How Is Sacral Nerve Stimulation Surgery Placed?
Sacral nerve stimulation surgery is a procedure that can provide relief for individuals suffering from certain bladder and bowel control disorders. This type of surgery involves the placement of a neurostimulator device that helps regulate the communication between the brain and the sacral nerves. If you or someone you know is considering this surgery, it is important to understand the process involved and what to expect. In this article, we will explore the different stages of sacral nerve stimulation surgery and provide insights into its effectiveness and potential risks.
Understanding Sacral Nerve Stimulation
Before diving into the details of the surgery itself, it is essential to have a basic understanding of how sacral nerve stimulation works. The sacral nerves play a crucial role in the body, transmitting signals between the brain and the bladder or bowel muscles. When these nerves are not functioning properly, it can lead to issues such as urinary or fecal incontinence. Sacral nerve stimulation aims to regulate these signals by implanting a neurostimulator device that delivers mild electrical pulses to the sacral nerves, helping restore normal communication and control.
The concept of nerve stimulation is not new and has been used for various medical purposes for many years. By targeting specific nerves with electrical impulses, healthcare providers can treat several conditions and improve patients’ quality of life significantly.
When it comes to sacral nerve stimulation, the procedure involves several steps. First, a thorough evaluation is conducted to determine if the patient is a suitable candidate for the surgery. This evaluation includes a detailed medical history review, physical examination, and various diagnostic tests to assess the severity of the condition and identify any underlying causes.
Once the patient is deemed eligible for sacral nerve stimulation, the surgical procedure can be scheduled. The surgery is typically performed under general anesthesia, ensuring that the patient remains comfortable and pain-free throughout the procedure.
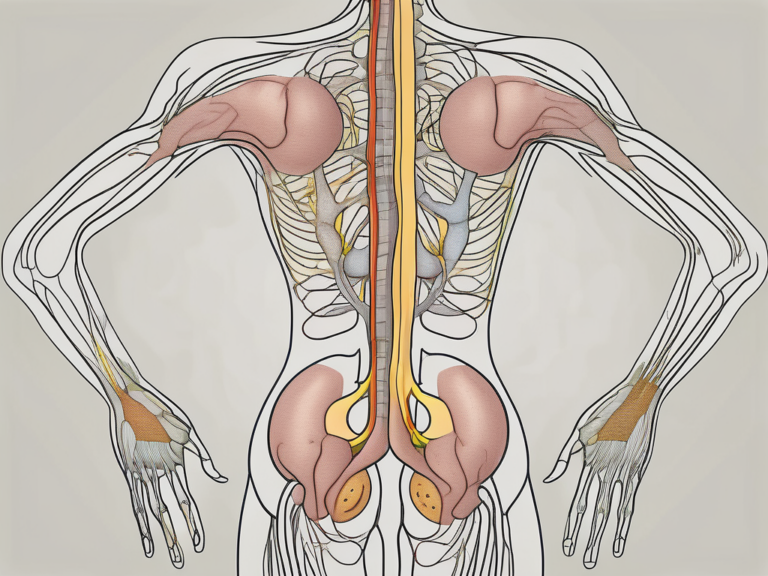
During the surgery, a small incision is made in the lower back to access the sacral nerves. The neurostimulator device, which is about the size of a stopwatch, is then implanted under the skin. The device is connected to thin wires, called leads, which are carefully placed near the sacral nerves. These leads will deliver the electrical pulses to the nerves, helping to regulate their activity.
After the surgery, patients are usually monitored closely to ensure that the device is functioning correctly and that there are no complications. The neurostimulator device can be adjusted and programmed to deliver the appropriate level of electrical stimulation for each patient’s specific needs. This customization allows healthcare providers to optimize the treatment and achieve the best possible outcomes.
It is important to note that sacral nerve stimulation is not a cure for the underlying condition but rather a management technique. While it can significantly improve symptoms and quality of life, ongoing follow-up appointments and adjustments may be necessary to maintain the desired results.
In conclusion, sacral nerve stimulation is a valuable treatment option for individuals experiencing urinary or fecal incontinence due to sacral nerve dysfunction. By understanding the basics of how this procedure works and the steps involved, patients can make informed decisions about their healthcare and potentially find relief from their symptoms.
Preparing for Sacral Nerve Stimulation Surgery
Before undergoing sacral nerve stimulation surgery, patients will go through a series of preparatory steps to ensure their safety and optimize the procedure’s success. The initial stage involves a pre-surgery consultation and evaluation with a healthcare professional experienced in this type of surgery. During this consultation, the doctor will assess the patient’s medical history, symptoms, and previous treatments. It is crucial to provide accurate and detailed information to help the healthcare team make the best decisions regarding the surgery.
During the pre-surgery consultation, the healthcare professional will also discuss the benefits and potential risks of sacral nerve stimulation surgery. They will explain how the procedure works and what to expect during the recovery period. This detailed discussion aims to ensure that the patient fully understands the procedure and can make an informed decision about moving forward.
