What Is the Function of the Sacral Nerve?
The function of the sacral nerve is a crucial aspect of the human body’s overall nervous system. Understanding the role it plays in motor and sensory functions, as well as its contribution to pain management, is essential for maintaining optimal health and well-being. Additionally, being aware of the potential disorders related to the sacral nerve and the advancements in sacral nerve research can help individuals make informed decisions about their healthcare. In this article, we will delve deeper into these topics and explore the various aspects of the sacral nerve. It is important to note that while this information provides a general overview, consulting with a healthcare professional is always advised for specific concerns or conditions.
Understanding the Sacral Nerve
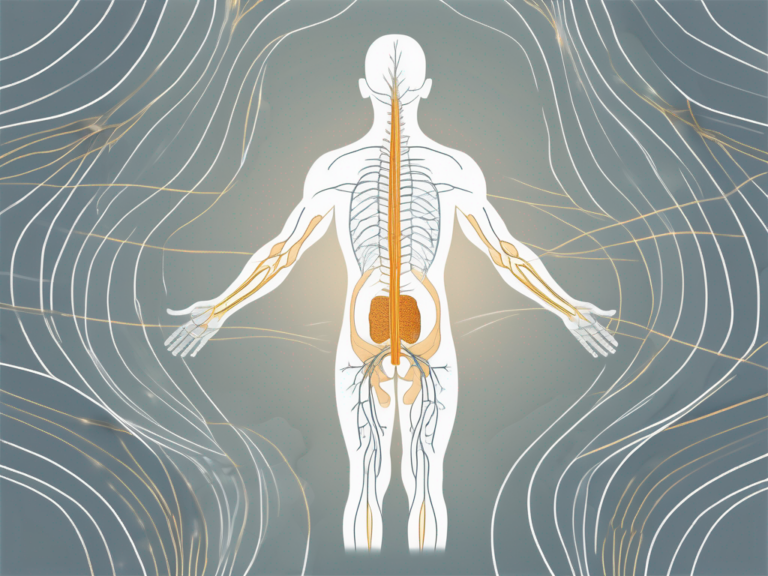
The sacral nerve is a crucial part of the peripheral nervous system and is responsible for transmitting signals between various parts of the body and the brain. It is located in the lower back, branching out from the spinal cord’s sacral vertebrae, which are connected to the pelvis and lower limbs. This intricate network of nerves regulates many bodily functions and plays a significant role in motor and sensory functions.
The sacral nerve is a complex and fascinating part of the human body. Let’s dive deeper into its anatomy and functions to gain a comprehensive understanding.
Anatomy of the Sacral Nerve
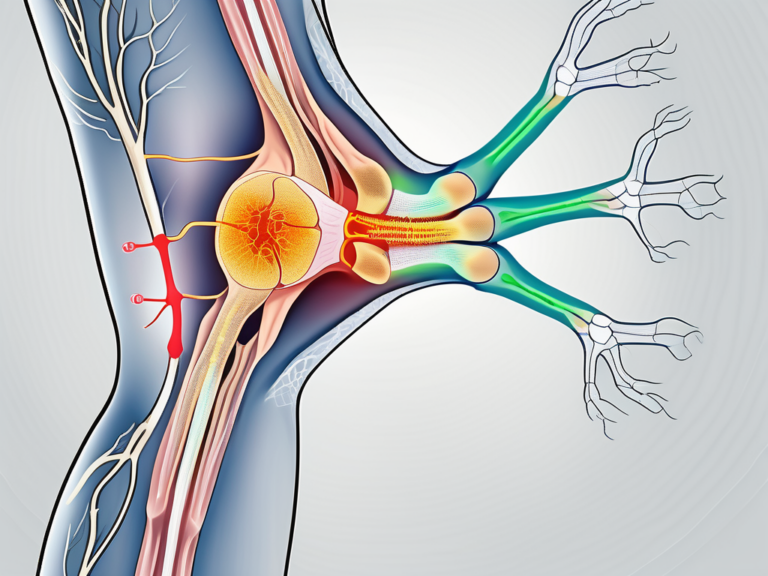
The sacral nerve consists of multiple nerves that extend from the sacral region. These nerves form the sacral plexus, which serves as the main connection between the spinal cord and the lower body. The sacral plexus comprises nerves that supply various pelvic organs, muscles, and skin of the buttocks, groin, and lower limbs. These nerves play a crucial role in transmitting sensory information and controlling motor functions in these areas.
Within the sacral plexus, there are several distinct nerves, each with its own specific functions. The sciatic nerve, for example, is the largest nerve in the body and originates from the sacral plexus. It provides sensation and motor control to the back of the thigh, lower leg, and foot. Other nerves within the sacral plexus include the pudendal nerve, which controls the muscles of the pelvic floor, and the superior and inferior gluteal nerves, which innervate the muscles of the buttocks.
