How Can the Sacral Nerve Get Inflamed: Causes and Treatment Options
The sacral nerve, also known as the sacral plexus, is an important part of the nervous system that plays a crucial role in transmitting signals between the spinal cord and the lower body. When this nerve becomes inflamed, it can cause a range of symptoms and discomfort. Understanding the causes of sacral nerve inflammation and the available treatment options is essential for managing this condition effectively.
Understanding the Sacral Nerve
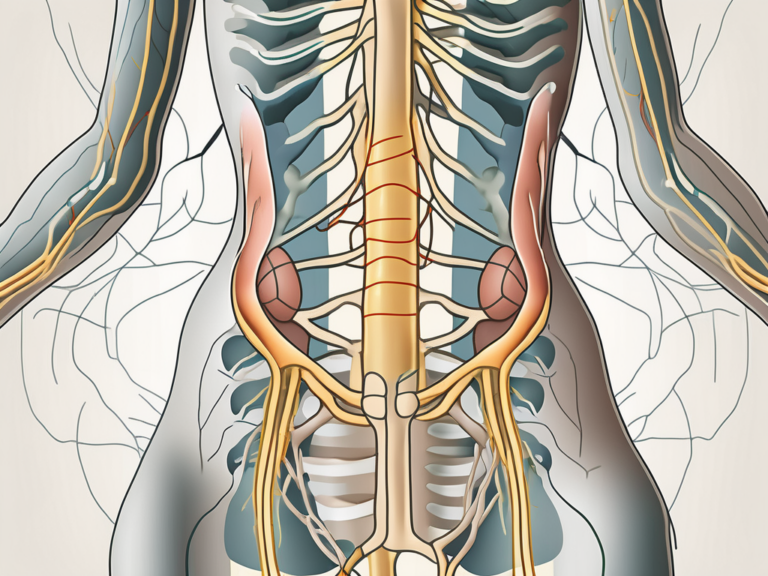
The sacral nerve is a complex network of nerves that originates from the lower spinal cord. It serves as a vital link between the central nervous system and the pelvic organs, lower limbs, and external genitalia. Comprised of five pairs of spinal nerves (S1-S5), the sacral nerve innervates various muscles and provides sensory input to different areas of the body.
The sacral nerve, although often overlooked, plays a crucial role in our daily lives. Without it, simple tasks such as walking, standing, and even controlling our bladder and bowel functions would be impossible. Let’s take a closer look at the anatomy and function of this remarkable nerve.
Anatomy of the Sacral Nerve
The sacral nerve consists of both motor and sensory fibers. The motor fibers control the movement of muscles in the lower body, such as those involved in walking, standing, and bowel and bladder function. These fibers act as the command center, sending signals from the brain to the muscles, allowing us to perform various movements effortlessly.
On the other hand, the sensory fibers transmit information from the pelvic organs, lower limbs, and external genitalia back to the brain, allowing us to perceive touch, pain, and temperature changes. Imagine a world without the ability to feel the warmth of a gentle touch or the pain of an injury. It is the sacral nerve that enables us to experience these sensations and navigate the world around us.
Function of the Sacral Nerve
The sacral nerve coordinates a variety of essential bodily functions, including bladder and bowel control, sexual function, and movement in the lower extremities. It is responsible for the contraction of the bladder muscles, the relaxation of the urinary sphincter, and the coordination of the muscles involved in sexual intercourse.
Additionally, the sacral nerve enables the proper coordination of movements in the lower limbs, allowing us to walk, run, and engage in various physical activities. Without the sacral nerve, our lower limbs would be rendered immobile, leaving us confined to a sedentary lifestyle.
It is important to note that the sacral nerve does not work in isolation. It is part of a larger network of nerves that make up the peripheral nervous system, working in harmony with other nerves to ensure the smooth functioning of our bodies.
In conclusion, the sacral nerve is a remarkable part of our anatomy, often underappreciated for its role in our daily lives. From enabling us to walk and move freely to controlling our bladder and bowel functions, the sacral nerve is an essential component of our overall well-being. Understanding its anatomy and function can help us appreciate the intricate workings of our bodies and the incredible complexity of the nervous system.
The Path to Inflammation
Inflammation is a natural response of the body’s immune system to injury or infection. It is a protective mechanism aimed at eliminating harmful substances and initiating the healing process. However, when inflammation affects the sacral nerve, it can lead to pain and dysfunction.
What is Inflammation?
Inflammation is a complex biological process that involves increased blood flow, immune cell activation, and changes in the affected tissues. When the immune system detects tissue damage or infection, it releases various chemical mediators that attract immune cells to the site of inflammation. These cells then work together to eliminate the harmful agent and repair any damage.
During the inflammatory response, blood vessels in the affected area dilate, allowing more blood to flow to the site. This increased blood flow brings with it immune cells, such as neutrophils and macrophages, which are responsible for engulfing and destroying pathogens. These immune cells release cytokines, which are signaling molecules that further amplify the immune response and recruit more immune cells to the area.
As the immune cells work to eliminate the harmful substances, they may release reactive oxygen species and other molecules that can cause damage to nearby tissues. This damage triggers the release of additional chemical mediators, such as prostaglandins and histamine, which further contribute to the inflammatory response.