Following the consultation, necessary preoperative tests will be ordered to evaluate the patient’s overall health condition. These tests may include blood work, urine tests, and imaging studies. Blood work helps assess the patient’s blood cell counts, liver and kidney function, and overall health status. Urine tests can detect any underlying urinary tract infections or abnormalities. Imaging studies, such as X-rays or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), may be performed to visualize the sacral nerve area and identify any potential anatomical variations or abnormalities.
In addition to these routine tests, patients may also undergo specialized evaluations to further assess their suitability for sacral nerve stimulation surgery. This may involve urodynamic testing, which evaluates the bladder’s function and capacity, as well as the coordination between the bladder and the sphincter muscles. Urodynamic testing helps determine if the patient’s symptoms are consistent with overactive bladder or other related conditions that may benefit from sacral nerve stimulation.
The results of these tests will help determine if the patient is a suitable candidate for sacral nerve stimulation surgery and identify any additional considerations to ensure a safe procedure. The healthcare team will review the test results in conjunction with the patient’s medical history and symptoms to make an individualized treatment plan. This plan may include specific recommendations for medication adjustments, lifestyle modifications, or additional treatments to optimize the outcome of the surgery.
Once all the necessary evaluations and tests are completed, the patient will be provided with detailed instructions on how to prepare for the surgery. This may include guidelines on fasting before the procedure, discontinuing certain medications, and arranging for transportation to and from the hospital. It is important for patients to follow these instructions carefully to minimize any potential risks and ensure a smooth surgical experience.
The Procedure of Sacral Nerve Stimulation Surgery
On the day of the surgery, the patient will be prepared for the procedure, which typically involves anesthesia and patient positioning. Depending on the specific case, either general anesthesia or local anesthesia with sedation may be used. The healthcare team will discuss the most appropriate option for each patient.
Once the patient is comfortably anesthetized, the surgeon will begin implanting the neurostimulator device. This device is usually placed under the skin of the buttock or lower abdominal area, where it can deliver the electrical impulses to the sacral nerves. The procedure is carried out using minimally invasive techniques, resulting in smaller incisions and reduced scarring.
In addition to the neurostimulator, a lead or wire will be placed near the sacral nerves to transmit the electrical pulses. The lead is carefully positioned using fluoroscopy or X-ray guidance to ensure accuracy. The surgeon takes great care to place the lead in the optimal position to achieve the desired outcomes.
Before the surgery begins, the patient’s medical history is thoroughly reviewed to ensure that they are a suitable candidate for sacral nerve stimulation surgery. This includes evaluating the patient’s symptoms, previous treatments, and any underlying medical conditions that may affect the success of the procedure.
During the surgery, the healthcare team closely monitors the patient’s vital signs, such as heart rate, blood pressure, and oxygen levels, to ensure their safety and well-being. Advanced monitoring equipment is used to provide real-time data to the surgical team, allowing them to make any necessary adjustments during the procedure.
Once the neurostimulator device and lead are in place, the surgeon tests the system to ensure proper functioning. This involves activating the electrical pulses and assessing the patient’s response. The patient may be asked to provide feedback on the sensations they experience, helping the surgeon fine-tune the settings for optimal symptom relief.
After the surgery, the patient is closely monitored in a recovery area to ensure they are stable and comfortable. Pain medication may be administered to manage any discomfort. The healthcare team provides instructions on post-operative care, including wound care, activity restrictions, and follow-up appointments.
Over time, the patient may need to have the neurostimulator device adjusted or reprogrammed to maintain optimal symptom control. This can be done during outpatient visits, where the healthcare team works closely with the patient to fine-tune the settings and address any concerns or questions they may have.
Sacral nerve stimulation surgery has been shown to be an effective treatment option for various conditions, such as overactive bladder, urinary incontinence, and fecal incontinence. It offers many patients a chance to regain control over their bodily functions and improve their quality of life.
Post-Operative Care and Recovery
After the surgery, patients will be closely monitored, and specific post-operative care instructions will be provided. Immediate post-surgery care may include pain management, wound care, and activity restrictions to promote proper healing. It is essential to follow these instructions diligently to minimize the risk of complications and optimize the recovery process.
During the immediate post-operative period, patients may experience some discomfort or pain at the surgical site. This is normal and can be managed effectively with the prescribed pain medication. The healthcare team will closely monitor the patient’s pain levels and adjust the medication as needed to ensure maximum comfort.
In addition to pain management, wound care is crucial for the proper healing of the surgical incision. Patients will receive detailed instructions on how to clean and dress the wound to prevent infection and promote optimal healing. It is important to follow these instructions carefully and report any signs of infection, such as increased redness, swelling, or drainage, to the healthcare provider immediately.
