Understanding the Significance of the Sacral Notch: What Nerve Lies Within?
The sacral notch, an important anatomical feature located in the back of the pelvis, holds a deep significance in the human body. It is the site where a crucial nerve, known as the sciatic nerve, resides. In this article, we will delve into the intricate details of the sacral notch, exploring its anatomy, its relationship with the sciatic nerve, common disorders associated with this area, and the future of research in this field. By gaining a deeper understanding of the sacral notch and the nerve within, we can better appreciate its significance in our overall well-being.
Anatomy of the Sacral Notch
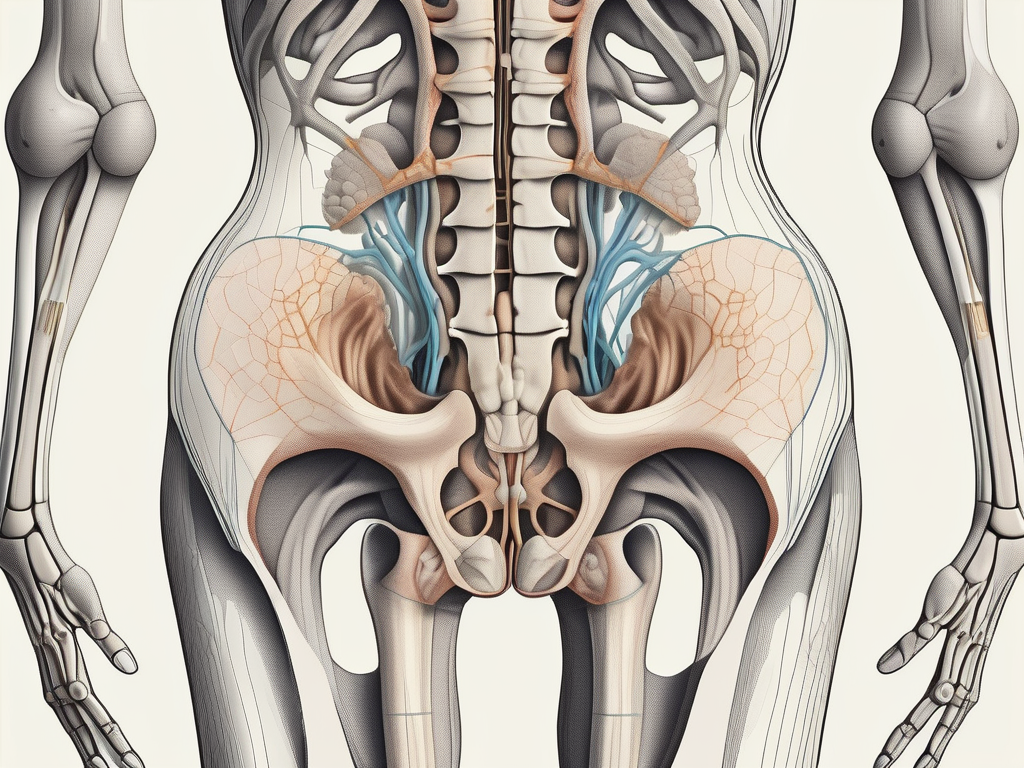
The sacral notch, also known as the sacral hiatus, is a fascinating anatomical feature located at the base of the sacrum bone. The sacrum, a triangular bone situated between the hip bones, is an essential component of the human skeletal system. It not only provides support and stability to the pelvis but also houses the sacral spinal nerves and the coccyx, commonly known as the tailbone.
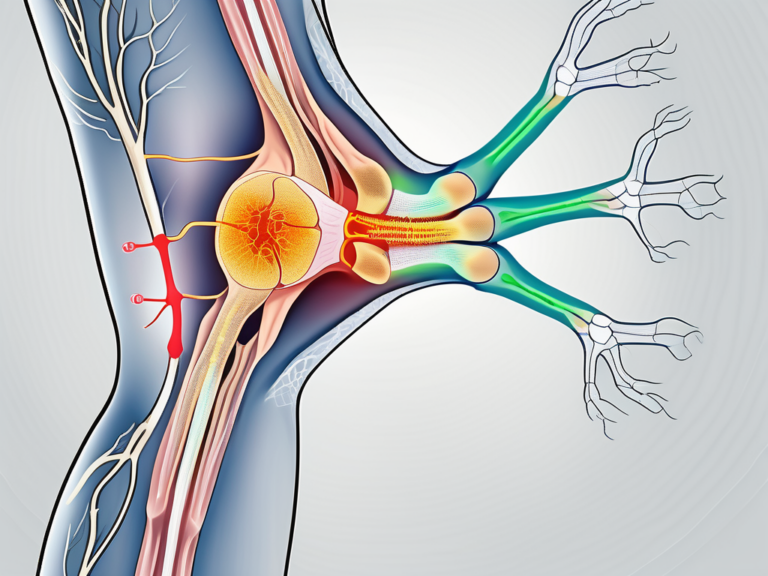
When we examine the sacrum closely, we can observe a concave depression known as the sacral notch. This notch serves a crucial purpose in the body, as it accommodates the sciatic nerve, one of the major nerves in the human body. Alongside the sciatic nerve, the sacral notch also provides a pathway for nearby blood vessels, ensuring proper circulation to the lower limbs.
