How to Determine if Your Sacral Nerve is Damaged
The sacral nerve plays a critical role in the functioning of our bodies. It is responsible for delivering signals to and from our lower extremities and pelvic region. However, various factors can lead to sacral nerve damage, which can significantly impact our overall well-being. In this article, we will explore how to determine if your sacral nerve is damaged, including understanding the anatomy and functions of the sacral nerve, recognizing common causes and symptoms of damage, diagnostic procedures for evaluation, available treatment options, and prevention and management strategies. It is important to note that if you suspect sacral nerve damage, it is advisable to consult with a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate medical guidance.
Understanding the Sacral Nerve and Its Functions
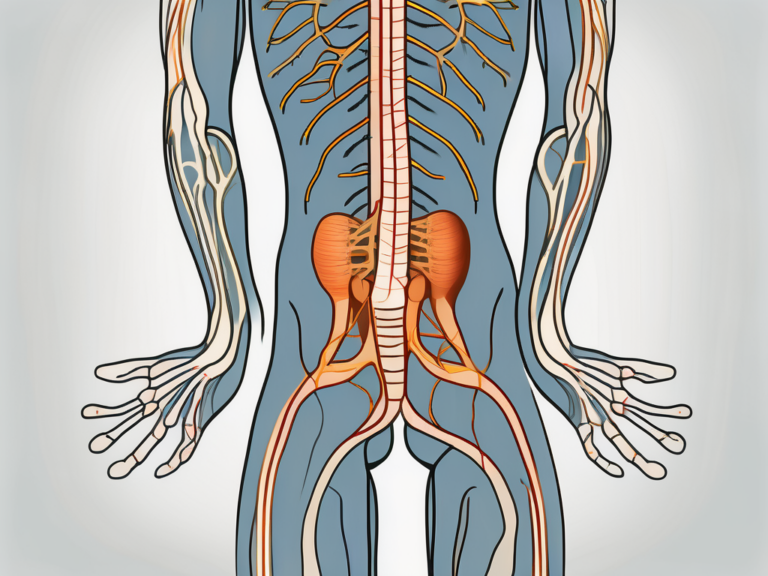
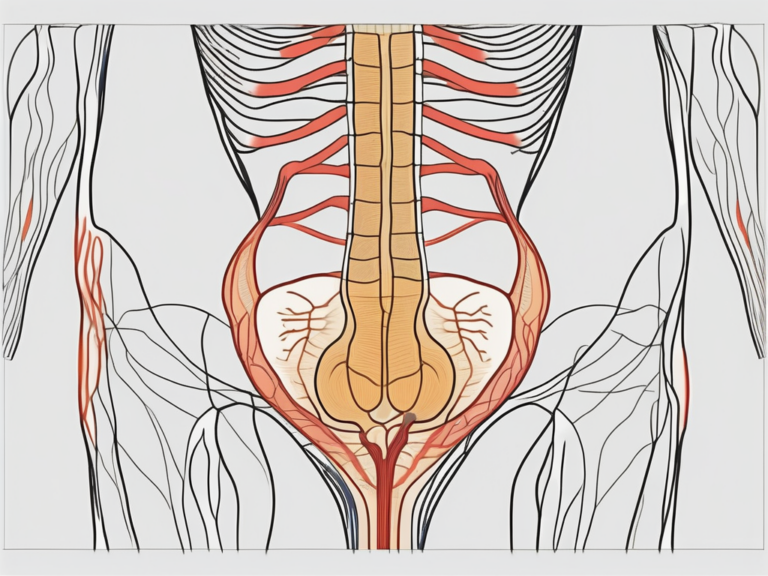
The sacral nerve is a major component of the peripheral nervous system, originating from the sacral plexus. It consists of five pairs of spinal nerves, S1 to S5, which branch out and innervate various structures in the pelvic region and lower limbs. These nerves play a vital role in transmitting motor signals to control muscle movements, as well as sensory signals for touch, temperature, and pain sensation.
The anatomy of the sacral nerve is fascinating. It is composed of a complex network of nerve fibers that extend from the spinal cord to the target organs and tissues. These fibers are responsible for carrying information between the brain and the lower body, allowing for seamless communication and coordination.
Each pair of spinal nerves within the sacral nerve has a specific function and innervates different areas of the body. For example, the S1 nerve supplies the skin on the outer side of the foot, while the S2 nerve innervates the back of the thigh and the buttocks. This intricate network ensures that every part of the lower body receives the necessary signals for proper functioning.
Role of the Sacral Nerve in the Body
The sacral nerve is responsible for coordinating functions such as walking, urinary and bowel control, sexual function, and sensation in the lower body. Without the sacral nerve, these essential bodily functions would be severely impaired, affecting one’s overall well-being and quality of life.
