The Formation of the Sacral Plexus: Nerve Roots Revealed
The sacral plexus is a complex network of nerves that plays a crucial role in the functioning of the lower body. Understanding its formation and the role of nerve roots is essential for comprehending its intricate anatomy and functions. In this article, we will explore the formation process of the sacral plexus and the vital role of nerve roots in its development and functionality.
Understanding the Sacral Plexus
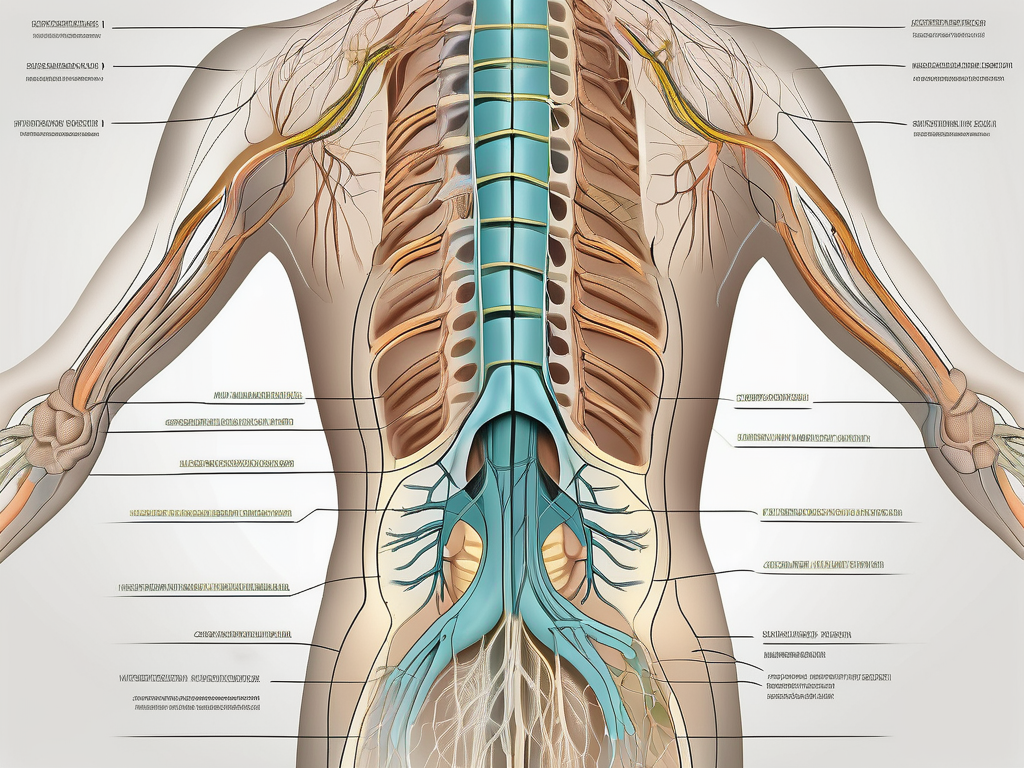
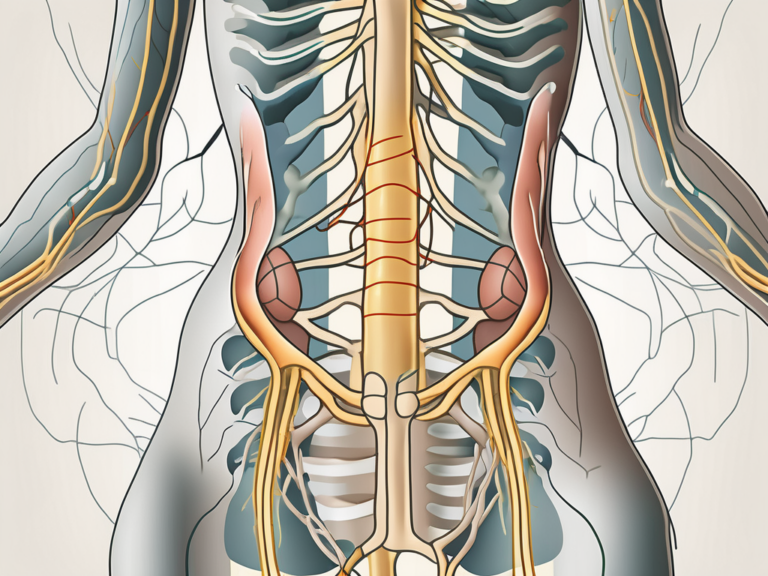
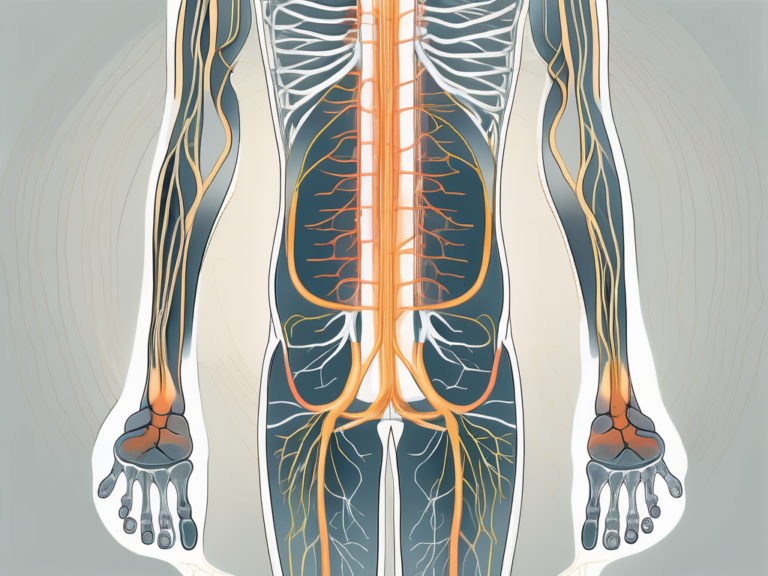
The sacral plexus is a network of nerves located in the pelvic region, specifically in the sacrum. It is formed by the fusion of the anterior rami of spinal nerves L4-S4. The complex interweaving of these nerve roots gives rise to the sacral plexus, making it a fascinating structure to study.
When exploring the anatomy of the sacral plexus, one cannot overlook its intricate branches and divisions that supply sensation and motor function to the lower limbs and pelvic structures. These branches work together harmoniously to ensure the proper functioning of the lower body.
Anatomy of the Sacral Plexus
One of the major branches of the sacral plexus is the sciatic nerve, which is the largest nerve in the human body. It originates from the sacral plexus and provides innervation to the muscles of the thigh, leg, and foot, as well as sensation to the same regions. The sciatic nerve is like a highway of communication, transmitting signals between the brain and the lower limbs.
In addition to the sciatic nerve, the sacral plexus gives rise to other important branches, such as the superior gluteal nerve, inferior gluteal nerve, and the pudendal nerve. Each of these nerves has its own specific functions and distributions within the pelvic region.
The superior gluteal nerve, for example, innervates the gluteus medius, gluteus minimus, and tensor fasciae latae muscles. These muscles are responsible for abduction and rotation of the hip joint, allowing us to move our legs in various directions.