Activity restrictions are another essential aspect of post-operative care. Patients will be advised to avoid strenuous activities, heavy lifting, or any movements that may strain the surgical area. These restrictions are put in place to allow the body to heal without any undue stress or pressure. It is important to adhere to these restrictions to prevent complications and ensure a successful recovery.
Long-term care and maintenance are also essential for the effectiveness of sacral nerve stimulation surgery. This procedure involves the implantation of a neurostimulator device, which helps regulate nerve signals and improve symptoms. Regular follow-up appointments with the healthcare provider are necessary to monitor the functionality of the device and ensure its optimal performance.
During these follow-up visits, the doctor will assess the patient’s symptoms and evaluate the effectiveness of the neurostimulator device. They may need to make adjustments to the programming settings to achieve the best possible outcome. The healthcare provider will also address any concerns or questions the patient may have, providing guidance and support throughout the recovery process.
Furthermore, the healthcare team will educate the patient on self-care techniques and strategies to manage their condition effectively. This may include lifestyle modifications, such as dietary changes or exercises, to complement the effects of the sacral nerve stimulation surgery. By actively participating in their own care, patients can optimize the long-term benefits of the procedure and maintain a good quality of life.
It is important for patients to communicate openly with their healthcare provider, reporting any changes in symptoms or concerns that may arise. By maintaining a strong partnership with the healthcare team, patients can receive the necessary support and guidance to navigate the recovery process successfully.
Potential Risks and Complications
As with any surgical procedure, sacral nerve stimulation surgery carries certain risks and potential complications. However, it is worth noting that serious complications are rare, and the majority of patients benefit greatly from this treatment option. Common side effects may include temporary pain, swelling, or discomfort at the incision site, which usually subside over time.
In rare cases, more serious complications can occur, such as infection, bleeding, or device-related issues. It is essential to be aware of the warning signs of these complications and promptly seek medical attention if they arise. Your healthcare provider will provide comprehensive information regarding these risks and will closely monitor your progress to minimize their occurrence.
One potential risk of sacral nerve stimulation surgery is infection. While the risk is low, it is important to take precautions to prevent infection. Your surgeon will provide you with detailed instructions on how to care for the incision site and keep it clean. Additionally, you may be prescribed antibiotics to reduce the risk of infection. It is crucial to follow these instructions diligently to minimize the chances of developing an infection.
Bleeding is another possible complication that can occur after sacral nerve stimulation surgery. Although uncommon, it is important to be aware of the signs of excessive bleeding, such as persistent or increasing pain, swelling, or redness at the incision site. If you experience any of these symptoms, it is crucial to contact your healthcare provider immediately. They will assess the situation and provide appropriate treatment to address the bleeding.
Device-related issues are also a potential concern with sacral nerve stimulation surgery. The implanted device may malfunction or fail over time. It is important to regularly follow up with your healthcare provider to ensure that the device is functioning properly. They will conduct routine checks and make any necessary adjustments or replacements to maintain the effectiveness of the treatment.
While the risks and complications associated with sacral nerve stimulation surgery are relatively rare, it is essential to be informed and prepared. Your healthcare provider will thoroughly discuss these potential risks with you before the procedure, ensuring that you have a clear understanding of what to expect. By closely following their guidance and promptly reporting any concerns, you can minimize the likelihood of experiencing complications and maximize the benefits of this treatment option.
The Effectiveness of Sacral Nerve Stimulation Surgery
Sacral nerve stimulation surgery has shown significant effectiveness in improving the symptoms associated with bladder and bowel control disorders. Expected outcomes vary depending on the individual case, but many patients experience a noticeable reduction in urinary or fecal incontinence, improved bladder or bowel control, and enhanced quality of life.
Factors affecting the effectiveness of the surgery include the underlying condition, overall health, and individual response to the neurostimulator device. It is important to have realistic expectations and understand that sacral nerve stimulation surgery may not provide a complete cure, but rather a significant improvement in symptoms.
Frequently Asked Questions about Sacral Nerve Stimulation Surgery
To address common queries about sacral nerve stimulation surgery, let’s answer a few frequently asked questions:
Can the Procedure be Reversed?
Sacral nerve stimulation surgery is generally considered reversible. If, for any reason, the patient decides to discontinue the treatment, the neurostimulator device can be explanted surgically. However, it is essential to consult with a healthcare professional before making any decisions regarding the reversal of the procedure.
How Long Does the Battery Last?
The battery life of a sacral nerve stimulation device varies depending on factors such as device type, settings, and individual usage. Typically, the battery can last several years before requiring replacement. During routine follow-up visits, the healthcare provider will monitor the battery’s status and inform the patient when it is time for a replacement.
In conclusion, sacral nerve stimulation surgery is a valuable treatment option for bladder and bowel control disorders. By understanding the process and what to expect, patients can make informed decisions and approach their surgery with confidence. If you or a loved one is considering this procedure, it is crucial to consult with a healthcare professional experienced in sacral nerve stimulation surgery. They can provide personalized guidance and ensure the best possible outcomes.