How Does Sacral Nerve Stimulation Work for Urinary Issues?
Sacral nerve stimulation is a medical procedure that has been proven effective for managing urinary issues such as urinary incontinence and overactive bladder. By understanding how sacral nerve stimulation works, individuals can make informed decisions about their treatment options. In this article, we will explore the science behind sacral nerve stimulation, the process involved, its benefits, potential risks, candidate suitability, and the life after undergoing this procedure.
Understanding Sacral Nerve Stimulation
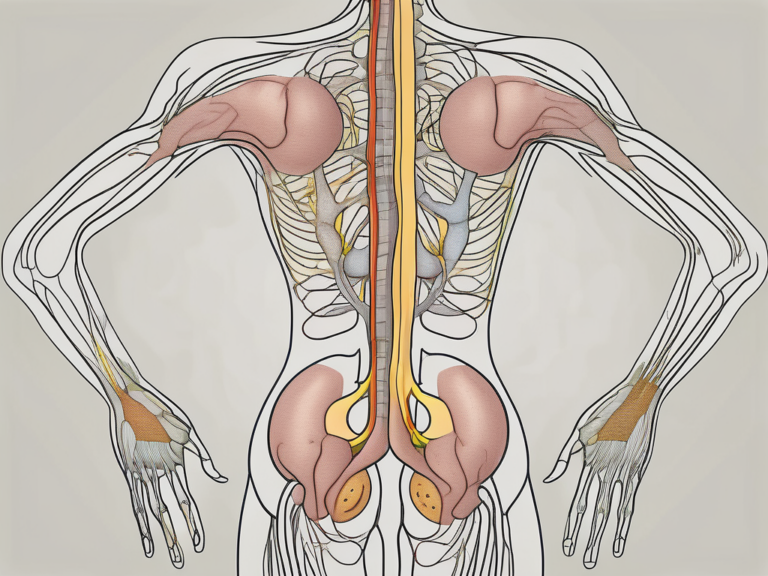
Sacral nerve stimulation, also known as sacral neuromodulation, is a minimally invasive procedure that involves the implantation of a small device called a neurostimulator. This device delivers mild electrical impulses to the sacral nerves, which play a crucial role in urinary function and control.
The Science Behind Sacral Nerve Stimulation
The sacral nerves are a set of nerves that innervate the pelvic region, including the bladder and surrounding muscles. These nerves control the sensation of bladder fullness, bladder contraction, and the relaxation of the muscles that control urine flow. When there is a dysfunction in these nerves, it can lead to urinary issues.
Sacral nerve stimulation works by modulating and restoring the normal functioning of these nerves. The electrical impulses generated by the neurostimulator help to regulate the signals between the bladder and brain, resulting in improved urinary control and a reduction in urinary urgency and frequency.
The Role of Sacral Nerves in Urinary Function
The sacral nerves transmit signals between the bladder, spinal cord, and brain. When the bladder is full, the nerves send signals to the brain, indicating the need for urination. In response, the brain sends signals back to the bladder to initiate the appropriate muscle contractions and relaxation for urine expulsion.
However, in individuals with urinary issues, such as overactive bladder or urinary incontinence, these signals can become disrupted. Sacral nerve stimulation aims to restore the normal communication between the bladder and brain, allowing for better coordination and control over urinary function.
It is important to note that sacral nerve stimulation is not the first-line treatment for urinary issues. Before considering this procedure, patients typically undergo a thorough evaluation, which may include urodynamic testing and other diagnostic procedures, to determine the underlying cause of their symptoms.
Once a patient is deemed a suitable candidate for sacral nerve stimulation, the procedure can be performed on an outpatient basis under local anesthesia. A small incision is made in the lower back, and the neurostimulator is implanted near the sacral nerves. The device is then programmed to deliver electrical impulses at specific frequencies and intensities, tailored to the individual’s needs.
After the procedure, patients may experience some discomfort or soreness at the implantation site, but this typically resolves within a few days. It may take several weeks for the full effects of sacral nerve stimulation to be realized, as the nerves and muscles need time to adjust to the therapy.
In addition to its use in urinary issues, sacral nerve stimulation has also shown promise in the treatment of other conditions, such as fecal incontinence and chronic pelvic pain. Ongoing research is exploring the potential benefits of this therapy in various patient populations.
Overall, sacral nerve stimulation offers a valuable treatment option for individuals with urinary issues that have not responded to conservative therapies. By restoring the normal functioning of the sacral nerves, this procedure can significantly improve quality of life and reduce the burden of urinary symptoms.
The Process of Sacral Nerve Stimulation
The process of sacral nerve stimulation involves several steps, beginning with the evaluation and preparation of the patient.
Preparing for Sacral Nerve Stimulation
Prior to the procedure, a comprehensive evaluation is conducted by a healthcare professional specializing in urinary disorders. This evaluation typically includes a thorough medical history review, physical examination, and urodynamic testing to assess the function of the bladder and urinary sphincter.
During the medical history review, the healthcare professional will ask the patient about their symptoms, previous treatments, and any underlying medical conditions. This information helps in determining the suitability of sacral nerve stimulation as a treatment option.
