What Is Your Sacral Nerve? A Comprehensive Guide
The sacral nerve is a vital component of the human nervous system, playing a crucial role in various bodily functions. Understanding the intricacies of this nerve can provide valuable insights into maintaining its health and preventing potential disorders. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the function and anatomy of the sacral nerve, common disorders associated with it, strategies for maintaining its health, and the future of sacral nerve research.
Understanding the Nervous System
The human nervous system is a complex network of nerves that facilitates communication between different parts of the body and the brain. It can be broadly categorized into two divisions: the central nervous system (CNS), consisting of the brain and spinal cord, and the peripheral nervous system (PNS), comprising the nerves that branch out from the CNS.
The central nervous system, composed of the brain and spinal cord, serves as the command center of the body. It receives and processes information from the peripheral nervous system, allowing us to perceive and respond to our environment. The brain, with its billions of neurons, is responsible for higher cognitive functions such as thinking, memory, and emotions. The spinal cord, on the other hand, acts as a pathway for signals between the brain and the rest of the body.
The peripheral nervous system, consisting of nerves that extend from the CNS, plays a crucial role in transmitting information to and from the central nervous system. These nerves are like electrical cables, carrying signals to and from various parts of the body. They connect the brain and spinal cord to the sensory organs, muscles, and glands, allowing for coordinated movement and bodily functions.
The Role of Nerves in the Human Body
Nerves are specialized cells that transmit signals throughout the body, allowing for the coordination of various bodily functions. They serve as pathways for sensory input, motor output, and the regulation of internal processes, ensuring the seamless functioning of our bodies.
Sensory nerves are responsible for transmitting information from sensory organs, such as the eyes, ears, nose, and skin, to the central nervous system. These nerves allow us to perceive our surroundings, enabling us to see, hear, smell, taste, and touch. Without sensory nerves, our ability to interact with the world around us would be severely impaired.
Motor nerves, on the other hand, carry signals from the central nervous system to the muscles, enabling voluntary and involuntary movements. These nerves allow us to walk, talk, eat, and perform various other activities. They also control involuntary actions, such as the beating of the heart and the contraction of the digestive system, ensuring the proper functioning of our internal organs.
Different Types of Nerves and Their Functions
There are three main types of nerves in the human body: sensory nerves, motor nerves, and mixed nerves. Sensory nerves transmit information from sensory organs to the brain, allowing us to perceive our surroundings. For example, when you touch a hot stove, sensory nerves in your skin send a signal to your brain, which then interprets it as pain and prompts you to withdraw your hand.
Motor nerves, on the other hand, carry signals from the brain to the muscles, enabling voluntary and involuntary movements. For instance, when you decide to move your arm, motor nerves transmit the signal from your brain to the muscles in your arm, causing it to contract and move.
Mixed nerves, as the name suggests, possess both sensory and motor functions, enabling the bidirectional transmission of signals. These nerves play a crucial role in coordinating complex movements and sensory experiences. For example, the sciatic nerve, one of the largest nerves in the body, is a mixed nerve that extends from the lower back down to the feet. It allows for both sensory perception, such as feeling pain or temperature changes in the leg, and motor control, enabling movements like walking and running.
The sacral nerve, another example of a mixed nerve, is located in the lower back and plays a vital role in controlling the functions of the pelvic organs, including the bladder, bowel, and reproductive organs. It enables the transmission of signals between the brain and these organs, ensuring their proper functioning.
In conclusion, the human nervous system is a complex and intricate network of nerves that allows for communication and coordination between different parts of the body and the brain. Understanding the role of nerves and their functions is essential in comprehending how our bodies function and respond to the world around us.