Surrounding the sacral notch are various bony structures that play a vital role in protecting and stabilizing the delicate nerve within. These structures include the sacral cornua, which are small bony projections on either side of the sacral notch, and the sacral tuberosity, a roughened area that provides attachment for ligaments and muscles.
Identifying the Sacral Notch
Locating the sacral notch is relatively straightforward. By palpating the area just above the buttock crease in the lower back, one can feel the depression where the sacral notch is situated. It is important to note that while the presence of the sacral notch is universal, its size and shape may vary among individuals.
Familiarizing oneself with the location and characteristics of the sacral notch is not only interesting but also beneficial in understanding the human body’s intricate design. By appreciating the anatomical features of the sacral notch, one can gain a deeper understanding of its role in maintaining bodily function.
The Role of the Sacral Notch in the Human Body
The sacral notch plays a crucial role in the human body, primarily as a passageway for the sciatic nerve. The sciatic nerve, originating from the lower back, extends down through the sacrum and into the lower limbs. It is the largest nerve in the body and provides motor and sensory innervation to the muscles and skin of the buttocks, thighs, legs, and feet.
Without the sacral notch, the communication between the brain and the lower limbs would be compromised. The nerve impulses responsible for movement and sensation would not be able to travel efficiently, leading to various functional impairments. Therefore, the sacral notch acts as a vital conduit, ensuring the smooth transmission of signals necessary for coordinated movement and sensory perception.
In addition to its role in nerve transmission, the sacral notch also contributes to the overall stability of the pelvis. The bony structures surrounding the sacral notch, such as the sacral cornua and sacral tuberosity, provide support and prevent excessive movement that could potentially damage the delicate nerve within.
In conclusion, the sacral notch is a remarkable anatomical feature that deserves our attention and appreciation. Its concave depression serves as a crucial pathway for the sciatic nerve and nearby blood vessels, allowing for proper nerve function and circulation to the lower limbs. By understanding the intricacies of the sacral notch, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the remarkable design of the human body.
The Nerve within the Sacral Notch
At the heart of the sacral notch lies the sciatic nerve, a complex structure that deserves our attention. Understanding its characteristics and functions can give us valuable insight into the significance of the sacral notch.
The sacral notch, also known as the sacral hiatus, is a V-shaped indentation located at the base of the sacrum, the triangular bone at the lower end of the spine. It is an important anatomical landmark that serves as a passageway for the sciatic nerve, one of the largest nerves in the human body.
The sciatic nerve is a bundle of nerve fibers that originates from the spinal cord in the lower back. It is comprised of the ventral rami of the fourth and fifth lumbar nerves, as well as the first, second, and third sacral nerves. These nerve fibers come together to form a thick, rope-like structure that extends down the back of the thigh and branches out to innervate various muscles and tissues in the lower limb.
Its diameter can vary among individuals, ranging from a few millimeters to over a centimeter. This variability is influenced by factors such as genetics, body composition, and overall health. Despite these differences, the sciatic nerve remains a vital component of the body’s nervous system, playing a crucial role in our ability to move and perceive sensations in the lower body.
Functions of the Sciatic Nerve
The sciatic nerve performs a multitude of functions that are essential for our daily activities. It provides motor control to the muscles of the lower limbs, allowing us to walk, run, and perform various physical tasks. Without the sciatic nerve, our ability to move our legs and feet would be severely compromised.
In addition to motor control, the sciatic nerve carries sensory information from the skin, muscles, and joints of the lower body to the brain. This enables us to perceive touch, pain, temperature, and proprioception, which is the sense of our body’s position in space. For example, when we step on a sharp object, the sciatic nerve quickly transmits the pain signal to the brain, prompting us to remove our foot from harm’s way.
Furthermore, the sciatic nerve plays a crucial role in maintaining the body’s balance and coordination. It receives constant feedback from the muscles and joints of the lower limb, allowing us to adjust our movements and posture accordingly. This feedback loop is essential for activities such as walking on uneven surfaces or maintaining stability during physical exertion.