Furthermore, the sacral nerve is not limited to motor and sensory functions. It also plays a crucial role in the autonomic nervous system, which governs involuntary bodily functions. The sacral nerves are involved in regulating digestion, urinary function, and sexual functions. They work in harmony with other nerves in the autonomic nervous system to maintain homeostasis and ensure the proper functioning of these vital bodily processes.
The Nervous System and the Sacral Nerve
As part of the peripheral nervous system, the sacral nerve collaborates with the central nervous system, which includes the brain and spinal cord, to facilitate communication throughout the body. This intricate interaction allows the brain to send signals to different parts of the body, and in turn, receive sensory information vital for keeping the body functioning optimally.
The sacral nerve, specifically, plays a vital role in relaying sensory information from our environment to the brain. For instance, it helps us perceive sensations such as touch, pain, and temperature in the lower part of the body. Moreover, it enables us to effortlessly control our leg muscles, enabling smooth and coordinated movements crucial for locomotion and balance.
Understanding the sacral nerve’s role in the nervous system helps us appreciate its significance in our daily lives. From simple actions like walking and sitting to more complex functions like digestion and sexual arousal, the sacral nerve is constantly at work, ensuring our bodies function harmoniously.
In conclusion, the sacral nerve is a remarkable component of the peripheral nervous system. Its intricate anatomy and multifaceted functions make it an essential part of our overall well-being. By understanding the sacral nerve’s role in transmitting signals and maintaining bodily functions, we can develop a deeper appreciation for the complexity and beauty of the human body.
Functions of the Sacral Nerve
The sacral nerve performs essential functions related to both motor control and sensory perception. Understanding these functions is crucial in comprehending the potential impact of sacral nerve disorders on an individual’s overall well-being.
Role in Motor Functions
The sacral nerve is responsible for controlling various motor functions in the lower body, including the movements of the legs, hips, and pelvic floor muscles. It facilitates activities such as walking, sitting, and maintaining posture. Moreover, it plays a pivotal role in bladder and bowel control, facilitating the contraction and relaxation of the muscles involved in these functions.
When it comes to walking, the sacral nerve coordinates the movement of the legs, ensuring that each step is taken with precision. It sends signals to the muscles in the legs, instructing them to contract and relax in a coordinated manner, allowing for smooth and efficient movement.
In addition to walking, the sacral nerve also plays a crucial role in sitting. It helps maintain the balance and stability of the pelvis, allowing individuals to sit comfortably for extended periods. Without the sacral nerve’s control, sitting would be challenging, and maintaining proper posture would be nearly impossible.
Furthermore, the sacral nerve is vital for bladder and bowel control. It enables the muscles in the bladder to contract and relax, allowing for the storage and release of urine. Similarly, it facilitates the contraction and relaxation of the muscles in the rectum, aiding in the elimination of waste from the body. Without the sacral nerve’s involvement, individuals would experience difficulties in controlling their bladder and bowel movements.
Role in Sensory Functions
The sacral nerve is integral to sensory perception in the lower body, enabling individuals to interpret sensations such as touch, pain, and temperature. It carries sensory information from the periphery, such as the skin, muscles, and organs of the lower body, to the brain. This sensory feedback is essential for maintaining a sense of bodily awareness and coordinating movements smoothly.
Through the sacral nerve, individuals are able to feel sensations on their skin, allowing them to detect various stimuli, such as pressure, vibration, and temperature. This sensory information is crucial for avoiding potential harm, as it alerts individuals to dangerous situations, such as extreme heat or sharp objects.
Moreover, the sacral nerve plays a role in pain perception. It carries pain signals from the lower body to the brain, allowing individuals to experience and interpret pain. This function is essential for identifying injuries or potential health issues that may require medical attention.
Additionally, the sacral nerve enables individuals to perceive changes in temperature. It carries temperature-related signals from the lower body to the brain, allowing individuals to sense and respond to hot or cold environments. This sensory function helps individuals maintain their body temperature within a safe range and adapt to different climates.
In conclusion, the sacral nerve is not only responsible for motor control in the lower body but also plays a vital role in sensory perception. Its functions are essential for maintaining proper movement, bladder and bowel control, as well as interpreting sensations such as touch, pain, and temperature. Understanding the role of the sacral nerve is crucial in recognizing the potential impact of sacral nerve disorders and the importance of maintaining its health.
Disorders Related to the Sacral Nerve
Disorders related to the sacral nerve can significantly impact an individual’s quality of life and ability to perform daily activities. The sacral nerve, also known as the S1-S5 nerve roots, plays a crucial role in transmitting sensory and motor signals to and from the lower limbs, as well as controlling bladder and bowel function. When this nerve is affected by injury, compression, or disease, it can lead to a variety of symptoms and complications.
