How Many Pairs of Nerve Roots Are in the Sacral Region?
The sacral region is a vital part of the human body, playing a crucial role in our overall health and well-being. Understanding the intricacies of this region, including its anatomy, function, and the number of nerve roots it contains, can provide valuable insights into our body’s functioning. In this article, we will delve into the topic of how many pairs of nerve roots exist in the sacral region and explore its implications on our health.
Understanding the Sacral Region
The sacral region refers to the area located at the base of the spine, just below the lumbar region. It consists of five fused vertebrae known as the sacrum, forming a triangular bone. The sacrum is essential for supporting the weight of the upper body and transferring it to the pelvis and lower limbs.
Additionally, the sacral region plays a vital role in numerous physiological functions, including the functioning of the nervous system.
The sacrum, with its unique shape and structure, not only provides support but also offers protection to the delicate nerves and structures within it. This triangular bone is composed primarily of bone, ensuring the stability and integrity of the region.
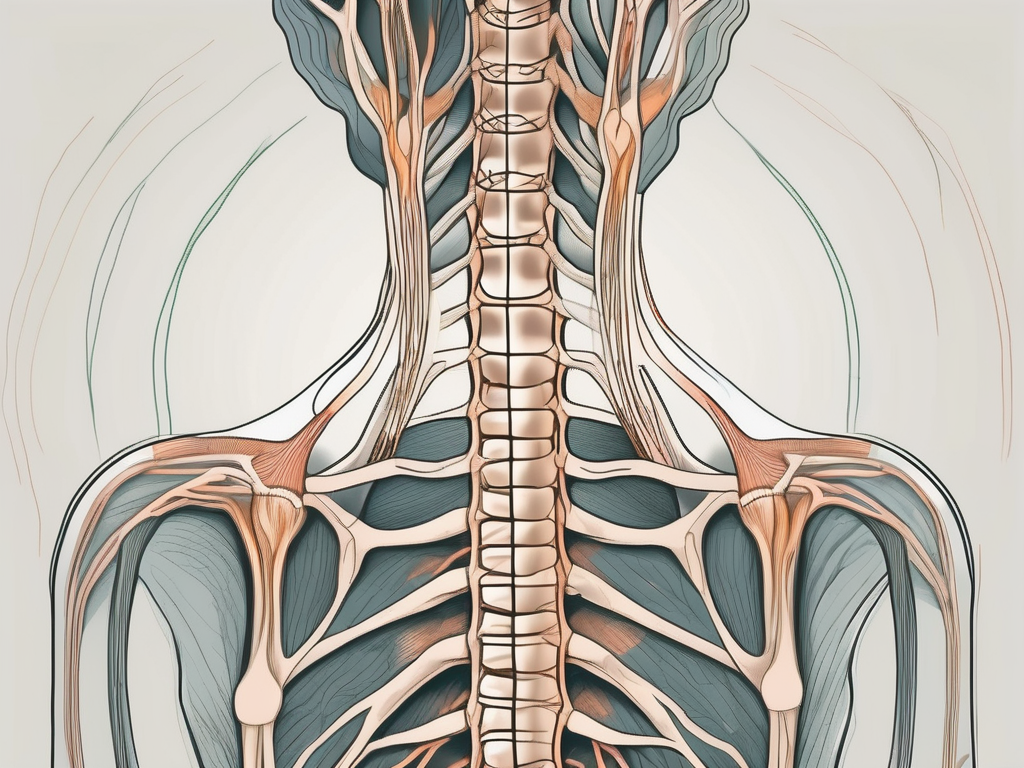
Within the sacrum, there are a number of small holes known as the sacral foramina. These foramina serve as passageways for nerve roots to exit the spinal canal and supply different regions of the body. These nerve roots originate from the spinal cord and form part of the peripheral nervous system, a complex network of nerves that transmit signals between the central nervous system (the brain and spinal cord) and the rest of the body.
Each sacral foramen allows for the passage of a specific nerve root, ensuring the proper functioning of various bodily systems. These nerve roots play a crucial role in transmitting sensory and motor signals, allowing for the coordination of movements and the perception of sensations.
Anatomy of the Sacral Region
The sacral region is a fascinating area of the body, with its intricate anatomy contributing to its multifaceted functions. Understanding the anatomy of the sacral region provides valuable insights into its role in maintaining overall health and well-being.
One of the remarkable features of the sacrum is its ability to adapt and change during different stages of life. In childhood, the sacrum consists of five separate vertebrae, which gradually fuse together as a person grows. This fusion process is crucial for the development and stability of the pelvic region.
Furthermore, the sacrum is not just a solid bone; it also contains a network of blood vessels that supply oxygen and nutrients to the surrounding tissues. These blood vessels ensure the proper functioning and nourishment of the sacral region, supporting its role in various physiological processes.