The inferior gluteal nerve, on the other hand, innervates the gluteus maximus muscle, which is the largest muscle in the buttocks. This muscle plays a crucial role in extending and laterally rotating the hip joint, providing stability and power during activities such as walking, running, and climbing stairs.
Lastly, the pudendal nerve is responsible for providing sensation to the perineum, external genitalia, and the skin around the anus. It also innervates the muscles of the pelvic floor, which are essential for maintaining continence and supporting the pelvic organs.
Functions of the Sacral Plexus
The sacral plexus plays a vital role in various bodily functions, including walking, running, and maintaining balance. Without the proper functioning of the sacral plexus, these activities would be challenging, if not impossible, to perform.
Motor control of the lower limbs is one of the primary functions of the sacral plexus. It allows us to move our legs with precision and coordination. Whether it’s taking a step forward, climbing stairs, or kicking a ball, the sacral plexus ensures that the appropriate muscles are activated at the right time, making our movements smooth and efficient.
In addition to motor control, the sacral plexus also provides sensory feedback. This allows us to perceive touch, pain, and temperature in the lower body. It is through the sacral plexus that we are able to feel the ground beneath our feet, sense the warmth of the sun on our skin, and react to potential dangers or discomfort.
Furthermore, the sacral plexus plays a significant role in the function of pelvic organs, such as the bladder, rectum, and reproductive organs. The nerves of the sacral plexus innervate these organs, allowing for proper control and regulation of their activities. From emptying the bladder to achieving sexual arousal, the sacral plexus ensures that these essential functions occur smoothly and without any complications.