One of the common symptoms of sacral nerve disorders is muscle weakness or paralysis in the lower limbs. This can make it difficult for individuals to walk, stand, or perform activities that require lower body strength. Numbness or tingling sensations in the legs or feet are also frequently reported, indicating sensory nerve involvement. Additionally, sacral nerve dysfunction can affect bladder and bowel control, leading to urinary or fecal incontinence. Sexual dysfunction, such as erectile dysfunction in men or decreased sexual sensation in both men and women, may also be experienced.
It is important to note that these symptoms can also indicate other underlying conditions, such as spinal cord injury, peripheral neuropathy, or pelvic floor dysfunction. Therefore, seeking medical attention and consulting with a healthcare professional is essential for an accurate diagnosis. A thorough evaluation is typically conducted, starting with a detailed medical history and physical examination. In some cases, additional diagnostic tests may be ordered, such as nerve conduction studies, electromyography, or imaging studies like magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) or computed tomography (CT) scans.
Once a diagnosis is confirmed, appropriate treatment options can be explored. The choice of treatment will depend on the underlying cause of the sacral nerve disorder and the severity of the symptoms. In many cases, conservative management approaches are initially recommended. This may include medication to alleviate pain or inflammation, physical therapy to improve muscle strength and mobility, and lifestyle modifications to manage bladder or bowel dysfunction.
In more severe cases, where conservative measures fail to provide adequate relief, surgical interventions may be considered. Surgery aims to address the specific cause of the sacral nerve disorder, such as removing a herniated disc that is compressing the nerve roots or repairing a damaged nerve. Surgical procedures can vary widely depending on the individual’s condition and may involve minimally invasive techniques or more extensive open surgeries.
Managing sacral nerve disorders requires a multidisciplinary approach, involving healthcare professionals from various specialties, such as neurology, urology, orthopedics, and physical therapy. Collaborative care ensures that the treatment plan is tailored to the individual’s needs, taking into account their specific symptoms, functional goals, and overall health.
In conclusion, disorders related to the sacral nerve can have a profound impact on an individual’s daily life. Recognizing the symptoms and seeking timely medical attention is crucial for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment. With advancements in medical knowledge and therapeutic options, individuals with sacral nerve disorders have a better chance of managing their condition effectively and improving their quality of life.
The Sacral Nerve and Pain Management
Pain management is another significant aspect concerning the function of the sacral nerve. Several interventions can help alleviate sacral nerve-related pain and improve the overall quality of life for individuals facing such challenges.
The sacral nerve, also known as the S2-S4 nerve, plays a crucial role in transmitting sensory and motor signals to and from the pelvic region. When this nerve becomes damaged or dysfunctional, it can lead to various symptoms, including pain, bladder and bowel control issues, and sexual dysfunction.
Sacral Nerve Stimulation
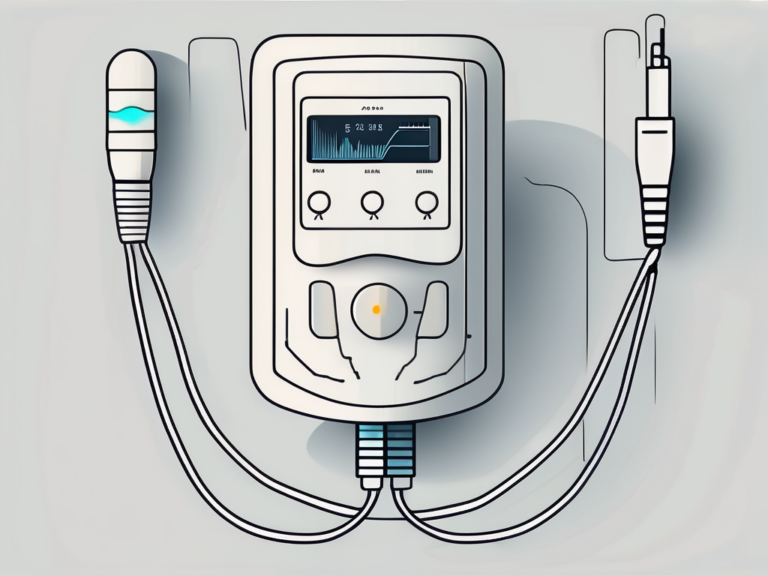
Sacral nerve stimulation, also known as neuromodulation, is a technique that involves the use of low-level electrical impulses to modulate or regulate the activity of the sacral nerve. This method aims to reduce pain or improve bladder and bowel control in individuals experiencing sacral nerve-related disorders.
The electrical impulses are delivered via a small device implanted under the skin, typically near the buttocks. This device, often referred to as a neurostimulator, is connected to thin wires that are carefully placed near the sacral nerve. The settings of the neurostimulator can be adjusted to meet individual needs, allowing for personalized pain management.