In the physical examination, the healthcare professional may perform a pelvic exam to assess the condition of the pelvic floor muscles and check for any abnormalities. They may also conduct a neurological examination to evaluate the function of the nerves in the pelvic region.
Urodynamic testing is a series of diagnostic tests that measure the pressure and flow of urine in the bladder. These tests provide valuable information about the bladder’s capacity, muscle function, and ability to store and empty urine properly.
Based on the evaluation results, the healthcare professional will determine if sacral nerve stimulation is an appropriate treatment option. It is important to note that not all individuals may be suitable candidates for this procedure. Factors such as the severity of symptoms, previous treatments, and overall health condition play a role in the decision-making process.
The Procedure of Sacral Nerve Stimulation
The actual procedure for sacral nerve stimulation involves the surgical placement of the neurostimulator device. This is typically done in two stages: the trial phase and the permanent implantation phase.
During the trial phase, a temporary lead wire is inserted near the sacral nerves, which is then connected to an external neurostimulator device. The patient is allowed to go about their daily activities with the external device for a trial period of approximately one to two weeks. This trial period serves as an opportunity to assess the effectiveness of the treatment before committing to the permanent implantation.
Throughout the trial phase, the patient may be asked to keep a diary to track their urinary symptoms and any changes they experience. This information helps the healthcare professional evaluate the impact of sacral nerve stimulation on the patient’s quality of life and overall well-being.
If the trial phase is successful and significant improvement in urinary symptoms is observed, the patient may proceed with the permanent implantation. In this stage, the temporary lead wire is replaced with a permanent lead wire, and the neurostimulator device is implanted under the skin, usually in the buttock area. The lead wire is then connected to the neurostimulator, completing the setup.
After the permanent implantation, the patient will undergo a period of recovery and adjustment. The healthcare professional will provide detailed instructions on how to care for the incision site, manage any discomfort, and gradually increase the stimulation settings to achieve optimal results.
Regular follow-up appointments will be scheduled to monitor the patient’s progress, make any necessary adjustments to the stimulation settings, and address any concerns or questions that may arise.
It is important to note that sacral nerve stimulation is not a cure for urinary disorders, but rather a management option that can significantly improve symptoms and enhance the patient’s quality of life. The long-term success of the treatment depends on various factors, including individual response, adherence to recommended lifestyle modifications, and ongoing medical care.
Benefits of Sacral Nerve Stimulation for Urinary Issues
Sacral nerve stimulation has shown promising benefits for individuals with urinary issues, providing notable improvements in urinary control and quality of life.
Improvement in Urinary Control
One of the primary benefits of sacral nerve stimulation is the improvement in urinary control. Many individuals experience a significant reduction in urinary incontinence episodes, allowing them to regain control over their bladder function and leading to increased confidence and freedom in daily activities.
Imagine being able to participate in social gatherings or physical activities without constantly worrying about leakage or the need to rush to the bathroom. With sacral nerve stimulation, individuals can experience a newfound sense of freedom and independence.
Research studies have shown that sacral nerve stimulation can lead to a 50% or more reduction in urinary incontinence episodes. This means fewer embarrassing moments and a greater ability to engage in activities that were once limited by urinary issues.
It is essential to note that the degree of improvement may vary among individuals and that not everyone may achieve complete resolution of their urinary issues. Consulting with a healthcare professional specializing in urinary disorders is advised to determine individual expectations and potential outcomes.
Reduction in Urinary Urgency and Frequency
Another benefit of sacral nerve stimulation is the reduction in urinary urgency and frequency. Individuals with overactive bladder often experience a frequent urge to urinate, which can disrupt daily routines and quality of life.
Imagine constantly feeling the need to rush to the bathroom, even when your bladder is not full. This can be incredibly frustrating and can significantly impact your ability to focus on tasks or enjoy your day-to-day activities.
Through the modulation of sacral nerves, the electrical impulses generated by the neurostimulator help to normalize bladder signals and decrease the frequency of urinary urgency. This reduction in urinary urgency and frequency allows individuals to better plan their activities, reducing the need for frequent bathroom visits and improving their overall well-being.
Studies have shown that sacral nerve stimulation can lead to a significant decrease in urinary urgency and frequency, with some individuals experiencing a 75% or more reduction in these symptoms. This means fewer interruptions, improved sleep quality, and a greater ability to engage in activities without the constant worry of needing to find a restroom.
Furthermore, the reduction in urinary urgency and frequency can have a positive impact on mental health. Many individuals with overactive bladder often experience anxiety and stress due to their constant need to be near a bathroom. By alleviating these symptoms, sacral nerve stimulation can contribute to a better overall quality of life.
Potential Risks and Side Effects of Sacral Nerve Stimulation
Like any medical procedure, sacral nerve stimulation carries potential risks and side effects that individuals should be aware of. It is vital to have a thorough discussion with a healthcare professional to understand these risks and evaluate them against the potential benefits.