Walking, for instance, relies heavily on the sacral nerve’s ability to transmit motor signals to the muscles in the legs. These signals initiate a series of contractions and relaxations that allow for smooth and coordinated movements. Any disruption in the sacral nerve’s function can lead to difficulties in walking, such as weakness, imbalance, or even paralysis.
In addition to motor control, the sacral nerve also plays a crucial role in urinary and bowel control. It helps regulate the muscles of the bladder and the rectum, allowing for proper storage and elimination of waste. When the sacral nerve is damaged or compromised, individuals may experience issues such as urinary incontinence or difficulty controlling bowel movements.
Furthermore, the sacral nerve is involved in sexual function. It is responsible for transmitting sensory signals from the genital area to the brain, allowing for pleasurable sensations and sexual arousal. Dysfunction of the sacral nerve can lead to sexual dysfunction, including decreased sensation, erectile dysfunction, or difficulty achieving orgasm.
Overall, the sacral nerve is a vital component of the body’s nervous system, with its functions extending far beyond simple motor control. It is involved in various aspects of daily life, from walking and maintaining continence to sexual pleasure. Understanding the importance of the sacral nerve highlights the need for proper care and attention to maintain its health and functionality.
Common Causes of Sacral Nerve Damage
Injuries Leading to Sacral Nerve Damage
Accidents, falls, sports injuries, and other trauma to the lower back or pelvic region can result in sacral nerve damage. These injuries can cause compression, stretching, or severance of the nerve root, leading to disruptions in nerve conduction and functionality.
Accidents can occur in various settings, such as on the road, at home, or during sports activities. A car accident, for example, can cause a sudden impact to the lower back, leading to trauma to the sacral nerve. Similarly, a fall from a height can result in a direct blow to the pelvic region, causing damage to the nerve.
Sports injuries, especially those involving contact sports like football or rugby, can also contribute to sacral nerve damage. A hard tackle or collision can exert excessive force on the lower back or pelvic region, leading to nerve compression or stretching.
Diseases Affecting the Sacral Nerve
Certain medical conditions, such as herniated discs, spinal stenosis, tumors, infections, and autoimmune disorders, can contribute to sacral nerve damage. These conditions may exert pressure on the nerve, causing inflammation or direct damage to its structure.
Herniated discs, also known as slipped discs, occur when the soft inner core of a spinal disc protrudes through the tough outer layer. When a herniated disc affects the lower back, it can compress the sacral nerve roots, leading to pain and dysfunction.
Spinal stenosis is a condition characterized by the narrowing of the spinal canal, which can put pressure on the sacral nerve roots. This narrowing can be caused by age-related degeneration, spinal injuries, or abnormal growths.
Tumors, whether benign or malignant, can also affect the sacral nerve. As tumors grow, they can compress the nerve roots, leading to pain and other neurological symptoms.
Infections, such as meningitis or spinal abscesses, can cause inflammation in the spinal canal, affecting the sacral nerve. These infections can be caused by bacteria, viruses, or fungi, and if left untreated, can result in nerve damage.
Autoimmune disorders, such as multiple sclerosis or Guillain-Barré syndrome, can also impact the sacral nerve. In these conditions, the immune system mistakenly attacks the nerves, leading to inflammation and damage.
Symptoms Indicating Sacral Nerve Damage
Sacral nerve damage can have a variety of physical and emotional symptoms that can significantly impact an individual’s daily life. It is important to be aware of these symptoms in order to seek appropriate medical attention and support.
Physical Symptoms
Physical symptoms of sacral nerve damage may include pain or discomfort in the lower back, buttocks, hips, or legs. This pain can range from mild to severe and can be constant or intermittent. The sensation of pain can be described as sharp, shooting, or a dull ache.
In addition to pain, individuals with sacral nerve damage may experience weakness or numbness in the lower limbs. This can affect their ability to walk, stand, or perform daily activities that require lower body strength. Some individuals may also have difficulty maintaining balance, making them more prone to falls or accidents.
Changes in bladder or bowel control can also be indicative of sacral nerve damage. This can manifest as urinary incontinence, difficulty emptying the bladder completely, or bowel incontinence. These changes can be distressing and may require the use of assistive devices or modifications to daily routines.
It is important to remember that these symptoms can vary depending on the extent and location of the nerve damage. Some individuals may only experience a few of these symptoms, while others may have a combination of several.
Emotional and Cognitive Symptoms
Sacral nerve damage can also impact emotional and cognitive well-being. Individuals may experience anxiety, depression, mood swings, or difficulty concentrating. These symptoms can arise due to the challenges and limitations presented by the physical manifestations of sacral nerve damage.