However, it is important to note that this intervention is not suitable for everyone, and consulting with a healthcare professional is necessary to determine its viability and potential benefits. The healthcare professional will assess the individual’s medical history, symptoms, and overall health to determine if sacral nerve stimulation is an appropriate option.
Non-Surgical Interventions for Sacral Nerve Pain
In cases where surgery may not be necessary or suitable, individuals experiencing sacral nerve pain may benefit from non-surgical interventions. These interventions aim to provide relief from pain and improve overall function without the need for invasive procedures.
Physical therapy is often recommended as a non-surgical intervention for sacral nerve pain. Physical therapists can design specific exercises and stretches that target the muscles and nerves in the pelvic region, helping to alleviate pain and improve mobility.
Medication management is another non-surgical approach to sacral nerve pain. Depending on the individual’s symptoms and medical history, healthcare professionals may prescribe medications such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), muscle relaxants, or nerve pain medications to help manage the pain and reduce inflammation.
Nerve blocks, also known as nerve numbing injections, can provide temporary relief from sacral nerve pain. During this procedure, a healthcare professional injects a local anesthetic or a combination of anesthetics and steroids near the sacral nerve to block pain signals. Nerve blocks can provide immediate pain relief and allow individuals to engage in physical therapy or other rehabilitative treatments more comfortably.
Other non-surgical techniques, such as heat therapy, cold therapy, and transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS), may also be used to manage sacral nerve pain. These techniques aim to reduce inflammation, improve blood flow, and provide temporary pain relief.
Consulting with a healthcare professional will aid in determining the optimal approach for managing sacral nerve pain based on individual circumstances. The healthcare professional will consider the severity of the symptoms, the underlying cause of the pain, and the individual’s overall health to develop a personalized treatment plan.
The Future of Sacral Nerve Research
Advancements in medical research continue to shed light on the intricacies of the sacral nerve and open doors to innovative treatments and approaches for disorders related to its function. These developments hold promise for improving outcomes and quality of life for individuals facing sacral nerve-related challenges.
The sacral nerve, also known as the sacral plexus, is a complex network of nerves that plays a crucial role in the functioning of the lower body. It is responsible for transmitting signals between the brain and the pelvic organs, including the bladder, bowel, and sexual organs. Any disruption in the normal functioning of the sacral nerve can lead to a range of debilitating conditions, such as urinary incontinence, fecal incontinence, and sexual dysfunction.
Innovations in Sacral Nerve Treatment
Ongoing research in the field of sacral nerve treatment has paved the way for innovative approaches. These can include new medications, minimally invasive surgical techniques, or advancements in neurostimulation devices. For example, sacral nerve modulation, also known as sacral neuromodulation or sacral nerve stimulation, is a promising treatment option for individuals with overactive bladder or urinary incontinence. This technique involves the implantation of a small device that delivers electrical impulses to the sacral nerves, helping to regulate their activity and restore normal bladder function.
In addition to neurostimulation, researchers are exploring the potential of stem cell therapy for sacral nerve disorders. Stem cells have the unique ability to differentiate into various cell types, and scientists believe that they could be harnessed to repair damaged nerves and restore their normal function. Although still in the early stages of research, stem cell therapy holds great promise for individuals with sacral nerve injuries or degenerative conditions.
The Impact of Technology on Sacral Nerve Studies
Technological advancements have revolutionized the field of sacral nerve studies, enabling researchers to gain a deeper understanding of its function and potential avenues for treatment. Advanced diagnostic tools, imaging modalities, and research techniques contribute to ongoing progress in this field.
For instance, functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) allows researchers to visualize the activity of the sacral nerve in real-time, providing valuable insights into its role in various bodily functions. This non-invasive imaging technique has the potential to aid in the diagnosis and treatment planning for sacral nerve disorders.
Furthermore, the development of bioengineering techniques has opened up new possibilities for creating artificial nerve grafts or scaffolds that can support nerve regeneration. By combining biocompatible materials with growth factors and stem cells, scientists are working towards developing innovative solutions for repairing damaged sacral nerves and restoring their normal function.
The continued integration of technology is expected to propel sacral nerve research forward, leading to further breakthroughs and improved outcomes. As our understanding of the sacral nerve continues to expand, so too will our ability to develop targeted and effective treatments for sacral nerve disorders.
In conclusion, the function of the sacral nerve is integral to various aspects of human health and well-being. Understanding its role in motor and sensory functions, recognizing potential disorders, and staying informed about advancements in sacral nerve research empowers individuals to make informed decisions about their healthcare. However, it is crucial to consult with a healthcare professional for personalized assessment, accurate diagnosis, and appropriate treatment options tailored to individual needs. By combining medical expertise with ongoing research, individuals can navigate the complexities of the sacral nerve and optimize their overall health and quality of life.