Function of the Sacral Region
The sacral region is a powerhouse of functionality, contributing to numerous bodily functions that are essential for overall health and well-being.
One of the primary functions of the sacral region is its involvement in the reproductive and excretory systems. It plays a crucial role in maintaining bladder and bowel control, ensuring proper elimination and preventing incontinence. The sacral nerves that originate from this region are responsible for transmitting signals that regulate these functions, allowing for efficient and controlled excretion.
In addition to its role in the reproductive and excretory systems, the sacral region also contributes to sexual function. The nerves originating from the sacrum are involved in transmitting sensory signals, allowing for the perception of sexual stimuli and the initiation of sexual responses.
Furthermore, the sacral region is involved in motor control, coordinating movements of the lower limbs and facilitating proper balance and stability. The nerve roots originating from the sacrum play a crucial role in transmitting signals that control muscle contractions and movements, ensuring smooth and coordinated motion.
Overall, the sacral region is a complex and fascinating part of the human body. Its anatomy and functions are intricately intertwined, contributing to the overall well-being and functionality of the individual. Understanding the importance of the sacral region helps us appreciate the remarkable complexity of the human body and its ability to perform a wide range of functions.
The Nervous System and the Sacral Region
The nervous system is a complex network that enables communication between different parts of the body. It consists of the central nervous system (CNS) and the peripheral nervous system (PNS). The CNS comprises the brain and spinal cord, while the PNS includes all the nerves that branch out from the CNS.
The nervous system is responsible for coordinating and controlling all bodily functions. It allows us to sense the world around us, process information, and respond accordingly. Without the nervous system, our bodies would not be able to function properly.
Within the nervous system, the sacral region plays a crucial role in transmitting signals related to the lower extremities, pelvis, and reproductive organs. It is located at the base of the spine, just above the tailbone. The sacral region consists of five vertebrae, known as the sacrum, which are fused together to form a strong and stable structure.
Role of Nerve Roots in the Nervous System
Nerve roots are bundles of nerves that extend from the spinal cord and join together to form peripheral nerves. These nerve roots play a crucial role in transmitting sensory and motor signals between the body and the CNS. They act as highways for information flow, allowing us to feel sensations, move our muscles, and perform numerous bodily functions seamlessly.
Each nerve root is responsible for specific areas of the body, and they work together to ensure smooth communication between the CNS and the peripheral nerves. In the sacral region, the nerve roots contribute to the PNS’s functioning by transmitting signals related to the lower extremities, pelvis, and reproductive organs. They connect with various muscles, allowing for motor control, and provide sensory information from the lower body.
For example, when you touch a hot surface, the sensory nerve roots in the sacral region transmit the information to the brain, which then sends a signal back through the motor nerve roots to move your hand away from the heat source. This entire process happens in a fraction of a second, thanks to the efficient functioning of the nerve roots.
Connection between the Sacral Region and the Nervous System
The sacral region acts as a vital bridge between the CNS and the peripheral nerves. Issues in this region can have wide-ranging effects on our nervous system’s overall functioning, as disruptions can hinder the transmission of signals to and from the brain.
Common conditions that can affect the sacral region include sacroiliac joint dysfunction, sciatica, and spinal stenosis. These conditions can cause pain, numbness, tingling, and weakness in the lower back, hips, and legs. They can also impact bladder and bowel function, as the nerves responsible for controlling these organs pass through the sacral region.
Therefore, maintaining the health and integrity of the sacral region is of utmost importance for proper nervous system functioning. Regular exercise, proper posture, and a healthy lifestyle can help keep the sacral region in good condition. Additionally, seeking timely medical attention for any concerns or symptoms related to this region is crucial to receive appropriate evaluation and guidance.
In conclusion, the nervous system and the sacral region are intricately connected, with the nerve roots in the sacral region playing a vital role in transmitting signals between the body and the CNS. Understanding the importance of this connection and taking steps to maintain the health of the sacral region can contribute to overall nervous system well-being.