Understanding the sacral plexus is not only important for medical professionals but also for anyone interested in the intricacies of the human body. Its complex anatomy and crucial functions make it a fascinating subject of study, highlighting the remarkable design and functionality of our nervous system.
The Nerve Roots of the Sacral Plexus
Now that we have a foundational understanding of the sacral plexus, let’s delve deeper into the nerve roots that give rise to this intricate network.
Identifying the Nerve Roots
The sacral plexus is formed by the fusion of nerve roots from the lumbar and sacral spinal cord regions. Specifically, the anterior rami of spinal nerves L4 to S4 contribute to the formation of the sacral plexus. These nerve roots converge to create a web of interconnected nerves that supply the lower limbs and pelvic region.
The L4 nerve root, originating from the lumbar region, plays a crucial role in the sacral plexus. It carries motor fibers that innervate the muscles responsible for flexing the hip joint and extending the knee. Additionally, it carries sensory fibers that transmit signals from the skin on the inner thigh and the medial aspect of the lower leg.
The L5 nerve root, also originating from the lumbar region, contributes to the sacral plexus by providing motor fibers that control the muscles responsible for dorsiflexion of the foot and extension of the big toe. Sensory fibers from this nerve root transmit signals from the skin on the lateral aspect of the lower leg and the dorsum of the foot.
The S1 nerve root, originating from the sacral region, is another important component of the sacral plexus. It carries motor fibers that innervate the muscles responsible for plantar flexion of the foot and flexion of the toes. Sensory fibers from this nerve root transmit signals from the skin on the posterior aspect of the lower leg and the sole of the foot.
The S2 to S4 nerve roots, also originating from the sacral region, contribute to the sacral plexus by providing motor fibers that control the muscles responsible for the voluntary control of the anal sphincter and the external urethral sphincter. Sensory fibers from these nerve roots transmit signals from the skin around the perineum and the external genitalia.
Role of Nerve Roots in the Sacral Plexus
The nerve roots within the sacral plexus carry both motor and sensory information. Motor fibers control the contraction and relaxation of muscles, enabling movement and coordination. Sensory fibers transmit signals from the skin, muscles, and organs back to the central nervous system, allowing us to perceive sensations.
Motor fibers originating from the nerve roots of the sacral plexus are responsible for the complex movements of the lower limbs and the pelvic region. These movements include walking, running, jumping, and various activities involving the hips, knees, ankles, and toes.
Sensory fibers originating from the nerve roots of the sacral plexus play a vital role in our ability to perceive sensations. They allow us to feel touch, pressure, temperature, and pain in the lower limbs and the pelvic region. Additionally, they provide proprioceptive feedback, which helps us maintain balance and coordinate movements.
The fusion of these nerve roots allows for efficient communication between the brain, spinal cord, and the lower body. Any disruption or damage to these nerve roots can result in a variety of neurological conditions and disorders.
For example, damage to the L4 nerve root can lead to weakness or paralysis of the muscles responsible for flexing the hip joint and extending the knee. This can significantly impair a person’s ability to walk and perform daily activities.
Similarly, damage to the S1 nerve root can result in weakness or paralysis of the muscles responsible for plantar flexion of the foot and flexion of the toes. This can cause difficulties in walking, running, and maintaining balance.
Understanding the intricate network of nerve roots within the sacral plexus is crucial for healthcare professionals in diagnosing and treating neurological conditions affecting the lower limbs and pelvic region. By identifying the specific nerve roots involved, they can develop targeted treatment plans to restore function and improve quality of life for their patients.
The Formation Process of the Sacral Plexus
The development of the sacral plexus is a complex and fascinating process that occurs during embryonic development. Understanding the stages of this formation process can provide valuable insights into the functioning and potential clinical implications of the sacral plexus.
During embryonic development, the sacral plexus originates from various neural structures. As the spinal cord segments differentiate and grow, nerve fibers start to extend and organize into distinct patterns. Over time, these fibers fuse together and form nerve roots that contribute to the sacral plexus.
Throughout fetal development, the sacral plexus undergoes further refinement and growth to establish its mature anatomy. The timing and coordination of these developmental stages are critical for the proper functioning of the sacral plexus.