The Sacral Nerve: An Overview
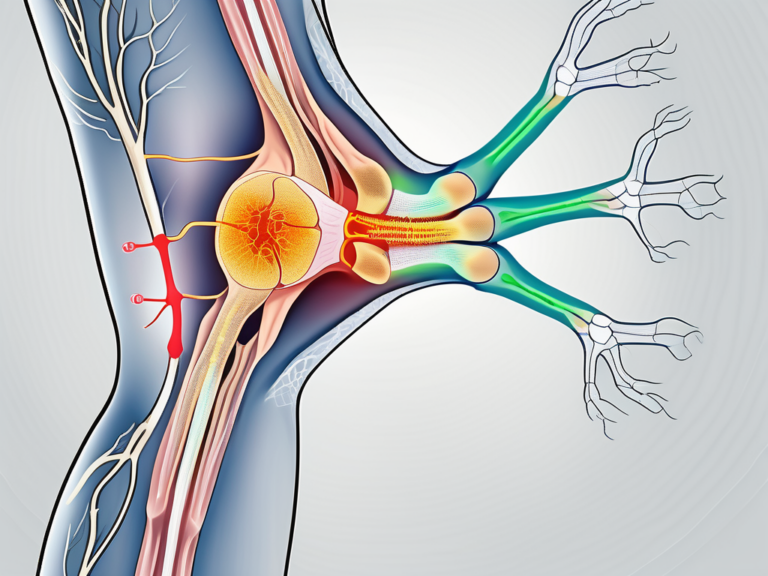
The sacral nerve, an integral part of the nervous system, plays a vital role in maintaining proper bodily functions. It originates from the sacral plexus, a complex network of nerves located in the lower back. This network consists of a group of nerves collectively known as the sacral roots, formed by the fusion of the spinal nerves originating from the fifth lumbar vertebra (L5) to the third sacral vertebra (S3).
As the sacral nerve travels through the pelvis, it branches out to innervate various pelvic organs, including the bladder, rectum, and reproductive organs. This intricate web of nerves ensures the smooth functioning of these organs, allowing them to carry out their respective roles efficiently.
Anatomy of the Sacral Nerve
The sacral nerve, with its intricate anatomy, is a fascinating structure. It consists of both sensory and motor fibers, enabling it to transmit information to and from the brain. These fibers are responsible for relaying sensory information, such as touch, pain, and temperature, from the pelvic region to the brain, allowing us to perceive sensations accurately.
Furthermore, the motor fibers of the sacral nerve control the muscles in the pelvic region. These muscles play a crucial role in maintaining continence, allowing us to control the release of urine and feces. Without the proper functioning of the sacral nerve, these muscles would be unable to carry out their essential tasks, leading to various urinary and bowel disorders.
The Function of the Sacral Nerve
The sacral nerve is a multitasking marvel, responsible for regulating a multitude of bodily functions. One of its primary functions is to maintain proper bladder control. It does so by coordinating the contraction and relaxation of the bladder muscles, ensuring the timely release of urine. This intricate dance between the sacral nerve and the bladder muscles allows us to maintain continence and avoid embarrassing situations.
In addition to bladder control, the sacral nerve also plays a crucial role in bowel control. It regulates the muscles responsible for the movement of feces through the intestines, ensuring smooth and efficient bowel movements. Without the proper functioning of the sacral nerve, individuals may experience difficulties in controlling bowel movements, leading to conditions such as fecal incontinence.
Another significant function of the sacral nerve is its involvement in sexual function. It transmits sensory information from the pelvic region to the brain, allowing us to experience pleasurable sensations during sexual activity. Additionally, the sacral nerve controls the muscles involved in sexual response, enabling the intricate dance of arousal and climax.
Overall, the sacral nerve is a remarkable component of our nervous system, responsible for maintaining proper bladder and bowel control, sexual function, and sensation in the pelvic region. Its intricate anatomy and multifaceted functions make it an essential part of our overall well-being.
Disorders Related to the Sacral Nerve
Sacral nerve disorders can significantly impact an individual’s quality of life. The sacral nerve, also known as the S1-S5 nerve roots, plays a crucial role in the functioning of the bladder, bowel, and sexual organs. When this nerve is affected by a disorder or injury, it can lead to a range of symptoms that can have a profound impact on daily life.