Counting the Pairs of Nerve Roots in the Sacral Region
Identifying Nerve Roots in the Sacral Region
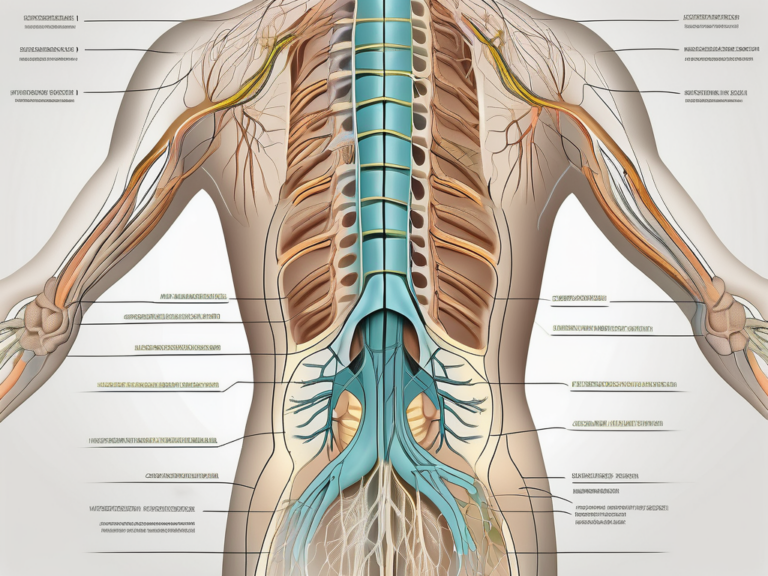
To understand the number of nerve roots in the sacral region, it is crucial to identify their location within the sacrum. The sacral foramina, mentioned earlier, provide openings for the nerve roots to exit the spinal canal.
When looking at the sacrum, it is important to recognize its unique shape. The sacrum is a triangular bone located at the base of the spine, consisting of five fused vertebrae. Its curvature and position play a significant role in the distribution and function of the nerve roots in this region.
Identifying the specific nerve roots in this region requires specialized knowledge and expertise. It is a task best left to medical professionals, such as neurologists or neurosurgeons, who can utilize diagnostic imaging techniques and perform thorough examinations to assess the sacral nerve roots.
Diagnostic imaging techniques, such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) or computed tomography (CT) scans, can provide detailed images of the sacral region. These images allow healthcare professionals to visualize the nerve roots and assess any abnormalities or variations in their structure.
How Many Pairs of Nerve Roots Exist
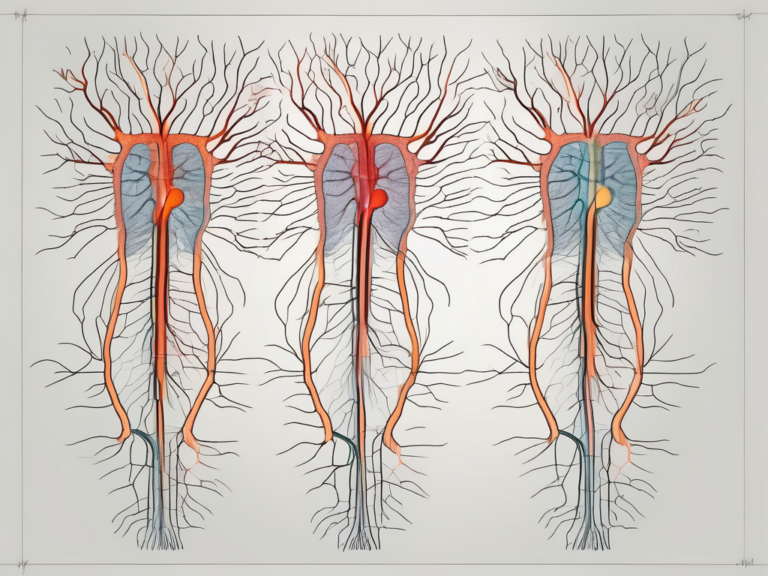
In the sacral region, there are typically five pairs of nerve roots that emerge from the sacral foramina. These nerve roots are numbered S1 to S5, with each pair supplying different areas of the lower body.
The S1 nerve root, for example, supplies sensation and motor function to the back of the thigh, calf, and foot. It plays a crucial role in walking, running, and maintaining balance. The S2 nerve root, on the other hand, innervates the back of the thigh, knee, and lower leg.
As we move up the sacral region, the S3 nerve root supplies the buttocks and perineum, while the S4 nerve root contributes to the sensation and function of the perineum, genitals, and anal region. Finally, the S5 nerve root, the last in the sacral region, provides innervation to the perineum and anal sphincter.
It is important to note that the exact number of nerve roots can vary between individuals, as anatomical variations exist. Some individuals may have an additional pair of nerve roots, known as the Co1 nerve roots, which emerge from the sacral region. These additional nerve roots can supply sensation and motor function to the tailbone and surrounding areas.
Consulting with a healthcare professional is essential for accurate assessment and interpretation of the nerve root count in an individual’s sacral region. They can evaluate the specific anatomy and provide personalized insights into the functioning of the nerve roots in the sacral region.
Implications of Nerve Root Count in the Sacral Region
Impact on Body Function
Alterations in the number or functionality of sacral nerve roots can have significant implications on various bodily functions. Reduced or impaired nerve root function can lead to symptoms such as pain, numbness, weakness, or altered sensation in the lower extremities or pelvic region.
