting in sacral nerve pain.
In some cases, fractures of the sacrum, the triangular bone at the base of the spine, can also cause sacral nerve pain. The fractures can occur due to high-impact accidents or severe trauma to the lower back or pelvic region. The pressure exerted on the sacral nerves can lead to inflammation and pain.
Another common cause of sacral nerve pain is the compression of the nerve roots. This compression can occur due to herniated discs or spinal stenosis. Herniated discs, also known as slipped discs, can put pressure on the sacral nerves, causing pain and discomfort. Spinal stenosis, a condition characterized by the narrowing of the spinal canal, can also lead to nerve compression and subsequent sacral nerve pain.
Diseases and Conditions Affecting Sacral Nerves
Several medical conditions can impact the sacral nerves and cause pain. One such condition is degenerative disc disease. This condition occurs when the discs between the vertebrae in the spine start to deteriorate. The degeneration can lead to nerve compression and sacral nerve pain.
Osteoarthritis, a common form of arthritis, can also affect the sacral nerves. The degeneration of the joints in the lower back and pelvis can cause inflammation and nerve compression, resulting in sacral nerve pain.
Sciatica, a condition characterized by pain radiating from the lower back down the leg, can also be a cause of sacral nerve pain. The compression or irritation of the sciatic nerve, which originates in the sacral region, can lead to pain and discomfort.
Sacroiliac joint dysfunction, a condition that affects the joints connecting the sacrum and the pelvis, can contribute to sacral nerve pain. The dysfunction can cause inflammation and irritation of the sacral nerves, leading to discomfort and pain.
Endometriosis, a condition in which the tissue lining the uterus grows outside of it, can also impact the sacral nerves. The abnormal growth of tissue can put pressure on the nerves, resulting in sacral nerve pain.
Tumors in the pelvic region can be another cause of sacral nerve pain. These tumors can exert pressure on the sacral nerves, leading to pain and discomfort.
Inflammation or infection in the sacral area, such as sacroiliitis, can also contribute to sacral nerve pain. The inflammation or infection can irritate the sacral nerves, causing pain and discomfort.
It is important to note that sacral nerve pain can have various causes, and a proper diagnosis by a healthcare professional is essential for effective treatment and management. By identifying the underlying cause, appropriate interventions can be implemented to alleviate the pain and improve the individual’s quality of life.
Symptoms Associated with Sacral Nerve Pain
Physical Symptoms and Discomfort
Sacral nerve pain can manifest in various ways, including sharp or shooting pain in the lower back, buttocks, hips, or legs. This pain can be debilitating, making it difficult for individuals to engage in their daily activities. The intensity of the pain can vary from person to person, with some experiencing a constant ache while others may have intermittent episodes of severe pain.
In addition to pain, individuals with sacral nerve pain may also experience other physical symptoms. Some may feel a numbness or tingling sensation in the affected areas, which can be accompanied by a burning sensation. These sensations can be disruptive and uncomfortable, making it challenging for individuals to find relief or comfort.
Furthermore, muscle weakness is another common symptom associated with sacral nerve pain. This weakness can make it difficult for individuals to perform simple tasks that require strength, such as lifting objects or climbing stairs. It can also impact their ability to maintain balance and stability, increasing the risk of falls and injuries.
Additionally, sacral nerve pain can lead to changes in bowel or bladder function. Some individuals may experience difficulty controlling their bladder or bowels, leading to incontinence or an increased frequency of urination. These changes can be distressing and have a significant impact on an individual’s quality of life.
Impact on Mobility and Daily Activities
The physical symptoms associated with sacral nerve pain can greatly affect an individual’s mobility and ability to carry out daily activities. Simple tasks like walking, sitting, or standing for prolonged periods may become challenging and painful. Individuals may find it necessary to modify their daily routines to accommodate their pain, such as using assistive devices like canes or walkers to aid in mobility.
Engaging in recreational activities or exercise may also be limited for individuals with sacral nerve pain. The pain and discomfort can make it difficult to participate in activities that require physical exertion or involve repetitive movements. This limitation can have a negative impact on an individual’s overall well-being, as regular exercise is important for maintaining physical fitness and mental health.
Furthermore, the impact of sacral nerve pain on an individual’s daily life extends beyond physical limitations. The constant presence of pain and discomfort can take a toll on their mental and emotional well-being. It can lead to feelings of frustration, sadness, and even depression. The inability to carry out daily activities without pain can also cause individuals to feel a sense of loss and decreased self-esteem.
In conclusion, sacral nerve pain is a condition that can cause a range of physical symptoms and discomfort. It can significantly impact an individual’s mobility, daily activities, and overall well-being. Seeking appropriate medical treatment and management strategies is crucial in order to alleviate symptoms and improve quality of life for individuals living with sacral nerve pain.