How Inflammation Affects the Sacral Nerve
When the sacral nerve becomes inflamed, it can disrupt the normal functioning of the nerves and muscles it innervates. Inflammation can compress or irritate the nerve fibers, leading to pain, numbness, tingling, and weakness in the lower body. Additionally, it can affect the transmission of sensory signals, causing disturbances in bladder and bowel control, sexual function, and mobility.
The inflammation of the sacral nerve can be caused by various factors, including trauma, infection, autoimmune disorders, and chronic conditions such as diabetes. When the immune response becomes dysregulated, it can result in chronic inflammation, leading to persistent symptoms and long-term damage to the nerve.
Chronic inflammation of the sacral nerve can have a significant impact on an individual’s quality of life. The constant pain and discomfort can limit mobility and hinder daily activities. It can also cause emotional distress and affect mental well-being. Therefore, early diagnosis and appropriate management of sacral nerve inflammation are crucial for minimizing its impact on overall health.
Common Causes of Sacral Nerve Inflammation
Sacral nerve inflammation, also known as sacral neuritis, can be caused by various factors, ranging from physical trauma to infections and lifestyle choices. Understanding these causes can help in identifying potential risk factors and adopting preventive measures.
Physical Trauma and Injuries
Physical trauma, such as a fall, car accident, or sports injury, can lead to sacral nerve inflammation. The impact or compression of the nerve can result in nerve damage and subsequent inflammation. It is essential to seek immediate medical attention if you experience any trauma to the lower back or pelvic region to determine the extent of the injury and prevent further complications.
In some cases, the sacral nerve inflammation may occur as a result of repetitive strain injuries (RSIs) caused by activities that involve repetitive movements or prolonged pressure on the lower back and pelvic region. Examples of such activities include long hours of sitting, heavy lifting, or participating in sports that require repetitive motions.
When the sacral nerve becomes inflamed due to physical trauma or injuries, individuals may experience symptoms such as lower back pain, radiating pain down the legs, numbness or tingling in the buttocks or legs, and muscle weakness. These symptoms can vary in severity depending on the extent of the nerve damage.
Infections and Diseases
Infections, such as urinary tract infections (UTIs), pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), or sexually transmitted infections (STIs), can also cause inflammation of the sacral nerve. These infections can spread to the nerves and surrounding tissues, leading to inflammation and subsequent symptoms.
Additionally, certain diseases like diabetes, autoimmune disorders, and inflammatory conditions can also contribute to sacral nerve inflammation. In individuals with diabetes, high blood sugar levels can damage the nerves over time, including the sacral nerve. Autoimmune disorders, such as multiple sclerosis or lupus, can cause the immune system to mistakenly attack the nerves, leading to inflammation. Inflammatory conditions like sacroiliitis, an inflammation of the sacroiliac joint, can also affect the sacral nerve.
When sacral nerve inflammation is caused by infections or diseases, individuals may experience symptoms such as pain in the lower back or pelvic area, urinary problems, sexual dysfunction, and bowel disturbances. These symptoms may vary depending on the specific infection or disease involved.
Lifestyle Factors
Unhealthy lifestyle habits can put excessive pressure on the sacral nerve and increase the risk of inflammation. Prolonged sitting, especially in a slouched or hunched position, can compress the nerve and lead to irritation. Obesity can also contribute to sacral nerve inflammation as the excess weight puts additional strain on the lower back and pelvic region.
Poor posture, both while sitting and standing, can affect the alignment of the spine and increase the risk of nerve compression. Slouching or hunching forward can put undue pressure on the sacral nerve, leading to inflammation over time. Engaging in regular physical activity can help strengthen the muscles supporting the lower back and pelvic region, reducing the strain on the sacral nerve.
In addition to physical activity, maintaining a healthy weight is crucial in preventing sacral nerve inflammation. Excess weight can contribute to nerve compression and inflammation, so adopting a balanced diet and incorporating regular exercise can help alleviate the strain on the nerve.
By understanding the common causes of sacral nerve inflammation, individuals can take proactive steps to prevent or manage the condition. It is important to consult with a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment plan tailored to individual needs.
Symptoms of Sacral Nerve Inflammation
The symptoms of sacral nerve inflammation can vary depending on the severity and location of the inflammation. However, there are common signs that may indicate nerve involvement and the need for further evaluation.
Pain and Discomfort
One of the primary symptoms of sacral nerve inflammation is pain. The pain may be localized to the lower back, buttocks, thighs, or radiate down the legs. It may be described as sharp, shooting, or burning and can worsen with movement or prolonged sitting. In some cases, the pain can be accompanied by muscle spasms and stiffness.
Mobility Issues
Inflammation of the sacral nerve can affect mobility and coordination in the lower body. Some individuals may experience weakness or difficulty walking, standing, or performing daily activities. Changes in gait and balance issues can also be observed.
Other Physical Symptoms
Additional physical symptoms of sacral nerve inflammation may include numbness, tingling, or a pins-and-needles sensation in the lower body. Sensory disturbances, such as altered sensation to touch or temperature changes, may also be present. In some cases, there may be disturbances in bladder and bowel control, sexual function, or menstruation.