Furthermore, issues in this region can impact bladder and bowel control, sexual function, and motor control of the lower limbs. The sacral nerve roots play a crucial role in transmitting signals between the brain and these important bodily functions. When the nerve roots are compromised, the communication between the brain and these areas may be disrupted, resulting in a range of symptoms and functional limitations.
Understanding the nerve root count and function can provide insights into potential underlying causes of these symptoms and guide appropriate treatment and management strategies. Healthcare professionals often conduct thorough examinations and diagnostic tests to assess the integrity of the sacral nerve roots and determine the best course of action for each individual patient.
It is crucial to emphasize that any concerns regarding sacral nerve roots should be addressed with a healthcare professional. They possess the knowledge and expertise to provide accurate diagnosis and guidance based on individual circumstances. Early detection and intervention can significantly improve outcomes and quality of life for individuals experiencing issues related to sacral nerve roots.
Potential Health Issues Related to Nerve Roots
Various health issues can affect the sacral nerve roots, ranging from trauma to degenerative conditions or structural abnormalities. These issues can manifest in different ways, depending on the specific nerve roots involved and the underlying cause.
Common conditions affecting the sacral nerve roots include herniated discs, spinal stenosis, nerve root compression, and sacroiliac joint dysfunction. These conditions may lead to symptoms such as sciatica, lower back pain, or radiating pain or weakness in the lower extremities.
Herniated discs occur when the soft cushioning discs between the vertebrae in the spine rupture or bulge, putting pressure on the adjacent nerve roots. This pressure can cause pain, numbness, and weakness in the areas supplied by the affected nerve roots. Spinal stenosis refers to the narrowing of the spinal canal, which can compress the sacral nerve roots and result in similar symptoms.
Nerve root compression occurs when there is excessive pressure on a nerve root, often due to a bone spur or a herniated disc. This compression can cause pain, tingling, and weakness in the areas supplied by the affected nerve root. Sacroiliac joint dysfunction refers to the dysfunction or misalignment of the joints connecting the sacrum and the pelvis. This dysfunction can irritate the nearby nerve roots, leading to pain and discomfort.
Given the wide range of potential health issues, it is essential to consult with a healthcare professional to receive an accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment plan tailored to individual needs. Treatment options may include physical therapy, medication, injections, or in severe cases, surgical intervention. The healthcare professional will consider various factors, such as the severity of symptoms, underlying cause, and the patient’s overall health, to determine the most appropriate course of action.
Frequently Asked Questions about Sacral Nerve Roots
When it comes to sacral nerve roots, there are often misconceptions that can lead to confusion and misunderstanding. One common misconception is that everyone has the same number of nerve roots in the sacral region. However, this is not the case. Anatomical variations can exist, leading to differences in the number and structure of sacral nerve roots. So, it’s important to understand that each individual may have a unique configuration of nerve roots in this area.
Another misconception to be aware of is that issues related to the sacral nerve roots will always present in the same way for everyone. In reality, symptoms can vary significantly from person to person. Factors such as the specific nerve roots affected, the underlying cause of the issue, and individual physiological characteristics can all play a role in how symptoms manifest. So, it’s crucial to recognize that there is no one-size-fits-all when it comes to sacral nerve root problems.
Common Misconceptions about Sacral Nerve Roots
There are various misconceptions surrounding sacral nerve roots that can lead to confusion and misunderstanding. One common misconception is that everyone has the same number of nerve roots in the sacral region. As mentioned earlier, anatomical variations can exist, leading to differences in the number and structure of sacral nerve roots.
Additionally, it is important to note that issues related to the sacral nerve roots can present differently in individuals. Symptoms can vary based on factors such as the affected nerve roots, underlying cause, and individual physiological characteristics.
Expert Answers to Your Questions about Sacral Nerve Roots
When it comes to understanding sacral nerve roots, it’s always best to consult with a healthcare professional, preferably a specialist in the nervous system. They possess the necessary expertise and experience to provide accurate information and guidance tailored to individual circumstances. So, if you have specific questions or concerns about sacral nerve roots, seeking professional advice is the most reliable approach.
It’s important to remember that self-diagnosis or relying solely on online sources for medical information is not recommended. Every individual is unique, and consulting with a professional ensures personalized care and appropriate management strategies. So, if you have any concerns about your sacral nerve roots, don’t hesitate to reach out to a healthcare professional who can provide the necessary support and guidance.
In conclusion, the sacral region plays a vital role in our body’s functioning, particularly in the nervous system. Identifying the number of nerve roots in this region is crucial for understanding its implications on our health. However, it is essential to seek professional medical advice to accurately assess and interpret individual circumstances. By prioritizing health and engaging with healthcare professionals, we can ensure optimal well-being and address any potential concerns related to the sacral nerve roots.