One common symptom of sacral nerve disorders is bladder dysfunction. This can manifest as urinary incontinence, difficulty emptying the bladder completely, or a frequent urge to urinate. Bowel dysfunction is another common symptom, which can result in constipation, diarrhea, or difficulty controlling bowel movements.
In addition to bladder and bowel dysfunction, sacral nerve disorders can also cause sexual dysfunction. Both men and women may experience a decrease in sexual desire, difficulty achieving or maintaining an erection (in men), or difficulty achieving orgasm. These symptoms can have a significant impact on intimate relationships and overall well-being.
Other symptoms of sacral nerve disorders can include numbness or tingling in the pelvic area, as well as pain or weakness in the legs. These symptoms can vary in severity and may be present on one side of the body or both.
Diagnosis and Treatment Options for Sacral Nerve Disorders
If you are experiencing symptoms related to the sacral nerve, it is crucial to consult with a healthcare provider for a proper diagnosis. The diagnostic process may involve a thorough medical history assessment, physical examination, and potentially specialized tests, such as electromyography (EMG) or imaging studies.
During the medical history assessment, your healthcare provider will ask about your symptoms, their duration and severity, as well as any factors that may worsen or alleviate them. They may also inquire about your medical history, including any previous injuries or conditions that may be contributing to your symptoms.
A physical examination will likely be conducted to assess your neurological function. This may involve testing your reflexes, muscle strength, and sensation in the affected areas. Your healthcare provider may also perform specific tests to evaluate bladder and bowel function, such as measuring urine flow or assessing the anal sphincter muscle.
In some cases, specialized tests may be necessary to further evaluate the sacral nerve and surrounding structures. Electromyography (EMG) is a test that measures the electrical activity of muscles and can help identify any abnormalities in nerve function. Imaging studies, such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) or computed tomography (CT) scans, may also be ordered to visualize the sacral nerve and identify any structural abnormalities.
The treatment options for sacral nerve disorders depend on the underlying cause and severity of the condition. In some cases, medication management may be recommended to alleviate symptoms and improve nerve function. Physical therapy can also be beneficial, as it can help strengthen the muscles surrounding the sacral nerve and improve overall function.
Lifestyle modifications, such as maintaining a healthy weight, practicing good bladder and bowel habits, and avoiding activities that exacerbate symptoms, may also be recommended. In more severe cases, surgical interventions may be necessary to repair or remove any structural abnormalities that are causing the sacral nerve disorder.
Consulting with a specialist, such as a neurologist or urologist, can help determine the most suitable treatment plan to address individual needs. It is important to seek appropriate medical advice and treatment to manage sacral nerve disorders effectively and improve quality of life.
Maintaining Sacral Nerve Health
Promoting sacral nerve health involves adopting habits that support overall wellness and minimize the risk of developing disorders. While it is important to note that certain conditions may be unavoidable, incorporating the following practices into your lifestyle can help optimize sacral nerve function:
Lifestyle Changes for Sacral Nerve Health
1. Regular exercise: Engaging in physical activity helps improve blood circulation and maintain muscle strength, which can support the functioning of the sacral nerve.
Regular exercise is not only beneficial for your overall health, but it can also have a positive impact on your sacral nerve health. When you engage in physical activity, your blood circulation increases, delivering oxygen and essential nutrients to the nerves in your sacral region. This improved blood flow helps nourish and support the proper functioning of the sacral nerve.
Additionally, regular exercise helps to maintain muscle strength in the pelvic region, which is important for the optimal functioning of the sacral nerve. Strengthening the muscles surrounding the sacral nerve can help provide stability and support, reducing the risk of nerve compression or damage.
2. Healthy diet: Consuming a balanced diet rich in essential nutrients can contribute to nerve health. Including fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins in your meals can provide the necessary vitamins and minerals.