Overall, the sciatic nerve is truly a remarkable structure that facilitates our mobility and sensory experiences. Its intricate network of nerve fibers connects the lower limbs to the central nervous system, enabling seamless communication between the brain and the lower body. Without the sciatic nerve, our ability to perform everyday tasks and enjoy a full range of motion would be severely compromised.
The Relationship Between the Sacral Notch and Sciatic Nerve
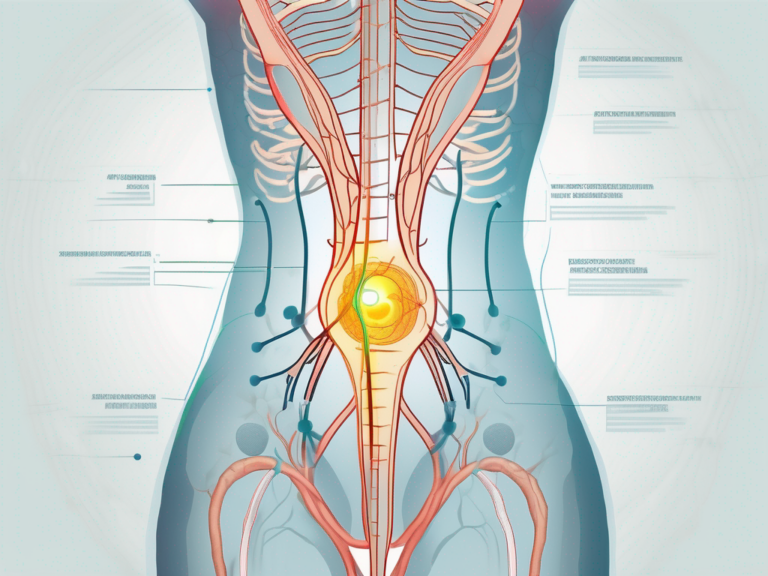
The sacral notch and the sciatic nerve share a unique and vital relationship in the human body. The sacral notch, a concave depression located on the posterior aspect of the sacrum, provides an anatomical pathway and protection for the sciatic nerve, ensuring its proper functioning. Let us dive deeper into the intricacies of this fascinating relationship.
The sacral notch, along with the surrounding bony structures, plays a crucial role in safeguarding the sciatic nerve from potential harm. Acting as a protective barrier, these structures shield the nerve from external forces and minimize the risk of compression or injury. Without this protective mechanism, the sciatic nerve, which is the longest and thickest nerve in the human body, would be vulnerable to damage.
However, it is important to note that even with the sacral notch’s protective function, certain factors can still predispose the sciatic nerve to damage. Trauma, such as a fall or accident, can exert excessive pressure on the nerve, leading to compression or injury. Additionally, degenerative conditions like herniated discs or spinal stenosis can also impinge on the sciatic nerve, causing pain and discomfort.
If you are experiencing persistent pain, numbness, or weakness in the lower limbs, it is crucial to consult with a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate management. They can evaluate the condition of your sacral notch and sciatic nerve, identify any potential issues, and recommend the most suitable treatment options.
How the Sacral Notch Protects the Sciatic Nerve
The sacral notch’s protective function is a result of its anatomical location and structure. Situated between the two sacral alae, the sacral notch forms a concave surface that cradles the sciatic nerve. This anatomical arrangement acts as a natural shield, safeguarding the nerve from external forces.
Moreover, the sacral notch is lined with a layer of connective tissue known as the sacral plexus sheath. This sheath provides an additional layer of protection, preventing direct contact between the nerve and the surrounding bony structures. It acts as a cushion, absorbing any impact or pressure that may be exerted on the sacral notch.
The sacral notch’s protective role extends beyond physical barriers. It also plays a crucial role in maintaining the overall health and function of the sciatic nerve. By providing a pathway for the nerve to pass through, the sacral notch ensures the unimpeded transmission of nerve impulses. This allows for the smooth and efficient communication between the brain and the lower limbs, enabling normal movement and sensation.
The Impact of Sacral Notch Size on Sciatic Nerve Function
While the sacral notch is generally designed to accommodate the sciatic nerve comfortably, there can be variations in its size and shape among individuals. Some people may have a naturally wider and more spacious sacral notch, while others may have a narrower space.
This anatomical variation in sacral notch size can potentially impact the function of the sciatic nerve. In individuals with a narrower sacral notch, there is an increased risk of nerve entrapment or compression. This can lead to a condition known as sciatica, characterized by pain, tingling, and numbness radiating down the lower back, buttocks, and legs.
It is important to note that the impact of sacral notch size on sciatic nerve function is not solely determined by the width of the notch itself. Other factors, such as the presence of bone spurs, herniated discs, or muscle tightness, can also contribute to nerve compression and subsequent symptoms.