Diagnosing Sacral Nerve Inflammation
Diagnosing sacral nerve inflammation typically involves a comprehensive evaluation of the patient’s medical history, physical examination, and diagnostic tests. It is essential to consult with a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment plan.
Medical History and Physical Examination
Your healthcare provider will start by obtaining a detailed medical history, including information about the onset and progression of symptoms, any relevant medical conditions or injuries, and lifestyle factors. They will then perform a physical examination to assess muscle strength, sensation, reflexes, and any visible signs of inflammation or nerve involvement.
Imaging and Laboratory Tests
To confirm the diagnosis and determine the underlying cause of sacral nerve inflammation, your healthcare provider may order various imaging tests, such as X-rays, CT scans, or MRI scans. These imaging modalities can help visualize the structures of the lower back and pelvis and identify any abnormalities or signs of inflammation. Additionally, laboratory tests, such as blood tests or cultures, may be performed to rule out infections or other systemic conditions.
Treatment Options for Sacral Nerve Inflammation
Treatment options for sacral nerve inflammation aim to relieve symptoms, reduce inflammation, and address the underlying cause. The specific treatment plan will depend on the severity of symptoms, the underlying cause, and the individual’s overall health. It is crucial to work closely with a healthcare professional to determine the most appropriate course of action.
Medication and Pain Management
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), such as ibuprofen or naproxen, may be prescribed to reduce pain and inflammation. For more severe or persistent symptoms, medications like muscle relaxants or nerve-pain medications may be considered. Physical therapy and rehabilitation can also play a significant role in pain management and helping restore mobility and function.
Physical Therapy and Rehabilitation
Physical therapy can help strengthen the muscles surrounding the sacral nerve, improve flexibility, and correct any postural or gait abnormalities. A physical therapist may incorporate exercises, manual therapy techniques, and modalities like heat or ice to provide relief and promote healing. Additionally, they can provide guidance on ergonomic modifications, such as proper sitting or lifting techniques, to prevent further strain on the nerve.
Surgical Interventions
In rare cases where conservative treatments fail to provide adequate relief, surgery may be considered. The specific surgical procedure will depend on the underlying cause and the extent of nerve damage. Surgical options may include decompression surgeries to relieve pressure on the nerve, nerve grafting or repair for damaged nerves, or the removal of any tumors or growths pressing on the nerve.
Preventing Sacral Nerve Inflammation
While not all cases of sacral nerve inflammation can be prevented, adopting certain lifestyle choices can help reduce the risk and severity of inflammation.
Healthy Lifestyle Choices
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet, adequate hydration, and proper sleep, can support overall nerve health and reduce the risk of inflammation. Avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption can also contribute to a healthy nervous system.
Regular Exercise and Stretching
Engaging in regular exercise and stretching routines can help improve muscle strength, flexibility, and circulation, reducing the strain on the sacral nerve. Incorporating exercises that target the core and lower body can provide additional support to the nerve and surrounding structures. It is essential to consult with a healthcare provider or a certified trainer to develop an appropriate exercise plan.
Proper Posture and Ergonomics
Poor posture and ergonomics can put unnecessary stress on the sacral nerve and increase the risk of inflammation. Maintaining proper posture while sitting, standing, or lifting heavy objects can help distribute the load evenly and prevent excessive strain on the nerve. Using ergonomic devices, like supportive chairs or adjustable workstations, can also contribute to good spinal alignment.
Living with Sacral Nerve Inflammation
Living with sacral nerve inflammation can be challenging, but there are strategies and resources available to help individuals cope with their symptoms and improve their quality of life.
Coping Strategies
Developing effective coping strategies can help individuals manage pain, reduce stress, and enhance overall well-being. Techniques like deep breathing, meditation, and relaxation exercises can provide relief and improve emotional and physical resilience. Seeking support from family, friends, or support groups can also play a crucial role in navigating the challenges associated with nerve inflammation.
Support and Resources
It is essential for individuals with sacral nerve inflammation to seek support and access helpful resources. Healthcare professionals, such as doctors, physical therapists, or pain management specialists, can provide guidance and expert advice tailored to individual needs. Additionally, connecting with reputable organizations or online forums dedicated to nerve health and chronic pain management can offer valuable insights and support.
Future Research and Developments
Ongoing research and advancements in the field of neurology continue to shed light on the causes, mechanisms, and treatment options for sacral nerve inflammation. As our understanding of this condition improves, new therapies, medications, or interventions may become available to alleviate symptoms and enhance recovery.
In conclusion, sacral nerve inflammation can occur due to various causes, such as physical trauma, infections, and lifestyle factors. Understanding the anatomy and function of the sacral nerve, recognizing the symptoms of inflammation, and seeking timely medical attention are crucial for appropriate diagnosis and treatment. While treatment options may include medication, physical therapy, or surgery, prevention through healthy lifestyle choices and proper self-care is equally important. Living with sacral nerve inflammation may present challenges, but with the right support and resources, individuals can effectively manage their symptoms and improve their quality of life.