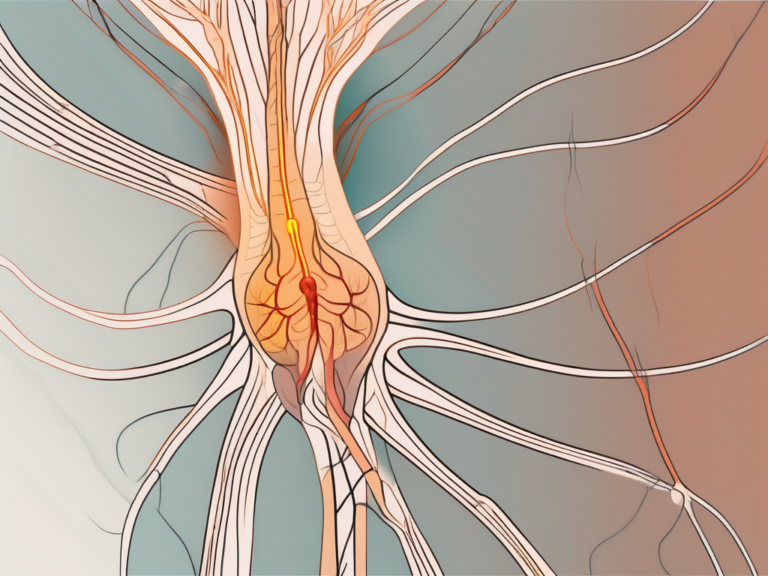
One of the key developmental stages of the sacral plexus is the formation of the ganglia. Ganglia are clusters of nerve cell bodies that play a crucial role in transmitting and processing sensory information. In the case of the sacral plexus, ganglia are responsible for receiving sensory input from the pelvic region and lower limbs.
As the nerve fibers continue to grow and extend, they navigate through a complex network of tissues and structures. This intricate pathway is guided by a combination of chemical signals and physical cues. The guidance cues help ensure that the nerve fibers reach their intended destinations within the sacral plexus.
Factors such as genetic and environmental influences can significantly impact the formation of the sacral plexus. Genetic factors determine the initial blueprint for the development of the nervous system, including the sacral plexus. Environmental factors, on the other hand, can either support or hinder the proper growth and organization of the nerve fibers.
It is essential to recognize the importance of prenatal care and the role of healthcare professionals in monitoring and supporting the healthy development of the sacral plexus. Regular check-ups and screenings can help identify any potential issues early on, allowing for timely interventions and treatments.
In conclusion, the formation process of the sacral plexus is a complex and intricate journey that begins during embryonic development. From the initial differentiation of nerve fibers to the establishment of ganglia and the guidance of nerve pathways, every step is crucial for the proper functioning of this important nerve network. Understanding the factors that influence its formation can help healthcare professionals provide better care and support for individuals with sacral plexus-related conditions.
Revealing the Intricacies of the Sacral Plexus
To gain a deeper understanding of the sacral plexus, advanced imaging techniques have been invaluable in revealing its intricate structures and functions.
The sacral plexus, a complex network of nerves located in the pelvis, plays a crucial role in the innervation of the lower body. Comprised of nerve roots originating from the spinal cord, this intricate web of nerves is responsible for transmitting signals that control movement and sensation in the lower extremities.
Technological advancements, such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and computed tomography (CT) scans, allow for detailed visualization of the sacral plexus. These imaging techniques provide healthcare professionals with important diagnostic tools to identify abnormalities, plan surgical interventions, and monitor the progress of various neurological conditions.
With the help of MRI, healthcare providers can obtain high-resolution images of the sacral plexus, enabling them to accurately assess its anatomical structures. This detailed visualization aids in the identification of any nerve compression, inflammation, or other abnormalities that may be causing symptoms in patients.
Computed tomography (CT) scans, on the other hand, utilize X-ray technology to create cross-sectional images of the sacral plexus. By capturing multiple images from different angles, CT scans provide a three-dimensional view of the nerve network, allowing for a comprehensive assessment of its integrity.
Insights Gained from Nerve Root Analysis
Furthermore, detailed analysis of the nerve roots within the sacral plexus contributes to our understanding of its functions and potential pathologies. Studying the nerve roots can provide valuable insights into the origin and propagation of neurological disorders affecting the lower body and pelvic region.
The nerve roots within the sacral plexus are responsible for transmitting sensory and motor signals to and from the lower limbs. By carefully examining these nerve roots, healthcare professionals can identify any abnormalities or damage that may be interfering with the proper functioning of the sacral plexus.