Diagnostic Procedures for Sacral Nerve Pain
Medical History and Physical Examination
When evaluating sacral nerve pain, healthcare professionals will typically begin by taking a detailed medical history to understand the patient’s symptoms, previous injuries, and any contributing factors. This information is crucial in determining the possible causes of the sacral nerve pain and guiding further diagnostic procedures.
The medical history may involve questions about the onset and duration of the pain, any triggering events or activities, and whether there are any accompanying symptoms such as numbness, tingling, or weakness. The healthcare professional may also inquire about the patient’s medical conditions, medications, and lifestyle factors that could potentially contribute to the pain.
Following the medical history, a physical examination may be performed to assess various aspects related to sacral nerve pain. This examination often includes evaluating the patient’s posture, gait, and overall mobility. The healthcare professional may also conduct tests to assess range of motion, muscle strength, and areas of tenderness in the sacral region.
Imaging and Other Diagnostic Tests
To aid in diagnosis, imaging tests such as X-rays, CT scans, or MRI scans may be ordered. These imaging modalities can provide detailed images of the sacral region, helping to identify any structural abnormalities or damage to the sacral nerves and surrounding tissues. X-rays can reveal fractures, dislocations, or degenerative changes, while CT scans and MRI scans can provide more comprehensive views of the bones, muscles, and nerves.
In addition to imaging tests, electromyography (EMG) and nerve conduction studies may also be conducted to assess nerve function and identify any abnormalities in nerve conduction. These tests involve the placement of small electrodes on the skin or into the muscles to measure electrical activity. EMG can help determine if there is any nerve damage or muscle dysfunction, while nerve conduction studies evaluate the speed and efficiency of nerve signals.
Furthermore, in some cases, additional diagnostic procedures may be recommended based on the specific symptoms and suspected causes of sacral nerve pain. These may include blood tests to check for certain infections or inflammatory conditions, bone scans to detect abnormalities in bone metabolism, or diagnostic injections to pinpoint the exact source of the pain.
Overall, the combination of a thorough medical history, comprehensive physical examination, and appropriate diagnostic tests allows healthcare professionals to accurately diagnose sacral nerve pain and develop an effective treatment plan tailored to the individual patient’s needs.
Treatment Options for Sacral Nerve Pain
Non-Surgical Treatments
Non-surgical treatment options are often the first line of management for sacral nerve pain. These may include physical therapy, chiropractic care, acupuncture, pain medications, and nerve blocks to alleviate pain and inflammation. Additionally, lifestyle modifications, such as maintaining proper posture, practicing good body mechanics, and engaging in regular exercise, can provide relief and improve overall well-being.
Surgical Interventions
In cases where conservative treatments do not provide sufficient relief, surgical intervention may be considered. Surgical options can involve decompression of compressed nerve roots, removal of herniated discs, or stabilization of the affected area through fusion or instrumentation. However, surgical procedures carry risks, and the decision to undergo surgery should be made in consultation with a healthcare professional.
Prevention and Management of Sacral Nerve Pain
Lifestyle Changes for Pain Management
Adopting a healthy lifestyle can contribute to the prevention and management of sacral nerve pain. This may include maintaining a healthy weight, practicing good posture, avoiding prolonged sitting or standing, and using proper body mechanics when lifting or carrying heavy objects. Incorporating stress management techniques, such as yoga or meditation, can also help reduce pain and improve overall well-being.
Exercises and Physical Therapy Techniques
Specific exercises and physical therapy techniques can target the muscles and structures associated with sacral nerve pain, helping to alleviate symptoms and improve mobility. A physical therapist can develop an individualized exercise program that includes stretches, strengthening exercises, and techniques to improve posture and body mechanics. It is essential to consult with a qualified healthcare professional before starting any exercise program.
Living with Sacral Nerve Pain
Emotional and Psychological Aspects
Living with sacral nerve pain can have a significant impact on a person’s emotional and psychological well-being. Chronic pain and limitations in daily activities can lead to feelings of frustration, anxiety, and depression. Seeking support from loved ones, joining support groups, or seeking counseling can help individuals cope with the emotional challenges associated with sacral nerve pain.
Support and Resources for Patients
There are numerous resources available to individuals who are living with sacral nerve pain. Support groups, both in-person and online, provide opportunities for individuals to connect with others who understand their experiences. Additionally, healthcare professionals specializing in pain management can offer guidance, support, and access to further resources to help individuals manage their condition effectively.
In conclusion, sacral nerve pain can significantly impact an individual’s daily life and overall well-being. By understanding the various causes of sacral nerve pain and the available treatment options, individuals can be better equipped to navigate their condition. It is important to consult with a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment plan. With the right support and management strategies, individuals can effectively manage their sacral nerve pain and improve their quality of life.