Sacral nerve stimulation is a minimally invasive procedure that involves the implantation of a neurostimulator device to help manage certain conditions, such as overactive bladder or fecal incontinence. While it can provide significant relief for many patients, it is important to be informed about the possible side effects and complications that may arise.
Common Side Effects
Common side effects associated with sacral nerve stimulation include mild discomfort or pain at the implantation site, infection, and temporary changes in bladder or bowel function. These side effects are generally temporary and resolve as the body adjusts to the neurostimulator.
The mild discomfort or pain at the implantation site can be managed with over-the-counter pain medications and usually subsides within a few days. Infection is a potential risk with any surgical procedure, but with proper care and hygiene, the risk can be minimized. Temporary changes in bladder or bowel function may occur as the nerves and muscles adapt to the stimulation, but these changes typically improve over time.
If persistent or concerning side effects occur, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional for further evaluation and management. They can provide guidance on how to alleviate discomfort or address any issues that may arise during the adjustment period.
Serious Complications and How to Manage Them
While rare, serious complications can occur with sacral nerve stimulation. These include lead migration or breakage, nerve damage, and infection around the implantation site.
Lead migration or breakage can happen if the implanted wires move out of position or become damaged. This can result in a loss of stimulation or discomfort. If any unusual sensations or changes in symptoms are experienced, it is important to contact a healthcare professional for evaluation. They may need to adjust the positioning of the leads or replace them if necessary.
Nerve damage is another potential complication, although it is rare. Symptoms of nerve damage may include persistent pain, weakness, or numbness. If any of these symptoms occur, it is crucial to seek immediate medical attention. Early intervention can help prevent further damage and improve the chances of a successful outcome.
Infection around the implantation site is a serious complication that requires prompt medical attention. Signs of infection may include redness, swelling, increased pain, or fever. If any of these symptoms are present, it is essential to contact a healthcare professional immediately. They will evaluate the situation and provide appropriate treatment, which may include antibiotics or, in severe cases, removal of the neurostimulator.
It is important to note that while these complications are possible, they are relatively rare. The majority of patients who undergo sacral nerve stimulation experience significant improvement in their symptoms with minimal side effects. However, being aware of the potential risks and knowing how to manage them is crucial for a successful treatment journey.
Who is a Suitable Candidate for Sacral Nerve Stimulation?
The suitability for sacral nerve stimulation is determined on an individual basis, taking into consideration several factors.
Criteria for Sacral Nerve Stimulation
Candidates for sacral nerve stimulation typically include individuals who have not responded to conservative treatments such as lifestyle modifications, pelvic floor exercises, and medications. They may also have a diagnosis of urinary incontinence or overactive bladder with symptoms that significantly impact their quality of life.
It is necessary to have a comprehensive evaluation by a healthcare professional specializing in urinary disorders to determine if sacral nerve stimulation is a suitable treatment option.
Contraindications for Sacral Nerve Stimulation
While sacral nerve stimulation can be highly effective for many individuals, there are certain contraindications that may exclude someone as a candidate for this treatment. These may include individuals with a pacemaker or other implanted electrical devices, an active urinary tract infection, an inability to properly operate the neurostimulator device, or a previous unsuccessful trial of sacral nerve stimulation.
Consulting with a healthcare professional specializing in urinary disorders is paramount in determining if sacral nerve stimulation is right for an individual.
Life After Sacral Nerve Stimulation
After undergoing sacral nerve stimulation, it is important to understand the necessary post-procedure care and what to expect in terms of long-term outcomes and improvements in quality of life.
Post-Procedure Care and Maintenance
Following the procedure, there will be specific guidelines provided by the healthcare professional regarding post-procedure care and maintenance. This may include avoiding excessive physical activities, keeping the incision site clean and dry, and regular follow-up appointments to monitor progress and make any necessary adjustments to the neurostimulator settings.
It is crucial to adhere to these guidelines and promptly report any concerns or issues to the healthcare professional responsible for the sacral nerve stimulation management.
Long-Term Outcomes and Quality of Life Improvements
For many individuals, sacral nerve stimulation can result in significant improvements in quality of life, including reduced urinary symptoms, increased confidence, and the ability to participate in daily activities without the constant worry of urinary issues. However, it is important to have realistic expectations and understand that the degree of improvement may vary among individuals.
Long-term outcomes of sacral nerve stimulation can vary, and some individuals may require ongoing adjustments to the neurostimulator settings or additional treatments to maintain optimal results. Regular follow-up appointments with the healthcare professional managing the sacral nerve stimulation are advised to monitor progress and ensure the best possible outcome.
In conclusion, sacral nerve stimulation offers a viable option for individuals experiencing urinary issues such as urinary incontinence or overactive bladder. By stimulating the sacral nerves, this procedure helps to restore and improve urinary control and reduce urgency and frequency. With careful evaluation and management by a healthcare professional specializing in urinary disorders, individuals can determine if sacral nerve stimulation is a suitable treatment option for their specific needs. It is important to engage in an open and informed discussion with a healthcare professional to fully understand the potential benefits, risks, and expected outcomes of this treatment. Through appropriate guidance and regular follow-up care, individuals can experience improved quality of life and regain control over their urinary function.