One common condition that can affect the sacral plexus is known as lumbosacral radiculopathy. This condition occurs when one or more nerve roots in the lower back become compressed or irritated, leading to pain, numbness, or weakness in the legs. Through nerve root analysis, healthcare providers can pinpoint the exact location and extent of the nerve compression, guiding appropriate treatment strategies.
Moreover, studying the nerve roots within the sacral plexus can also shed light on the development of certain neurological disorders. For instance, conditions such as cauda equina syndrome, which involves compression of the nerve roots at the base of the spinal cord, can be better understood through detailed nerve root analysis. This knowledge aids in the early detection and management of such conditions, preventing further complications.
In conclusion, advanced imaging techniques and detailed analysis of the nerve roots within the sacral plexus have revolutionized our understanding of this complex nerve network. By providing healthcare professionals with valuable insights into its structures and functions, these advancements have paved the way for improved diagnosis, treatment, and management of various neurological conditions affecting the lower body and pelvic region.
Implications for Neurological Health and Disorders
The sacral plexus plays a crucial role in neurological health and can be implicated in various conditions and disorders.
The sacral plexus, a complex network of nerves located in the lower back, is responsible for the innervation of the lower extremities, pelvic organs, and perineum. It is formed by the fusion of the anterior rami of the fourth and fifth lumbar spinal nerves and the first, second, third, and fourth sacral spinal nerves. This intricate formation allows for the transmission of sensory and motor signals, enabling the proper functioning of the lower body.
Sacral Plexus and Neurological Conditions
Neurological conditions, such as sciatica, pudendal neuralgia, and cauda equina syndrome, can arise from dysfunction or damage to the sacral plexus. Sciatica, a condition characterized by pain radiating from the lower back down the leg, often occurs due to compression or irritation of the sciatic nerve, which is a major component of the sacral plexus. Pudendal neuralgia, on the other hand, manifests as chronic pain in the perineum, genitals, or rectum, and is caused by irritation or injury to the pudendal nerve, another important nerve within the sacral plexus. Cauda equina syndrome, a rare but serious condition, occurs when the nerve roots of the sacral plexus are compressed, leading to severe lower back pain, bowel and bladder dysfunction, and even paralysis if left untreated.
These conditions can cause pain, numbness, weakness, and other debilitating symptoms that significantly impact daily life. Individuals affected by these conditions often experience limitations in mobility, difficulties with activities of daily living, and a decreased quality of life. Therefore, early diagnosis and appropriate treatment are crucial for managing symptoms and preventing further complications.
If you are experiencing any symptoms related to the sacral plexus or any other neurological issues, it is vital to consult with a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment options. A thorough medical evaluation, including a detailed history, physical examination, and possibly imaging studies, can help identify the underlying cause of the symptoms and guide the development of an individualized treatment plan.
Importance of the Sacral Plexus in Neurological Health
The deep understanding of the formation, anatomy, and functions of the sacral plexus contributes to our knowledge of the intricate mechanisms underlying neurological health. By studying the sacral plexus, researchers and healthcare professionals can gain insights into the pathophysiology of various neurological conditions and develop targeted interventions, therapies, and preventive measures to support the optimal functioning of the sacral plexus and overall neurological well-being.
Furthermore, the sacral plexus is not only essential for motor and sensory functions but also plays a crucial role in autonomic control. The autonomic nerves within the sacral plexus regulate important bodily functions such as bladder and bowel control, sexual function, and blood flow to the pelvic organs. Dysfunction or damage to these autonomic nerves can lead to urinary or fecal incontinence, sexual dysfunction, and other related issues.
Moreover, the sacral plexus is intricately connected to other components of the nervous system, including the spinal cord, brain, and peripheral nerves. This interconnectedness allows for the coordination of complex movements, reflexes, and sensory processing. Dysfunction in any part of this intricate network can disrupt the flow of information and result in various neurological symptoms.
In conclusion, the formation process of the sacral plexus and the elucidation of its nerve roots reveal the intricate nature of this essential network of nerves. Understanding the anatomy and functions of the sacral plexus provides a solid foundation for further exploration of its clinical implications and the development of innovative treatment approaches. Ongoing research and advancements in the field of neurology continue to shed light on the complex interplay between the sacral plexus and neurological health, offering hope for improved diagnosis, treatment, and management of neurological conditions.