If you have concerns about your sacral notch size and its potential impact on sciatic nerve function, seeking medical advice from a healthcare professional is essential. They can assess your specific anatomical characteristics, perform diagnostic tests if necessary, and provide appropriate guidance and treatment options tailored to your needs.
Disorders Related to the Sacral Notch and Sciatic Nerve
While the sacral notch and sciatic nerve play crucial roles in our well-being, they can also be subject to certain disorders that may disrupt their normal function. Recognizing the symptoms and understanding the available treatment options is essential in managing these conditions.
The sacral notch, also known as the sacral hiatus, is a small indentation at the base of the sacrum, the triangular bone located at the lower end of the spine. It serves as an important passageway for the sciatic nerve, the largest nerve in the body. The sciatic nerve originates from the lower back and extends down the back of each leg. It provides sensation and motor function to the lower limbs.
Disorders related to the sacral notch and sciatic nerve can manifest in various ways. Symptoms may include sharp or radiating pain in the lower back, buttocks, thighs, or legs, tingling sensations, numbness or weakness in the lower limbs, and difficulty in walking or performing daily activities. These symptoms can be debilitating and greatly impact an individual’s quality of life.
It is important to note that these symptoms can also arise from other underlying conditions, necessitating a thorough evaluation by a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment. Conditions such as herniated discs, spinal stenosis, piriformis syndrome, and sciatica can all cause similar symptoms, making it crucial to identify the root cause of the problem.
Treatment Options for Sacral Notch and Sciatic Nerve Disorders
The treatment options for sacral notch and sciatic nerve disorders may vary depending on the underlying cause and severity of the condition. In some cases, conservative approaches such as physical therapy, pain management techniques, and lifestyle modifications may be prescribed.
Physical therapy plays a vital role in the rehabilitation process, aiming to strengthen the muscles surrounding the affected area, improve flexibility, and alleviate pain. Therapeutic exercises, stretches, and manual techniques are commonly employed to target specific muscle imbalances and restore normal function.
Pain management techniques, such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), muscle relaxants, and nerve pain medications, may be utilized to alleviate discomfort and improve daily functioning. Additionally, alternative therapies like acupuncture, chiropractic care, and massage therapy may offer relief for some individuals.
However, more complex cases may require surgical intervention or specialized procedures to alleviate symptoms and restore normal nerve function. Surgical options may include discectomy, laminectomy, or spinal fusion, depending on the specific condition and its severity. These procedures aim to remove any impingement on the sciatic nerve and stabilize the affected area.
It is important to work closely with a healthcare professional to determine the most appropriate treatment plan tailored to individual needs. They will consider factors such as the underlying cause, the severity of symptoms, the individual’s overall health, and their personal preferences. Regular follow-ups and ongoing care are essential to monitor progress and make any necessary adjustments to the treatment plan.
In conclusion, disorders related to the sacral notch and sciatic nerve can cause significant pain and discomfort. Recognizing the symptoms and seeking appropriate medical attention is crucial in managing these conditions effectively. With the right treatment plan, individuals can find relief and regain their quality of life.
The Future of Sacral Notch and Sciatic Nerve Research
With advancements in medical technology and growing scientific interest, the field of sacral notch and sciatic nerve research is constantly evolving. Researchers are dedicated to unraveling the mysteries surrounding these intricate structures and exploring innovative treatment approaches. Let us take a glimpse into the future of this fascinating field.
Current Research Trends in Sacral Notch and Sciatic Nerve Studies
Researchers are actively investigating areas such as nerve regeneration, improved diagnostic techniques, and novel therapeutic interventions for sacral notch and sciatic nerve disorders. Cutting-edge technologies, such as bioengineered scaffolds and gene therapies, hold promise in promoting nerve healing and regeneration. Additionally, advancements in imaging techniques and nerve conduction studies offer valuable insights in diagnosing and monitoring these conditions. However, it is important to note that further research is needed to establish the efficacy and safety of these emerging approaches.
Potential Breakthroughs in Sacral Notch and Sciatic Nerve Treatments
The future of sacral notch and sciatic nerve treatments holds great potential for groundbreaking discoveries. From regenerative medicine to personalized therapeutics, scientists and healthcare professionals are dedicated to improving patient outcomes and quality of life. By embracing a multidisciplinary approach and fostering collaboration across various fields, we can envision a future where sacral notch and sciatic nerve disorders are managed with greater precision and effectiveness.
By understanding the significance of the sacral notch and the nerve within, we gain invaluable knowledge that empowers us to take charge of our health. If you are experiencing any symptoms related to the sacral notch or the sciatic nerve, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional who can guide you towards an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment options. Together, we can unlock the mysteries of the sacral notch and ensure the well-being of our nerves and bodies as a whole.