Living with chronic pain and physical limitations can be emotionally taxing. It can lead to feelings of frustration, helplessness, or sadness. The inability to engage in activities that were once enjoyed can also contribute to a sense of loss or decreased self-esteem.
In addition to the emotional impact, sacral nerve damage can affect cognitive function. Difficulty concentrating, memory problems, or a decreased ability to process information may be experienced. These cognitive symptoms can further impact an individual’s quality of life and ability to perform daily tasks.
It is important for individuals experiencing these emotional and cognitive symptoms to seek support from healthcare professionals, such as therapists or counselors, who can provide guidance and coping strategies.
In conclusion, sacral nerve damage can present with a range of physical and emotional symptoms. It is crucial to recognize and address these symptoms in order to manage the condition effectively and improve overall well-being.
Diagnostic Procedures for Sacral Nerve Damage
Medical History and Physical Examination
When assessing sacral nerve damage, a healthcare professional will begin by gathering your medical history and conducting a thorough physical examination. This process is crucial in understanding the patient’s overall health and identifying any potential risk factors or underlying conditions that may contribute to sacral nerve damage.
During the physical examination, the healthcare professional will carefully assess various aspects of the patient’s nervous system. They may evaluate muscle strength by asking the patient to perform specific movements or exercises. Reflexes will also be tested, as they can provide valuable information about the integrity of the sacral nerves. Additionally, the healthcare professional will assess sensation by using various stimuli, such as light touch or pinpricks, to determine if there are any areas of decreased or heightened sensitivity.
Furthermore, the healthcare professional may perform certain maneuvers to assess nerve function. For example, they may test the patient’s ability to walk on their heels or toes, as well as their ability to balance. These tests can help identify any abnormalities or weaknesses that may be indicative of sacral nerve damage.
In addition to the physical examination, the healthcare professional will inquire about any known injuries, symptoms, or underlying medical conditions. This comprehensive medical history will provide valuable insights into the potential causes or contributing factors of the sacral nerve damage.
Imaging Tests for Sacral Nerve Damage
To further aid in the diagnosis, imaging tests such as X-rays, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), or computed tomography (CT) scans may be recommended. These tests can provide detailed images of the spine, allowing healthcare professionals to identify any potential abnormalities or structural issues that could be causing sacral nerve damage.
X-rays are commonly used to evaluate the bony structures of the spine. They can help identify fractures, tumors, or other abnormalities that may be compressing the sacral nerves. MRI and CT scans, on the other hand, provide more detailed images of the soft tissues, including the nerves, muscles, and ligaments. These imaging techniques can help detect herniated discs, spinal stenosis, or other conditions that may be affecting the sacral nerves.
During these imaging tests, the patient will be positioned on a table and moved into a machine that captures the necessary images. It is important for the patient to remain still during the procedure to ensure clear and accurate images. The images obtained from these tests will be carefully analyzed by healthcare professionals to determine the extent and location of any potential sacral nerve damage.
Electromyography and Nerve Conduction Studies
In some cases, electromyography (EMG) and nerve conduction studies (NCS) may be conducted to assess nerve integrity and function. These tests provide valuable information about the electrical activity and communication between the nerves and muscles.
During an EMG, the healthcare professional will insert tiny needles into specific muscles to evaluate muscle and nerve responses. The needles are connected to a machine that records the electrical activity produced by the muscles. This test can help identify any abnormalities in the muscle or nerve function, such as muscle weakness or nerve damage.
NCS, on the other hand, involves the administration of small electrical currents to measure the speed and efficiency of nerve signal transmission. Electrodes are placed on the skin overlying the nerves, and small electrical pulses are delivered. The healthcare professional then measures the time it takes for the nerve signals to travel between the electrodes. This test can help determine if there is any nerve damage or dysfunction.
Both EMG and NCS are typically performed together to provide a comprehensive assessment of the sacral nerves. These tests are safe and generally well-tolerated, although some patients may experience mild discomfort during the needle insertion or electrical stimulation.
By utilizing these diagnostic procedures, healthcare professionals can gather valuable information about the sacral nerve damage and develop an appropriate treatment plan tailored to the patient’s specific needs.
Treatment Options for Sacral Nerve Damage
Sacral nerve damage can cause significant discomfort and impair daily activities. Fortunately, there are various treatment options available to manage this condition. Non-surgical treatments are often the first line of intervention, while surgical treatments may be considered in more severe cases.
Non-Surgical Treatments
Non-surgical treatments play a crucial role in managing sacral nerve damage. These interventions aim to alleviate symptoms and improve overall quality of life. One common non-surgical approach is the use of medications to manage pain and inflammation. Depending on the severity of the nerve damage, healthcare professionals may prescribe nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), muscle relaxants, or even opioids to help alleviate discomfort.