Your diet plays a crucial role in maintaining the health of your sacral nerve. Including a variety of fruits and vegetables in your meals ensures that you are getting a wide range of vitamins and minerals that are essential for nerve function. Vitamins such as B12, B6, and E, as well as minerals like magnesium and calcium, are particularly important for nerve health.
Whole grains, such as brown rice and quinoa, are rich in fiber and can help regulate blood sugar levels. This is important because high blood sugar levels can lead to nerve damage over time. Lean proteins, such as chicken, fish, and tofu, provide amino acids that are necessary for the repair and maintenance of nerve tissue.
3. Adequate hydration: Staying hydrated can support proper bladder function and prevent urinary problems. Aim to drink an adequate amount of water throughout the day.
Water is essential for maintaining the health of your sacral nerve and overall well-being. Staying hydrated helps to support proper bladder function, preventing urinary problems that can put pressure on the sacral nerve. Aim to drink at least eight glasses of water per day to ensure adequate hydration.
In addition to water, you can also incorporate herbal teas and natural fruit juices into your daily fluid intake. These can provide additional hydration while also offering various health benefits, such as anti-inflammatory properties or antioxidant effects.
4. Stress management: Chronic stress can affect nerve function. Practicing stress-management techniques, such as mindfulness meditation or engaging in hobbies, can help reduce the impact of stress on the sacral nerve.
Stress can have a detrimental effect on the health of your sacral nerve. When you are under chronic stress, your body releases stress hormones that can disrupt the normal functioning of your nerves. This can lead to symptoms such as pain, tingling, or numbness in the sacral region.
Engaging in stress-management techniques can help reduce the impact of stress on your sacral nerve. Mindfulness meditation, deep breathing exercises, and engaging in hobbies or activities that you enjoy can all help promote relaxation and reduce stress levels. Taking time for self-care and prioritizing your mental well-being can have a positive impact on your sacral nerve health.
Medical Interventions for Sacral Nerve Health
In addition to lifestyle changes, medical interventions may be beneficial for certain individuals. These may include medications prescribed by healthcare professionals to alleviate specific symptoms or surgical procedures to address underlying conditions. It is crucial to consult with a healthcare provider to determine the most appropriate course of action.
While lifestyle changes can greatly contribute to sacral nerve health, there may be cases where medical interventions are necessary. If you are experiencing severe symptoms or have an underlying condition affecting your sacral nerve, your healthcare provider may recommend medications to alleviate specific symptoms or surgical procedures to address the root cause of the problem.
It is important to consult with a healthcare professional who specializes in nerve health to determine the most appropriate course of action for your specific situation. They will be able to assess your symptoms, conduct any necessary tests, and provide personalized recommendations to optimize your sacral nerve health.
The Future of Sacral Nerve Research
Ongoing advances in medical research hold the promise of further advancements in the field of sacral nerve health. Scientists and healthcare professionals are continually exploring emerging treatments and therapies to improve the outcomes of sacral nerve disorders.
Emerging Treatments and Therapies
Researchers are investigating new treatments and therapies for sacral nerve disorders, including experimental medications, innovative surgical techniques, and medical devices. These advancements aim to improve symptom management and enhance overall quality of life for individuals affected by sacral nerve conditions.
The Impact of Technology on Sacral Nerve Health
Technological advancements, such as neuromodulation devices, biofeedback systems, and telemedicine, have the potential to revolutionize the management of sacral nerve disorders. These technologies can provide non-invasive treatment options and enhance communication between healthcare providers and patients, leading to improved care outcomes.
In conclusion, understanding the complexities of the sacral nerve is crucial for maintaining overall health and well-being. By recognizing the function and anatomy of the sacral nerve, identifying common disorders and symptoms, adopting healthy lifestyle habits, and staying informed about the latest research, individuals can take proactive steps to optimize sacral nerve health. If experiencing any symptoms or concerns related to the sacral nerve, it is always recommended to consult with a healthcare professional for proper evaluation and guidance.