In addition to medications, physical therapy is often recommended to improve muscle strength and mobility. Physical therapists can design personalized exercise programs that target the affected areas, helping to restore function and reduce pain. These exercises may include stretching, strengthening, and balance exercises, as well as techniques like electrical stimulation or ultrasound therapy.
Assistive devices can also be beneficial for individuals with sacral nerve damage. Devices such as canes, walkers, or specialized cushions can provide support and stability during walking or sitting, reducing pressure on the affected nerves. Healthcare professionals can assess the specific needs of each patient and recommend the most suitable assistive devices.
Lifestyle modifications can further complement non-surgical treatments. These modifications may include avoiding activities that exacerbate symptoms, maintaining a healthy weight to reduce pressure on the nerves, and practicing good posture to minimize strain on the affected areas. Additionally, alternative therapies like acupuncture or chiropractic care may be explored as adjunct treatments, although their effectiveness may vary from person to person.
It is crucial to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the most suitable treatment approach based on individual circumstances. They can assess the severity of the nerve damage, consider any underlying conditions, and tailor a comprehensive treatment plan that addresses the specific needs of each patient.
Surgical Treatments
In cases where conservative treatments do not provide sufficient relief or when nerve compression requires surgical intervention, various surgical options may be considered. Surgical treatments aim to alleviate pressure on the affected nerves, repair damaged nerves, or restore nerve function.
One common surgical procedure for sacral nerve damage is decompressive surgery. This procedure involves removing any structures or tissues that are compressing the nerves, such as herniated discs or bone spurs. By relieving the pressure on the nerves, decompressive surgery can help reduce pain and improve function.
In more severe cases, nerve grafting may be necessary. Nerve grafting involves taking a healthy nerve from another part of the body and using it to repair the damaged nerve. This technique can help restore nerve function and promote healing.
In extreme cases, nerve stimulation techniques or nerve repair surgeries may be considered. Nerve stimulation techniques, such as spinal cord stimulation or peripheral nerve stimulation, involve implanting devices that deliver electrical impulses to the affected nerves. These impulses can help block pain signals and provide relief. Nerve repair surgeries, on the other hand, aim to directly repair the damaged nerves, either by reconnecting severed nerve ends or by using grafts to bridge the gap.
It is important to note that surgical treatments for sacral nerve damage are typically reserved for cases where conservative treatments have failed to provide sufficient relief. A healthcare professional can evaluate the specific situation and recommend the most appropriate surgical approach if necessary.
Prevention and Management of Sacral Nerve Damage
Lifestyle Changes for Sacral Nerve Health
Adopting a healthy lifestyle can help reduce the risk of sacral nerve damage and promote overall nerve health. Maintaining a balanced diet rich in nutrients, engaging in regular exercise, practicing good posture, and avoiding smoking or excessive alcohol consumption are essential for maintaining the health of your nerves and preventing damage.
Physical Therapy and Exercises
Physical therapy and targeted exercises can be highly beneficial for individuals with sacral nerve damage. A qualified physical therapist can design a personalized program to improve strength, flexibility, and coordination, as well as mitigate pain and enhance functional capabilities. These exercises can also help manage symptoms and enhance overall well-being.
Living with Sacral Nerve Damage
Coping Mechanisms and Support
Living with sacral nerve damage can pose significant physical and emotional challenges. It is important for individuals to seek emotional support from loved ones, join support groups, or consider counseling to manage any psychological effects. Exploring coping mechanisms such as relaxation techniques, mindfulness, or engaging in activities that bring joy and fulfillment can also contribute to a better quality of life.
Long-Term Prognosis and Quality of Life
The long-term prognosis and quality of life for individuals with sacral nerve damage can vary depending on the extent of the damage, underlying causes, and effective management strategies. While some individuals may experience significant improvements with appropriate treatment and lifestyle modifications, others may require continued care and adaptive measures to maintain independence and well-being. Regular follow-up with healthcare professionals and adherence to recommended treatments can help optimize long-term outcomes.
Conclusion
Determining if your sacral nerve is damaged requires a comprehensive evaluation by a healthcare professional. Understanding the functions, causes, symptoms, and treatment options associated with sacral nerve damage can equip individuals with knowledge to seek appropriate medical guidance. While it is important to be proactive in taking care of our health, it is equally crucial to consult with healthcare professionals for accurate diagnosis, personalized advice, and a suitable treatment plan that aligns with individual needs. By identifying and addressing sacral nerve damage promptly, individuals can enhance their overall well-being and maintain a fulfilling and active lifestyle.